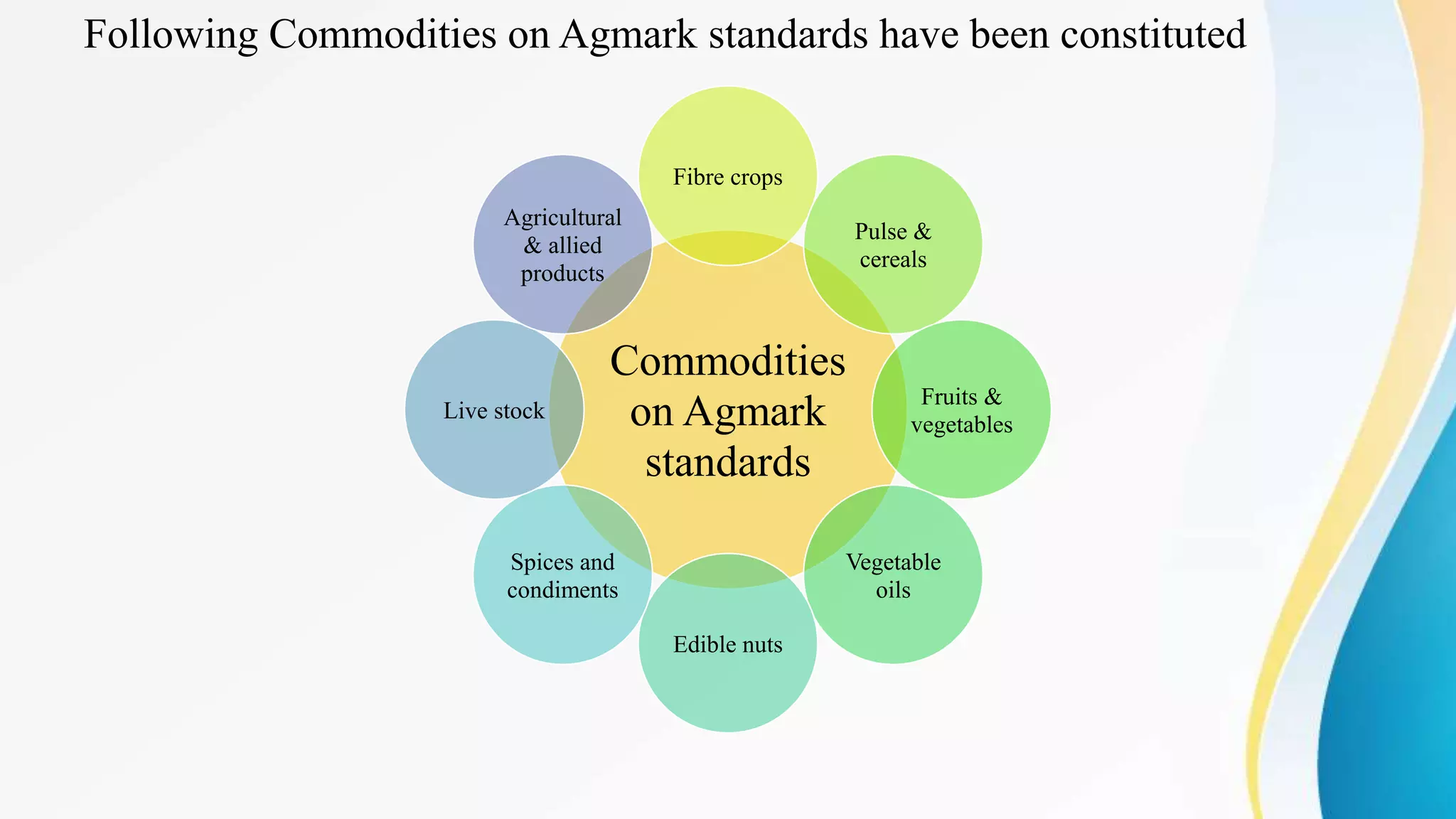
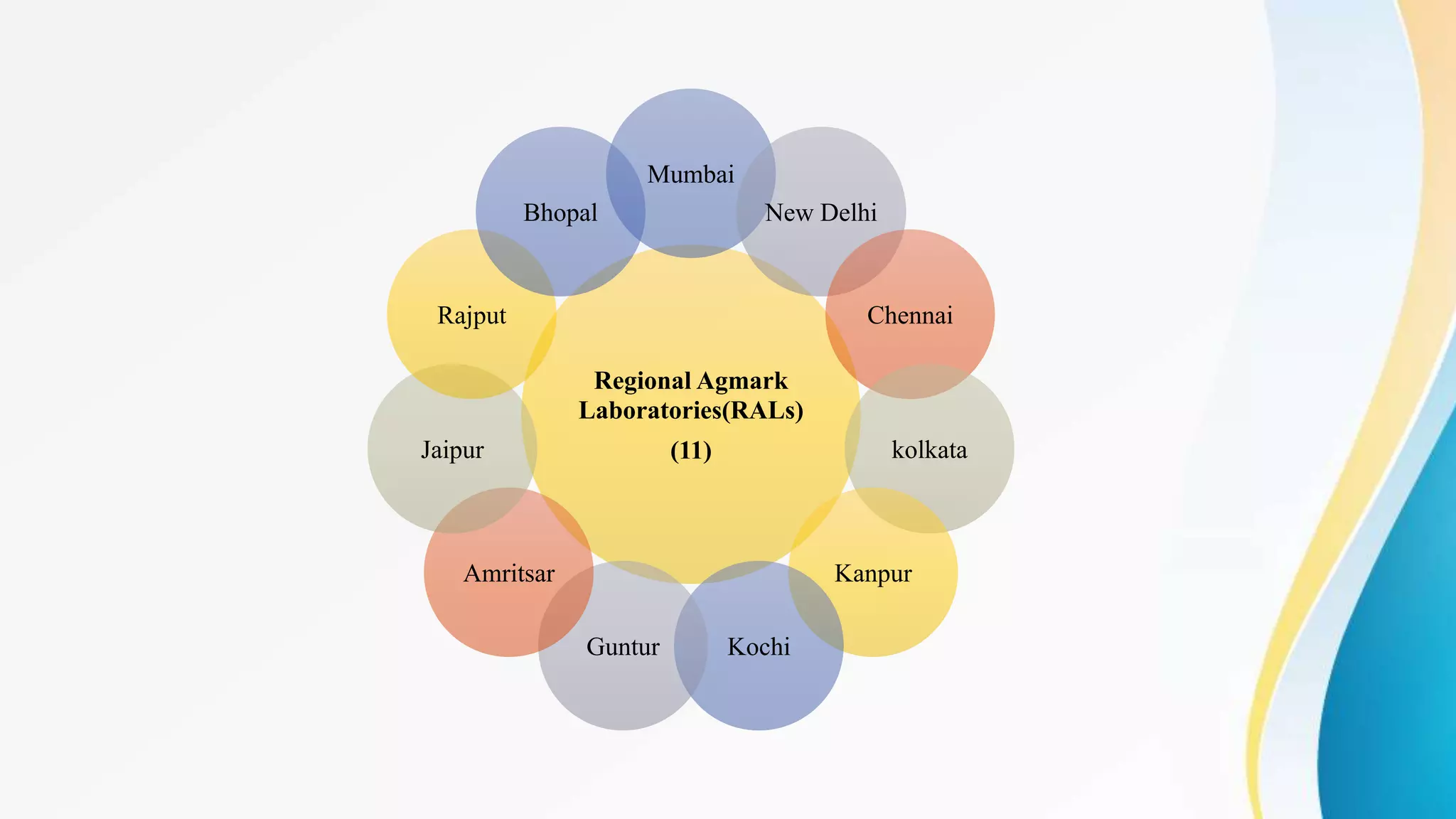
The document discusses the AGMARK certification process established by the Agricultural Produce (Grading and Marking) Act, 1937 in India, aimed at ensuring the quality and authenticity of agricultural products. It outlines the roles of the Directorate of Marketing and Inspection in implementing grading standards, authorizing packers, and maintaining a framework for quality assurance through the establishment of laboratories throughout the country. The certification facilitates better marketing practices, fair pricing for farmers, and consumer protection in the agricultural sector.