The document discusses inverse trigonometric functions, defining and explaining their properties, domains, and ranges. It emphasizes the need to restrict the domain of trigonometric functions to make them one-to-one and onto, allowing for the existence of inverse functions. Additionally, various illustrative examples and properties of inverse functions are provided to aid understanding.
![INVERSE CORCULAR FUNCTIONS
1.00 Inverse Function Definition
111
If1 function is one to one and onto from A to B, then function g which associates each element y
a B to
one and only one element x A, such that y = f(x), then g is called the inverse function of f, denoted by x
= g(y). Usually we denote g f –1 {Read as f inverse}
x f –1 ( y).
1.01 Inverse Trigonometric Function
111
We have seen that the trigonometric functions, sin, cos etc. are all periodic and thus, each of them
1
1
achieves the same numerical value at an infinite number of points. Thus, the equation sin x has an
2
infinite number of solutions, viz., x , – etc. If one is to answer the question : “ What is the angle
6 6
1
whose sine is ?”, there is no unique answer. The difficulty arises as the function f : R R defined by
2
f ( x) sin x is not one to one and thus, does not admit of an inverse. To achieve a unique answer to the
aforesaid question we restrict the domain of sin x so that the resulting function is invertible. Thus, the
function g : – , [–1, 1] defined by g ( x) sin x is one to one and onto and admits of an inverse
2 2
(denoted by h sin –1 and read as sin inverse or arc sin) defined as h :[–1, 1] – , where
2 2
h( y) x if y sin x . The function sin –1 is the inverse of the sin function when the sin function is viewed in
a restricted sense.
We similarly define the other inverse trigonometric functions
Important Points
1: sin –1 x is an angle and denotes the smallest numerical angle, whose sine is x.
2: If there are two angles one positive and the other negative having same numerical value. Then we
shall take the positive value.
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/75/Inverse-circular-function-1-2048.jpg)
![1.02 Inverse Trigonometric Function
111
Here, sin –1 x,cos ec –1 x, tan –1 x belongs to I and IV quadrant.
1
Here, cos –1 x, sec–1 x, cot –1 x belongs to I and II quadrant.
1. I quadrant is common to all the inverse functions.
2. III quadrant is not used inverse function.
3. IV quadrant is used in the clockwise direction i.e., – / 2 y 0 .
1.03 Domain, Range And Graphs of Inverse Functions
1. If sin y = x, then y sin –1 x under certain condition.
–1 sin y 1; but sin y x
–1 x 1
Again, sin y = –1 y = – /2 and sin y = 1 y = /2
Keeping in mind numerically smallest angles or real numbers.
– /2 y /2
These restrictions on the values of x and y provide us with the domain and range for the function
y sin –1 x .
i.e., Domain : x [–1, 1]
Range : y [– / 2, / 2]
2. Let cos y = x then y cos –1 x under certain condition –1 cos y 1 .
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-2-320.jpg)
![–1 x 1
cos y –1 y
cos y 1 y 0
0 y {as cos x is a decreasing function in [0, ]; hence cos cos y cos 0}
These restrictions on the values of x and y provide us the domain and range for the function
y cos –1 x .
i.e., Domain : x [–1, 1]
Range : y [0, ]
3. If tan y = x then y tan –1 x , under certain conditions.
Here, tan y R x R
– tan y – /2 y /2
Thus, domain x R
Range y (– / 2, / 2)
4. If cot y = x, then y cot –1 x (under certain conditions)
cot y R x R;
– cot y 0 y
These conditions on x and y make the function, cot y = x one–one
and onto so that the inverse function exists.
i.e., y cot –1 x is meaningful.
i.e., Domain: x R
Range : y (0, )
5. If sec y = x, then sec–1 x, where x 1 and 0 y ,y /2
Here, Domain : x R – (–1, 1)
Range : y [0, ] – { / 2}
6. If cosec y = x then y cos ec –1 x,
where x 1 and – /2 y / 2, y 0
Here, Domain : R – (–1, 1)
Range : [– / 2, / 2] – {0}
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-3-320.jpg)
![1.04 Principal values & Domains of Inverse Trigonometric / Circular Functions
Function Domain Range
(i ) y sin –1 x where –1 x 1 – y
2 2
–1
(ii ) y cos x where –1 x 1 0 y
(iii ) y tan –1 x where x R – y
2 2
(iv) y cos ec –1 x where x –1 or x 1 – y ,y 0
2 2
(v ) y sec –1 x where x –1 or x 1 0 y ;y
2
(vi ) y cot –1 x where x R 0 y
Note :
(a) 1st quadrant is common to the range of all the inverse functions.
