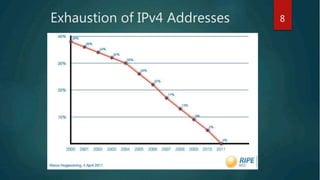
IPv4, the fourth revision of the Internet Protocol, is widely used to identify devices on networks but is facing exhaustion of available addresses due to rapid internet growth. To address this, IPv6 was introduced as its successor, offering a larger address space and enhanced features, though it presents challenges during its transition. While IPv4 remains prevalent, IPv6 is being deployed to accommodate the increasing demand for IP addresses.