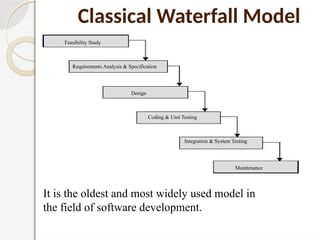
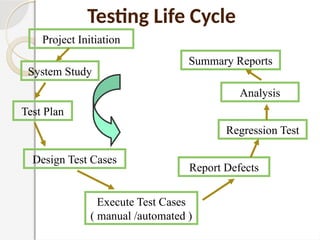
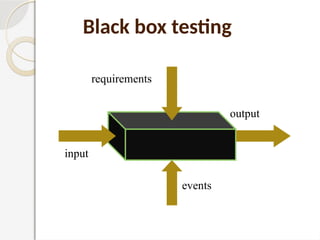
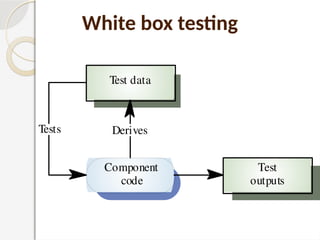
The document discusses software testing as a critical process for ensuring the correctness and quality of software through various methodologies and phases, including verification and validation. Key concepts such as error, bug, fault, and failure are defined, alongside different testing types and stages within the software development life cycle. It also emphasizes the importance of effective planning in testing to maximize resource efficiency and achieve desired quality outcomes.