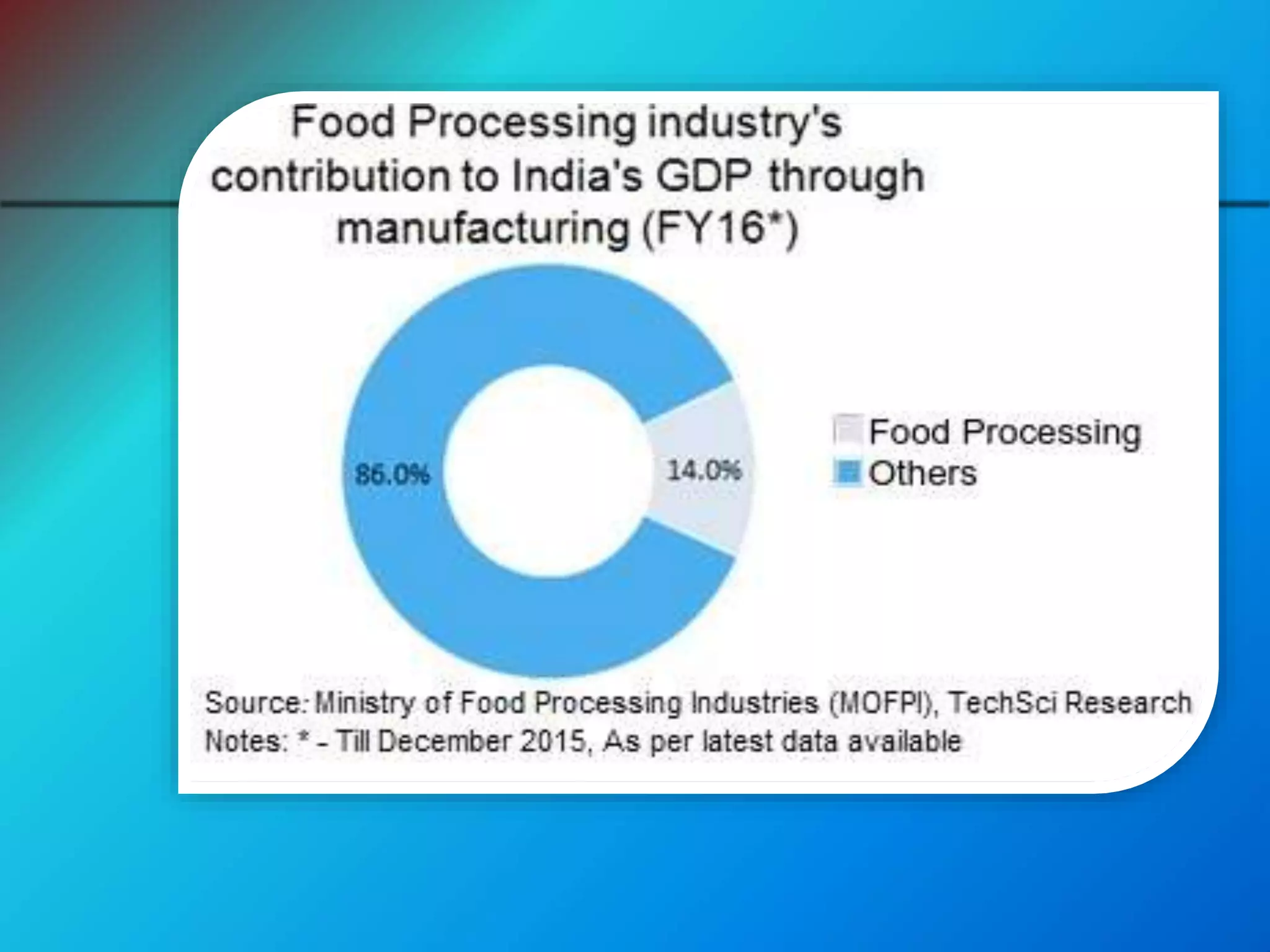
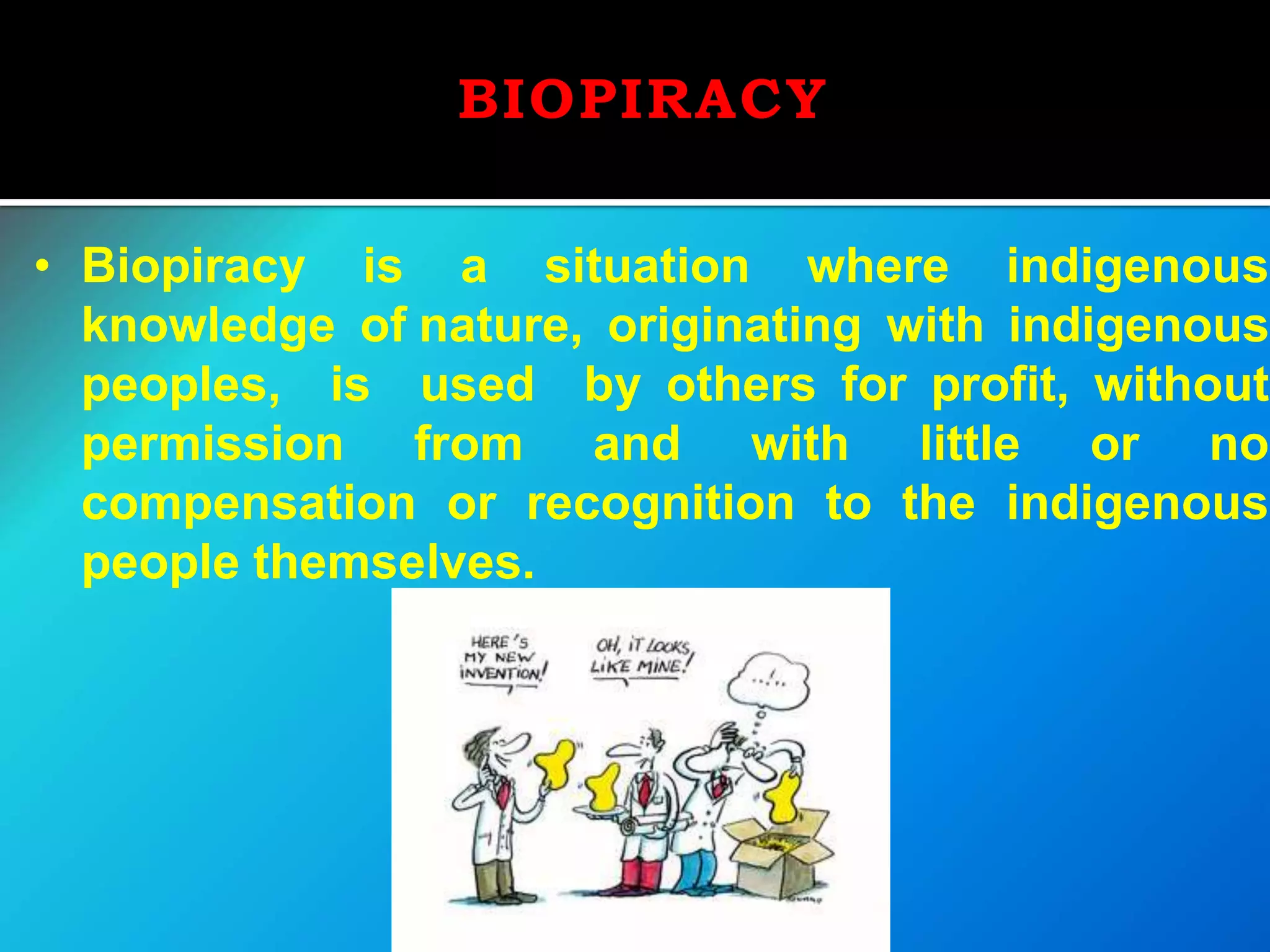
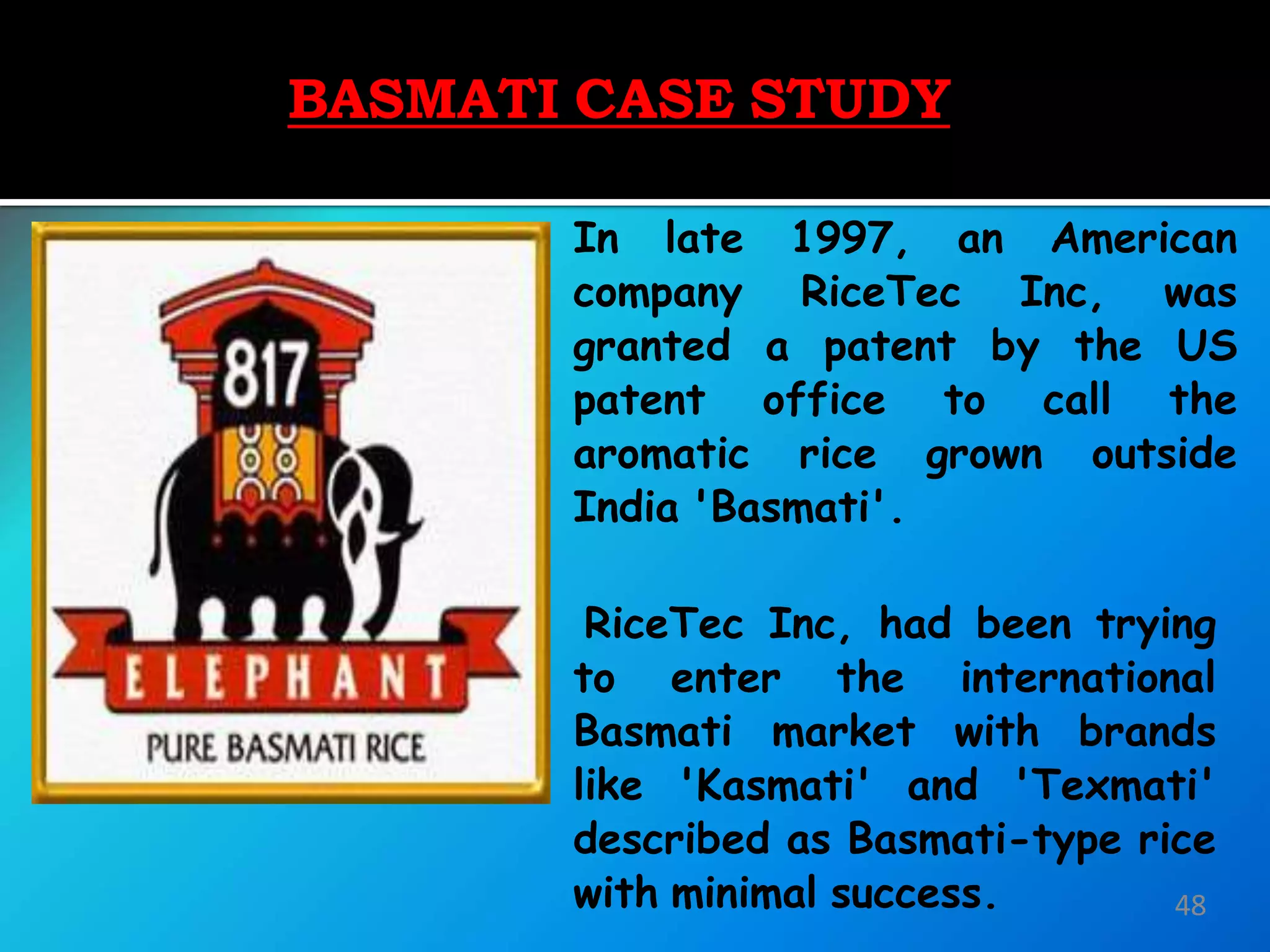
The document discusses intellectual property (IP) in the food processing industry, covering types of IP