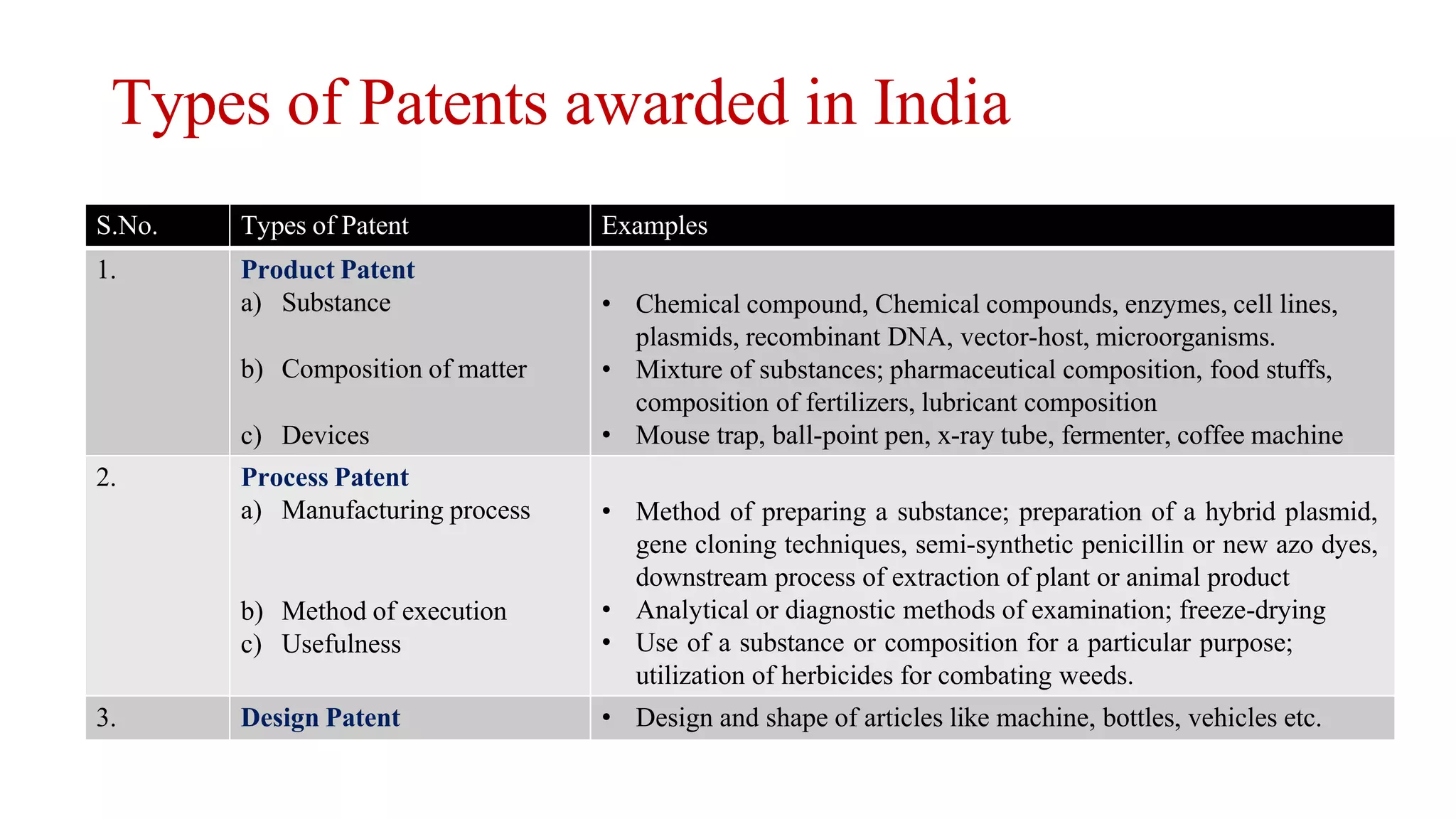
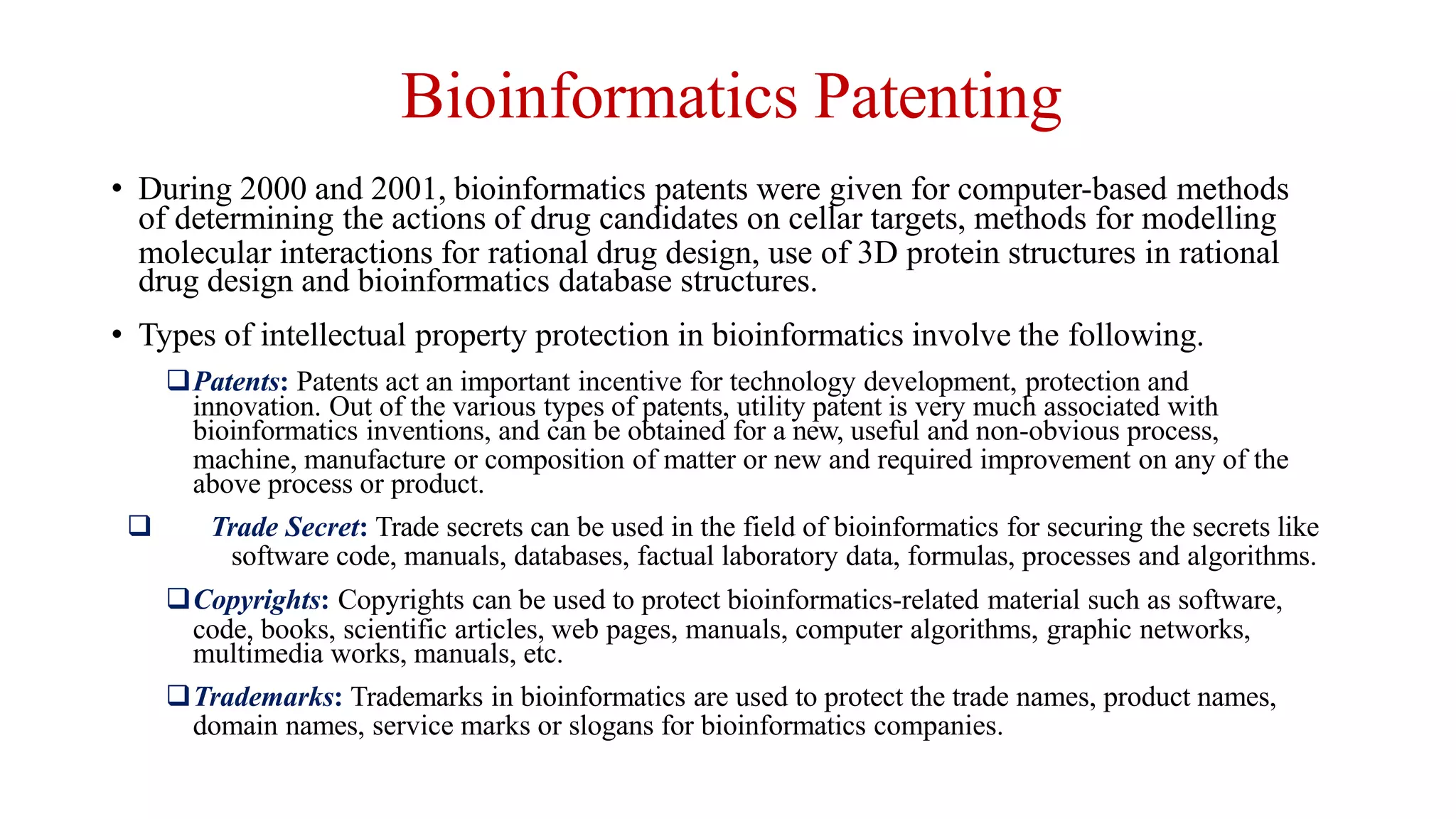
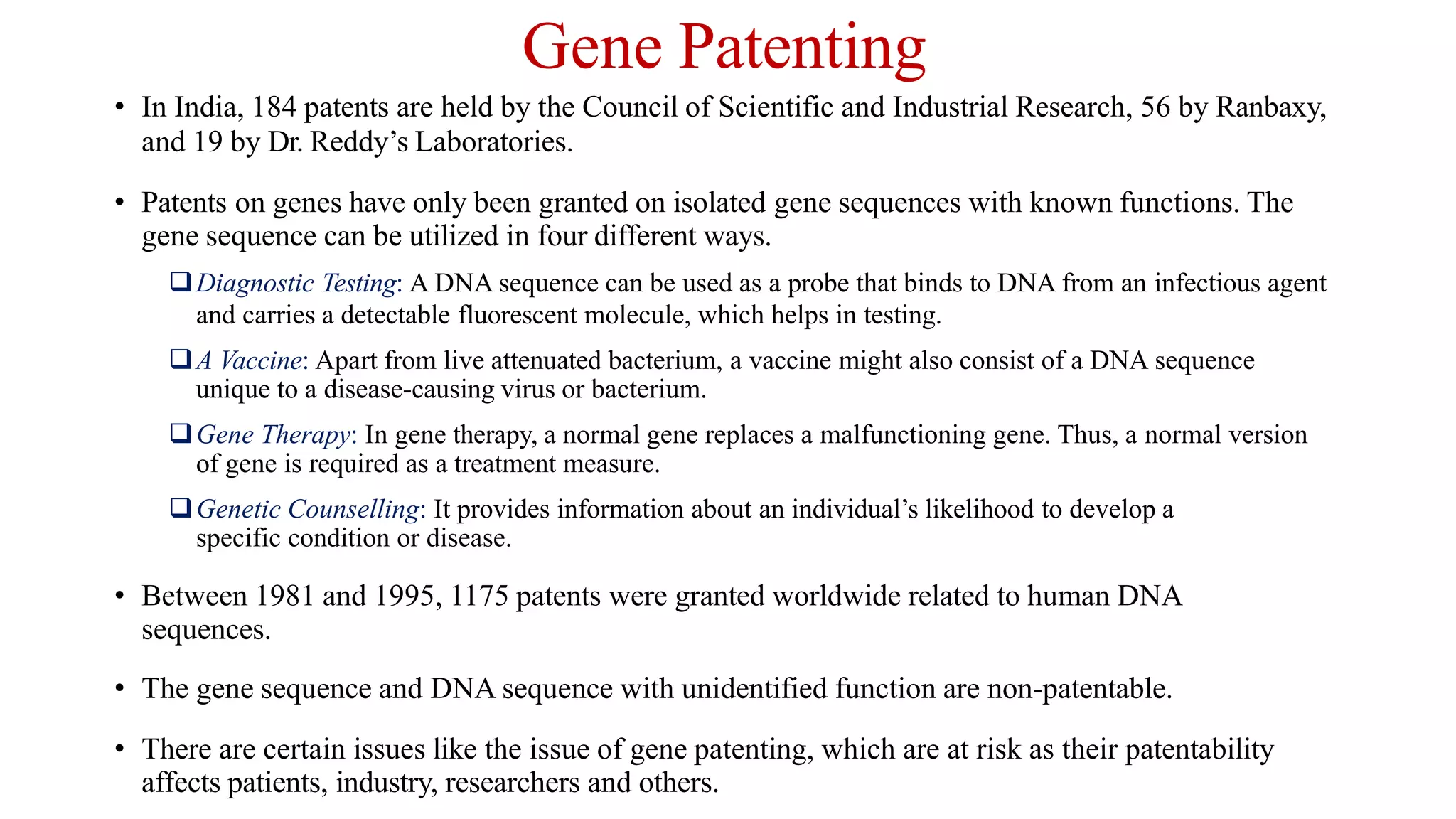
Intellectual property rights (IPR) refer to the legal ownership of intellectual property such as inventions, literary works, symbols and designs. IPR is limited by duration, scope, and geography. The importance of IPR was first recognized in the Paris Convention of 1883 and Berne Convention of 1886, which are administered by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). IPR promotes innovation and creativity by granting time-limited ownership rights over intellectual commodities and creations of the mind.