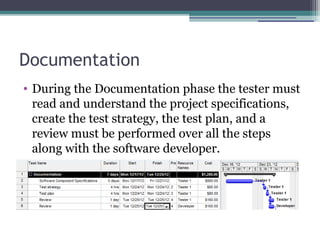
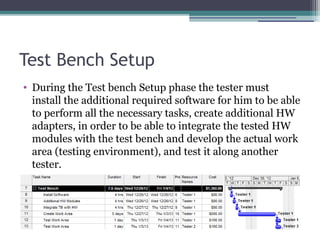
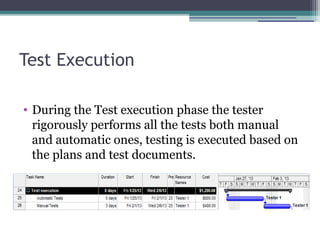
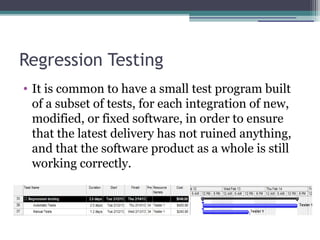
The document outlines the software validation process which includes test development to check if software meets customer specifications. It describes the human and material resources needed for testing as well as constraints like limited resources and budget. The validation process involves documentation, test setup, development and execution, reporting, result analysis, defect retesting, regression testing, and closure to archive results for future projects.