such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, and geographical indications, as well as the legal frameworks that govern them in India. It elaborates on patents related to food inventions, the issues of biopiracy, and notable case studies involving patents like turmeric and basmati rice. Additionally, it highlights the importance of protecting traditional knowledge and the role of various institutions in fostering innovation and safeguarding IP rights.












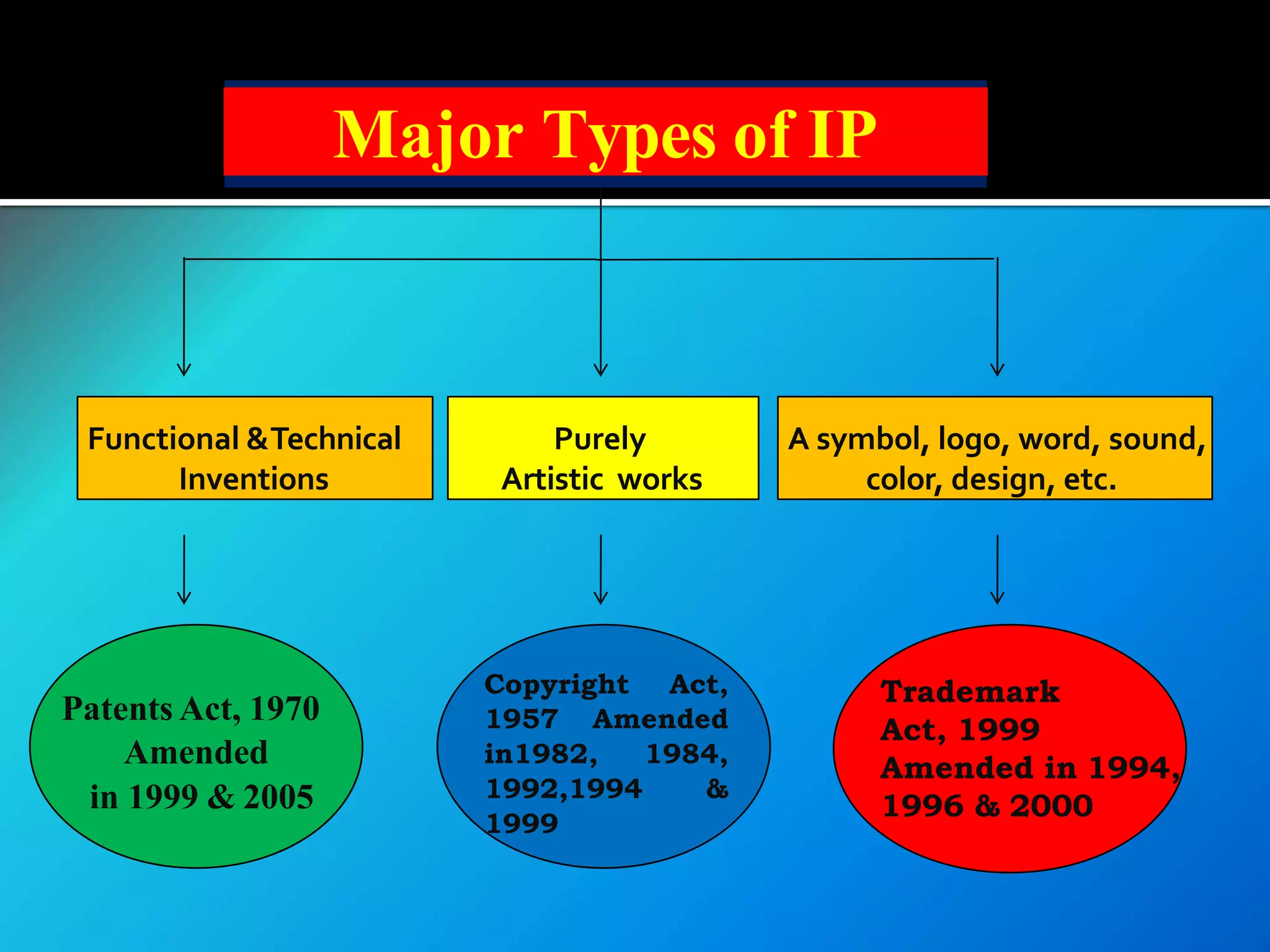















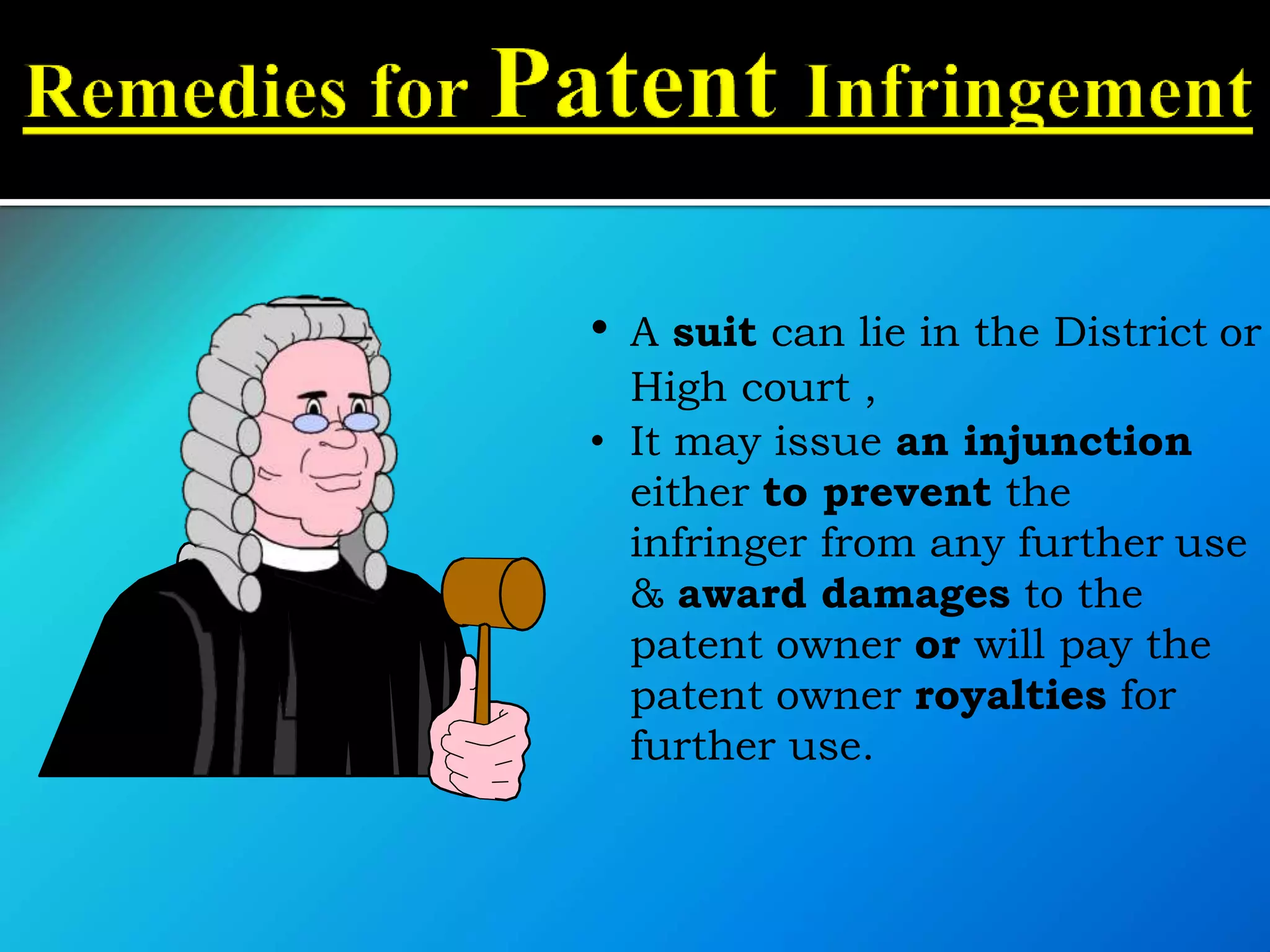
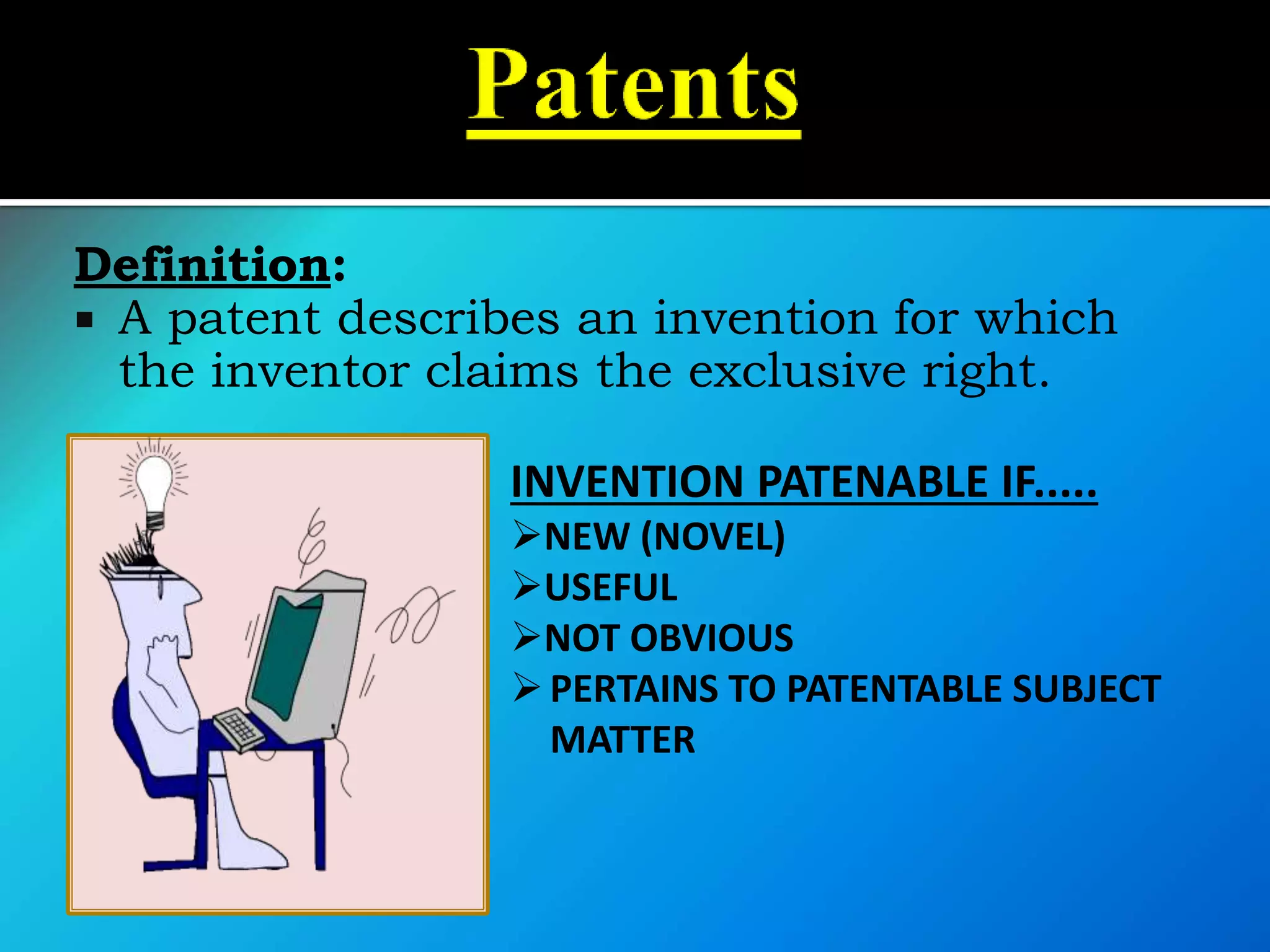
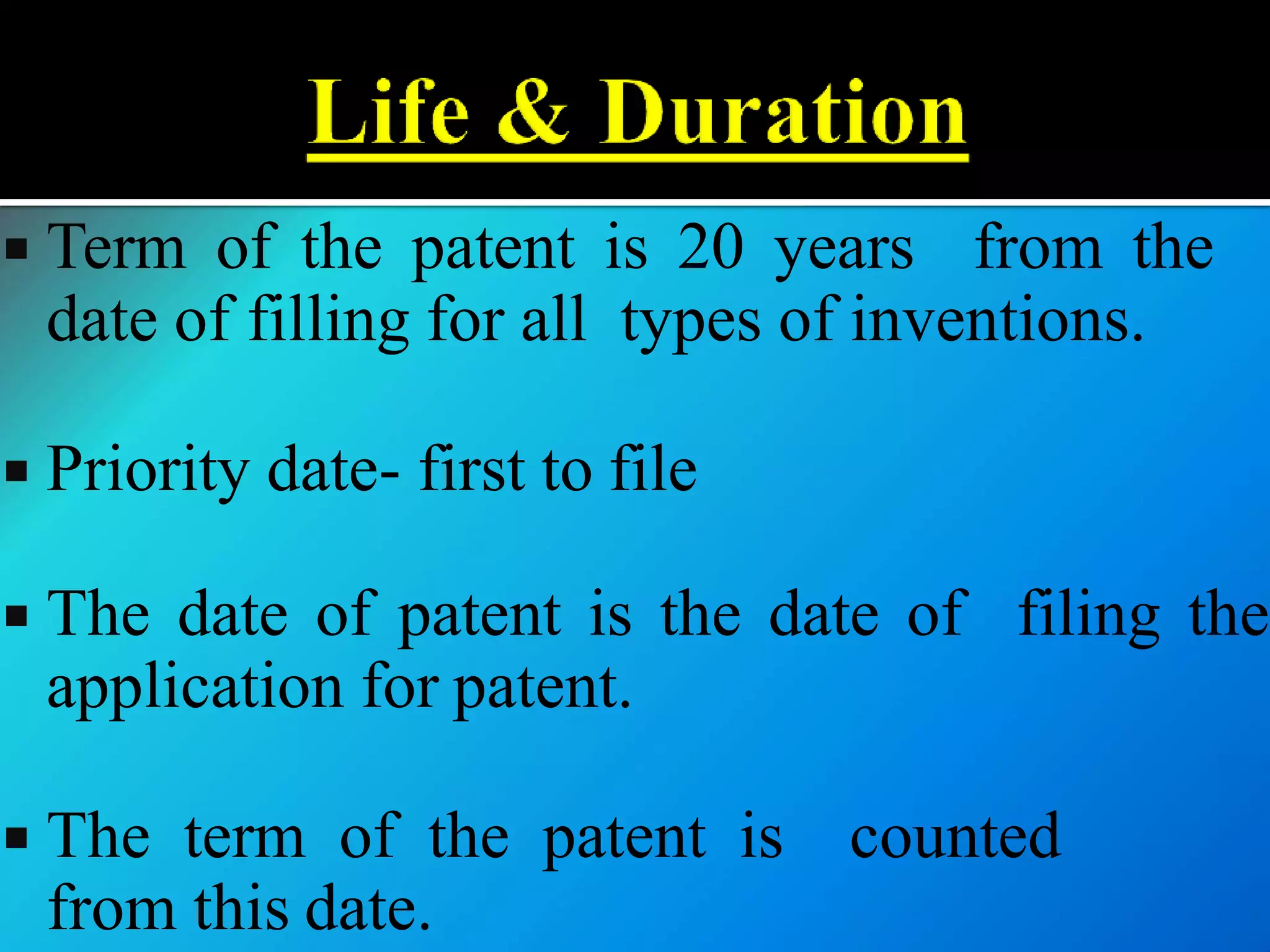
![(1) It is covered under the Act called the
