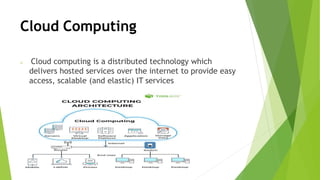
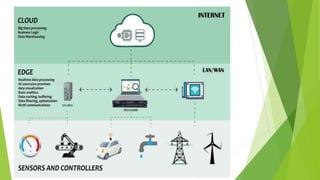
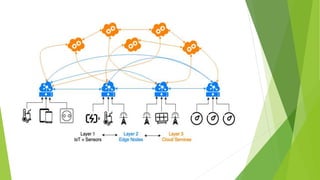
Edge computing is a distributed computing architecture that processes data closer to where it is generated, at the edge of the network, rather than sending all data to centralized cloud data centers for processing. It aims to provide quicker response times and reduce issues like hacking and random failures. Edge computing is geographically distributed, scalable, autonomous, and processes data locally with low latency for real-time interactions. While it has advantages like increased speed and reliability, it also has disadvantages like limited scalability and interoperability compared to cloud computing. Applications of edge computing include smart cities, manufacturing, healthcare, and augmented reality devices.