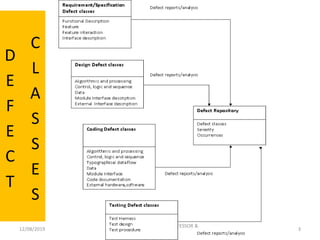
This document discusses different classes of defects that can occur during software development and testing. It identifies four main defect classes:
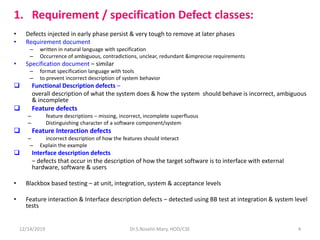
1. Requirement/specification defects that occur early in ambiguous, incomplete, or contradictory requirements documents.
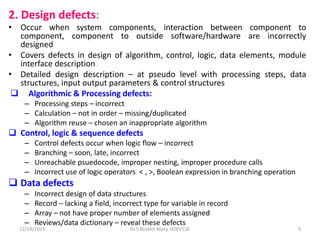
2. Design defects that happen when system components or their interactions are incorrectly designed, such as flaws in algorithms, control logic, or interface descriptions.
3. Coding defects resulting from errors implementing code, including issues with algorithms, control structures, data types, interfaces, and documentation.
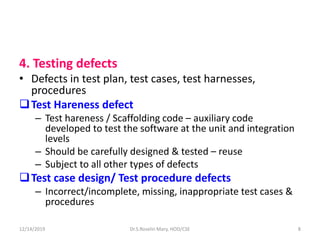
4. Testing defects in test harnesses, cases, and procedures that could lead to incorrect or incomplete testing. The classes of defects guide strategies for test planning and design.