Patents Act, 1970 [Amended by
Patents Act, 2005]
(2) It extends to the whole of India.
(3) It shall come into force on such date
as the Central Government may
publish, by notification in
the Official Gazette.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iprandfoodprocessingindustrybynaveenkumar-200420063119/75/IPR-and-GI-with-reference-to-food-processing-industry-by-naveen-kumar-30-2048.jpg)




















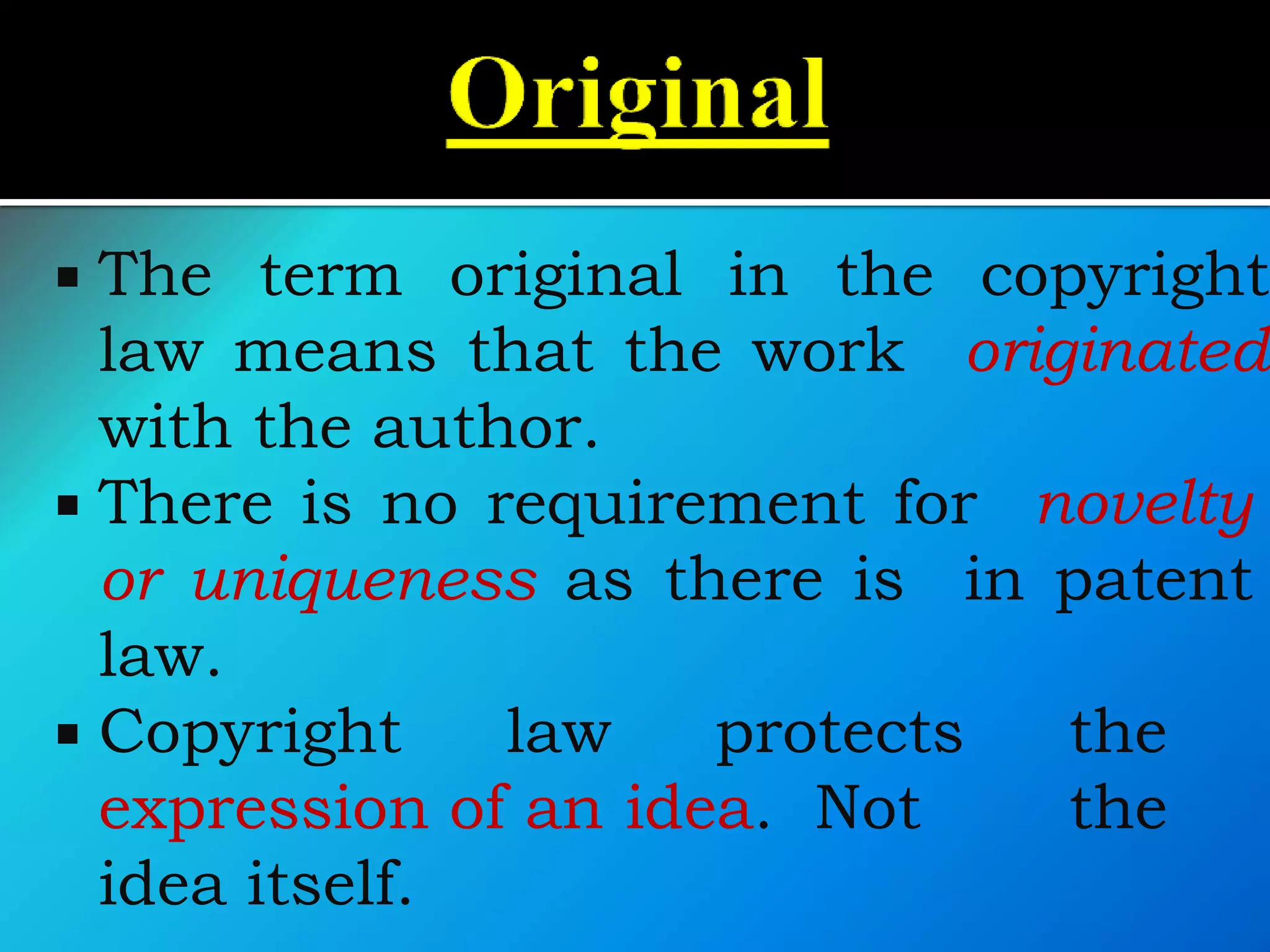
