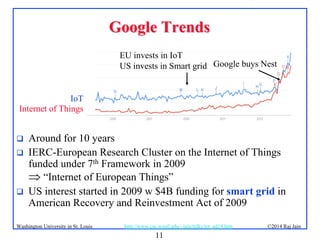
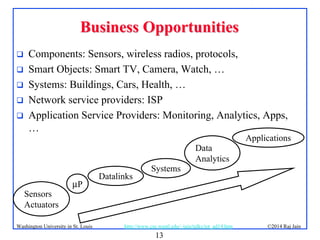
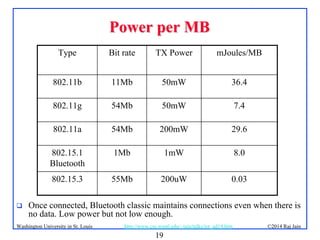
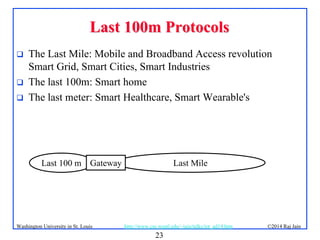
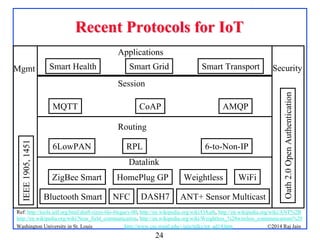
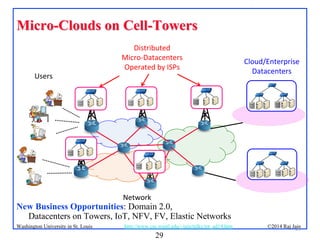
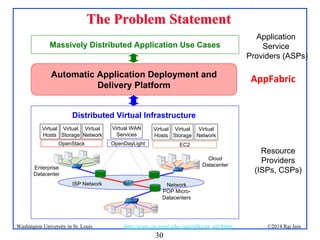
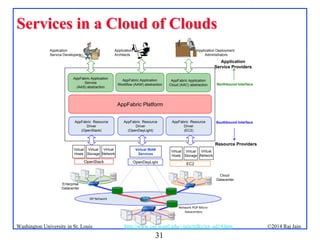
The document presents an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT), discussing its significance, current applications, and technological advancements. It highlights the growing connectivity of devices, the potential for numerous business opportunities, and outlines various challenges related to implementation, standardization, and security. The presentation also emphasizes recent investments and developments in IoT technologies and products.