(b) 2nd quadrant is not used in inverse functions.
(c) 4th quadrant is used in the clockwise direction i.e. – y 0.
2
(d) No inverse function is periodic. (See the graphs on page 17)
1 1
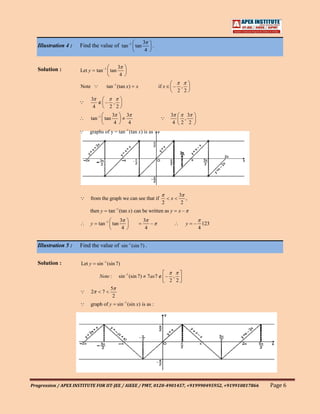
Illustration 1 : Find the value of tan cos –1 tan –1 – .
2 3
1 1
Solution : Let y tan cos –1 tan –1 –
2 3
tan – tan
3 6 6
1
y Ans.
3
Illustration 2 : Find the domain of sin –1 (2 x2 –1) .
Solution : Let y sin –1 (2 x 2 – 1)
For y to be defined
– 1 (2 x 2 – 1) 1
0 2x2 2 0 x2 1
x [–1, 1]
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-4-320.jpg)

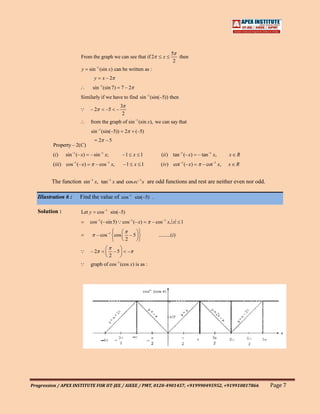

![1
Illustration 8 : Find the value of sin(2cos –1 x sin –1 x) when x .
5
Solution :
Let y sin[2 cos –1 x sin –1 x]
sin –1 x cos –1 x ,x 1
2
y sin 2 cos –1 x – cos –1 x
2
sin cos –1 x
2
1
cos(cos –1 x) x
5
1
y cos cos –1 .........(i )
5
cos(cos –1 x) x if x [–1, 1]
1 1 1
[–1, 1] cos cos –1
5 5 5
1
from equation (i), we get y
Property – 2( F ) 5
1
(i) sin(cos –1 x) cos(sin –1 x) 1 – x 2 , –1 x 1 (ii ) tan(cot –1 x) cot(tan –1 x) , x R, x 0
x
x
(iii ) cos ec(sec –1 x) sec(cos ec –1 x) , x 1
x –12
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-9-320.jpg)

![3– 5
from equation (iii), we get tan
2 2
3– 5
from equation (ii), we get y
2
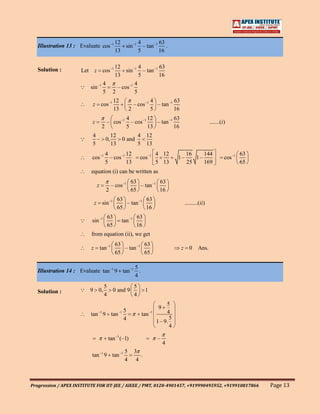
1
Illustration 11 : Find the value of cos(2cos–1 x sin –1 x) when x .
5
Solution : Lety cos[2 cos –1 x sin –1 x]
sin –1 x cos –1 x ,x 1
2
y cos 2 cos –1 x – cos –1 x cos cos –1 x
2 2
1
– sin(cos –1 x) x
5
1
y – sin cos –1 ........(i )
5
sin(cos –1 x) 1 – x2 , x 1
1 1 24
sin cos –1 1–
5 25 5
24
from equation (i), we get y –
5
1 1
Aliter : Let cos –1 cos and 0,
5 5 2
24
sin
5
24
sin –1 (sin ) sin –1 .........(ii )
5
0, sin –1 (sin )
2
equation (ii) can be written as
24 1
sin –1 cos –1
5 5
1 24
cos –1 sin –1
5 5
Now equation (i) can be written as
24
y – sin sin –1 ........(iii )
5
24 24 24
[–1, 1] sin sin –1
5 5 5
from equation (iii), we get
24
y –
5
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-11-320.jpg)

![C.