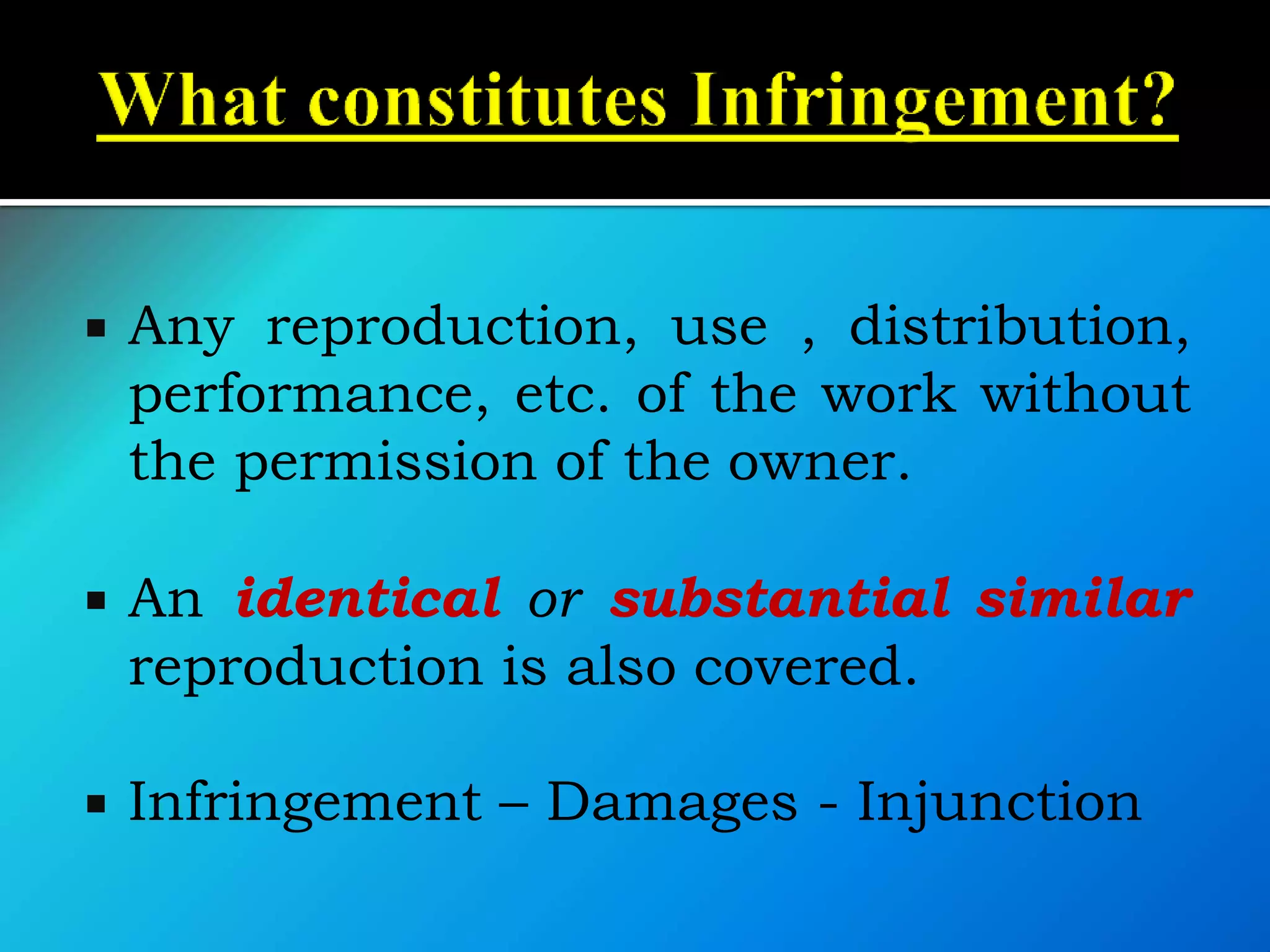
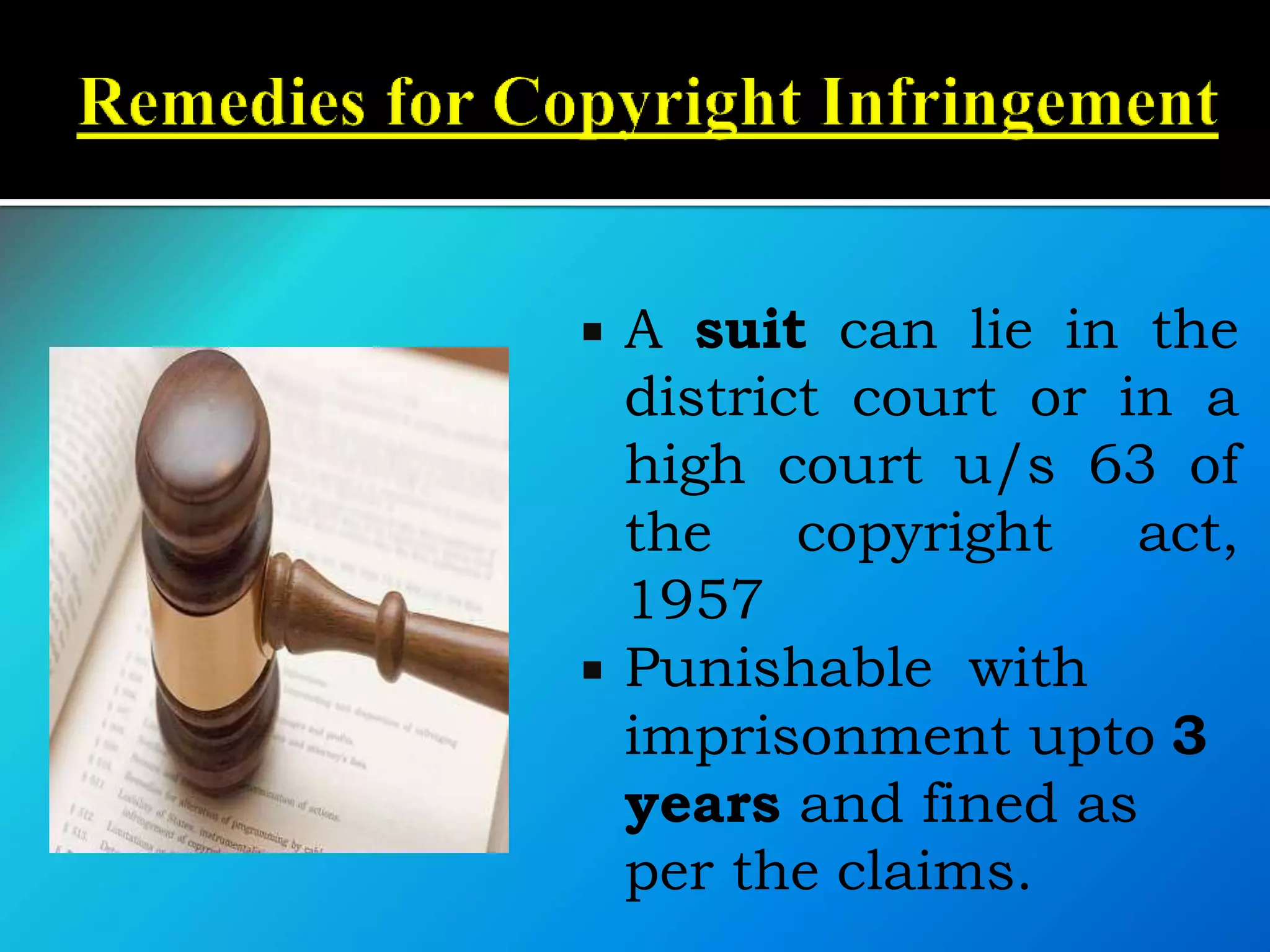
![ The Indian CopyrightAct,1957 governs the
system of copyrights in India. [Amended in
1982, 1984, 1992, 1994
& 1999]
Meaning : It is a right which Grants
protection to the unique expression of
Ideas.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iprandfoodprocessingindustrybynaveenkumar-200420063119/75/IPR-and-GI-with-reference-to-food-processing-industry-by-naveen-kumar-60-2048.jpg)