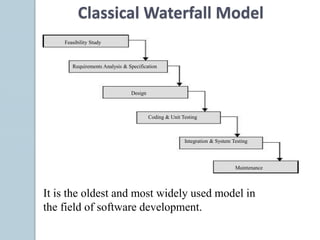
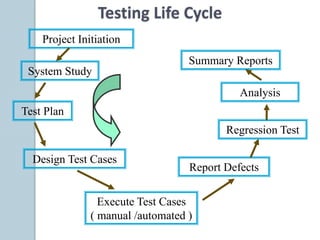
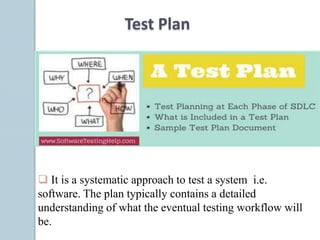
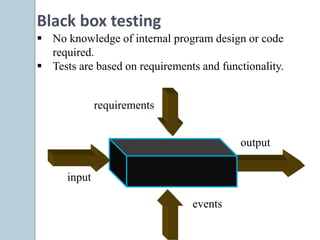
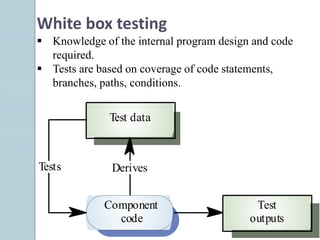
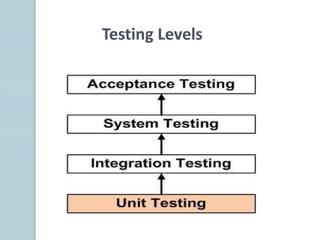
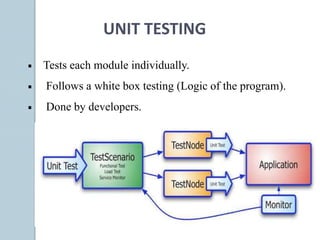
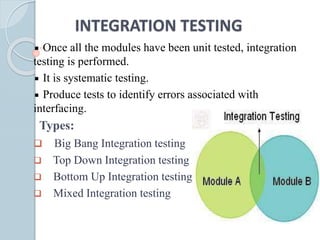
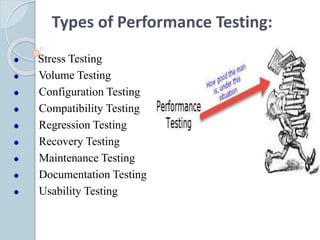
The document discusses various aspects of software testing such as the definitions of testing, different testing methodologies like black box and white box testing, testing levels from unit to acceptance testing, and performance testing types including stress, recovery, and compatibility testing. It also covers testing tools, test plans, test cases, and the software development life cycle.