1) For inverse trigonometric functions to exist, the original trigonometric function must be one-to-one. This means that each input has a single, unique output and vice versa.
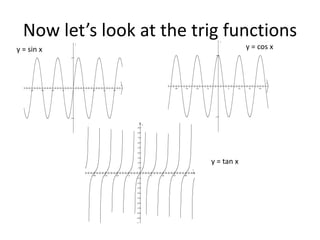
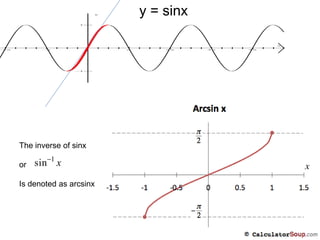
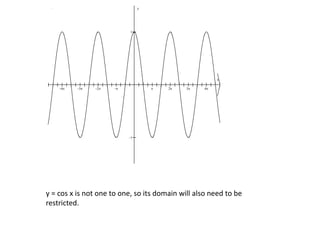
2) The sine and cosine functions are not one-to-one over their entire domains, so their domains must be restricted for the inverses to be defined. Restricting the domain of sine to [-π/2, π/2] and cosine to [0, π] makes them one-to-one.
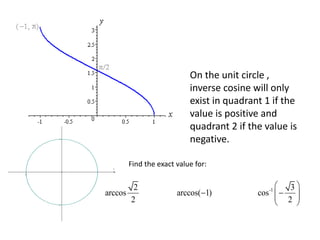
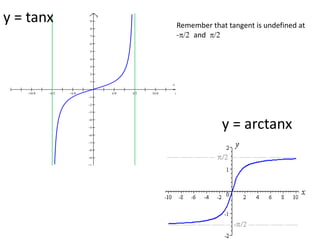
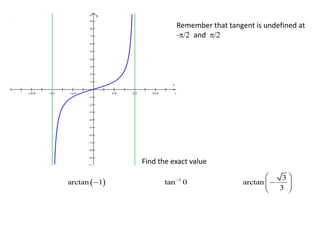
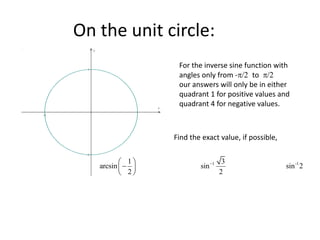
3) The inverse functions are denoted as arcsine, arccosine, and arctangent. Their values are restricted to certain quadrants based on the corresponding trigon



![
x
y
For the graph of y = sin x, the Domain is (-∞, ∞)
the Range is [-1, 1]
Not a 1-1 function
So it currently does
not have an inverse](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-7-240202144449-ca03f209/85/4-7-ppt-5-320.jpg)
![
x
y
However we can restrict the domain to [-/ , /]
Note the range will remain [-1, 1]
Now it’s 1-1!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-7-240202144449-ca03f209/85/4-7-ppt-6-320.jpg)
![/ / / / / /
x
y
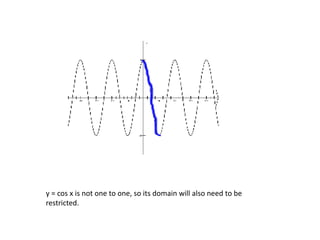
On this interval, [0, ] the
cosine function is one-to-
one and we can now
define the inverse cosine
function.
y = arccos x or y = cos-1 x
y = arccos x
y = cos x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-7-240202144449-ca03f209/85/4-7-ppt-11-320.jpg)