1
2sin –1 x if x
2
1
(i ) sin –1 2 x 1 – x 2 – 2sin –1 x if x
2
1
–( 2sin –1 x) if x –
2
2cos –1 x if 0 x 1
(ii) cos –1 (2x 2 –1) =
2 – 2cos –1 x if –1 x 0
2 tan –1 x if x 1
2x
(iii) tan –1 = 2 tan –1 x if x 1
1 – x2
–( 2 tan –1 x) if x –1
1 – x2 2 tan –1 x if x 0
(iv) cos –1 `
1 x2 –2 tan –1 x if x 0
Illustration 15 : Define y cos –1 (4 x3 – 3x) in terms of cos –1 x and also draw its graph.
Solution : Let y cos –1 (4 x 3 – 3 x)
Note Domain : [–1,1] and range : [0, ]
Let cos –1 x [0, ] and x cos
y cos –1 (4cos 3 – 3cos )
y cos –1 (cos 3 ) .........(i)
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-14-320.jpg)
![ [0, ] 3 [0,3 ]
to define y cos –1 (cos 3 ), we consider the graph of cos –1 (cos x) in the interval [0,3 ].
Now from the above graphs we can see that
(i ) if 0 3 cos –1 (cos 3 ) 3
from equation (i), we get
y 3 if 3
y 3 if 0
3
1
y 3cos –1 x if x 1
2
(ii ) if 3 2 cos –1 (cos 3 ) 2 –3
from equation (i), we get
y 2 –3 if 3 2
2
y 2 –3 if
3 3
1 1
y 2 – 3cos –1 x if – x
2 2
(iii ) 2 3 3 cos –1 (cos 3 ) –2 3
from equation (i), we get
y –2 3 if 2 3 3
2
y –2 3 if
3
1
y –2 3cos –1 x if –1 x –
2
from (i), (ii) & (iii), we get
1
3cos –1 x ; x 1
2
1 1
y cos –1 (4 x 3 – 3 x) 2 – 3cos –1 x ; – x
2 2
1
–2 3cos –1 x ; –1 x –
2
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-15-320.jpg)
![Graph :
For y cos –1 (4 x3 – 3 x)
domain :[–1,1]
range :[0, ]
1
(i ) if x 1, y 3cos –1 x
2
dy –3
–3(1 – x 2 ) –1/ 2 ..........(i )
dx 1 – x2
dy 1
0 if x ,1
dx 2
1
decreasing if x ,1
2
again if we differentiate equation (i) w.r.t. ' x ', we get
d2y 3x
–
dx 2 (1 – x 2 )3/ 2
d2y 1 1
0 if x ,1 concavity downwards if x ,1
dx 2 2 2
1 1
(ii ) if – x , y 2 – 3cos –1 x.
2 2
dy 3 dy 1 1
0 if x – ,
dx 1– x 2 dx 2 2
1 1 d2y 3x
increasing if x – , and
2 2 dx 2 (1 – x 2 )3/ 2
1 d2y
(a) if x – , 0 then 0
2 dx 2
1
concavity downwards if x – ,0
2
1 d2y
(b) if x 0, then 0
2 dx 2
1
concavity downwards if x 0,
2
1 dy d2y
(iii ) Similarly if –1 x – then 0 and 0.
2 dx dx 2
the graph of y cos –1 (4 x 3 – 3 x) is as
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-16-320.jpg)
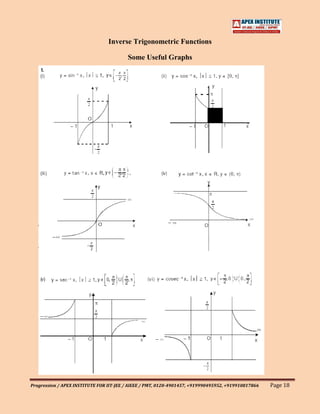
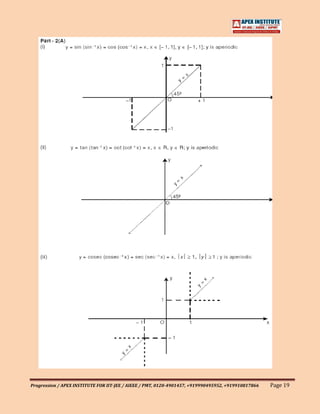
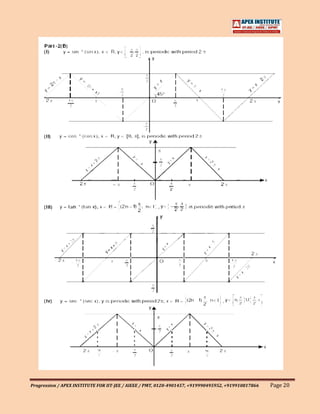
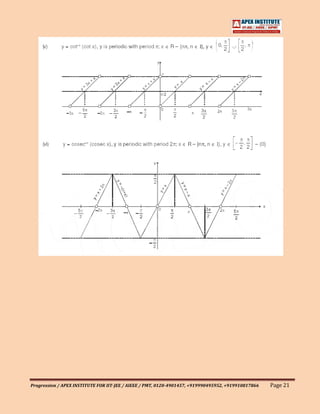
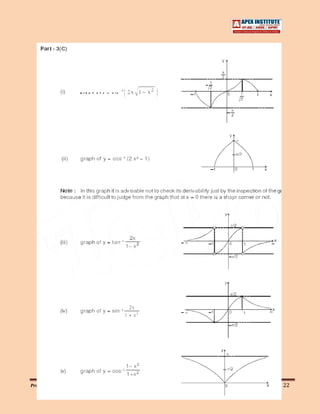
![1.07 General Definitions
111
1 1. sin –1 x, cos –1 x, tan –1 x etc. denote angles or real numbers whose sine is x , whose cosine is x and
whose tangent is x, provided that the answers given are numerically smallest available. These are
also written as arc sin x, arc cos x etc.
If there are two angles one positive & the other negative having same numerical value, then
positive angle should be taken.
EXERCISE-3
Part : (A)
1. If cos –1 cos –1 cos –1 v 3 then v v is equal to .
(a) –3 (b) 0 (c) 3 (d) –1
2. Range of f ( x) sin –1 x tan –1 x sec –1 x is.
3 3 3
(a) , (b) , (c) , (d) none of these
4 4 4 4 4 4
3
3. The solution of the equation sin –1 tan – sin –1 – 0 is.
4 x 6
(a) x = 2 (b) x = –4 (c) x = 4 (d) none of these
4. The value of sin –1[cos{cos –1 (cos x) sin –1 (sin x)}], where x , is
2
(a) (b) (c) – (d) –
2 4 4 2
5. The set of values of k for which x 2 – kx + sin –1 (sin 4) > 0 for all real x is
(a) {0} (b) (2, 2) (c) R (d) none of these
6. sin –1 (cos(sin –1 x)) cos –1 (sin(cos –1 x)) is equal to
3
(a) 0 (b) 4 (c) (d)
2 4
1 2 x2 x
7. cos –1 x 1– x 2 . 1– cos – – cos –1 x holds for
2 4 2
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-23-320.jpg)
![(a) x 1 (b) x R
(c) 0 x 1 (d) –1 x 0
8. tan –1 a tan –1 b, where a 0, b 0, ab 1, is equal to
a b a b
(a) tan –1 (b) tan –1 –
1 – ab 1 – ab
a b a b
(c) tan –1 (d) – tan –1
1 – ab 1 – ab
–1
9. The set of values of „x‟ for which the formula 2sin x sin –1 2 x 1– x2 is true, is.
(a) (–1, 0) (b) [0, 1]
3 3 1 1
(c) – , (d) – ,
2 2 2 2
2
10. The set of values of „a‟ for which x ax sin –1 ( x 2 – 4 x 5) cos –1 ( x 2 – 4 x 5) 0 has at
least one solution is
– , – 2 2 , – , – 2 2 ,
(a) (b)
(c) R (d) none of these
–1 3
11. All possible values of p and q for which cos p cos –1 1– p cos –1 1– q holds, is
4
1 1 1
(a) p 1, q (b) q 1, p (c) 0 p 1, q (d) none of these
2 2 2
[cot –1 x] [cos –1 x] 0
12. If , where [.] denotes the greatest integer function, then complete set of
values of „x‟ is
(a) cos1, 1 (b) (cot 1, cos 1) (c) cot1, 1 (d) none of these
–1 2 –1
13. The complete solution set of the inequality [cot x] – 6[cot x] 9 0 , where [.] denotes
greatest integer function, is
(a) – , cot 3 (b) [cot 3, cot 2] (c) cot 3, (d) none of
these
1 1
14. tan cos –1 x tan – cos –1 x , x 0 is equal to
4 2 4 2
Progression / APEX INSTITUTE FOR IIT-JEE / AIEEE / PMT, 0120-4901457, +919990495952, +919910817866 Page 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversecircularfunction-130304150838-phpapp02/85/Inverse-circular-function-24-320.jpg)


