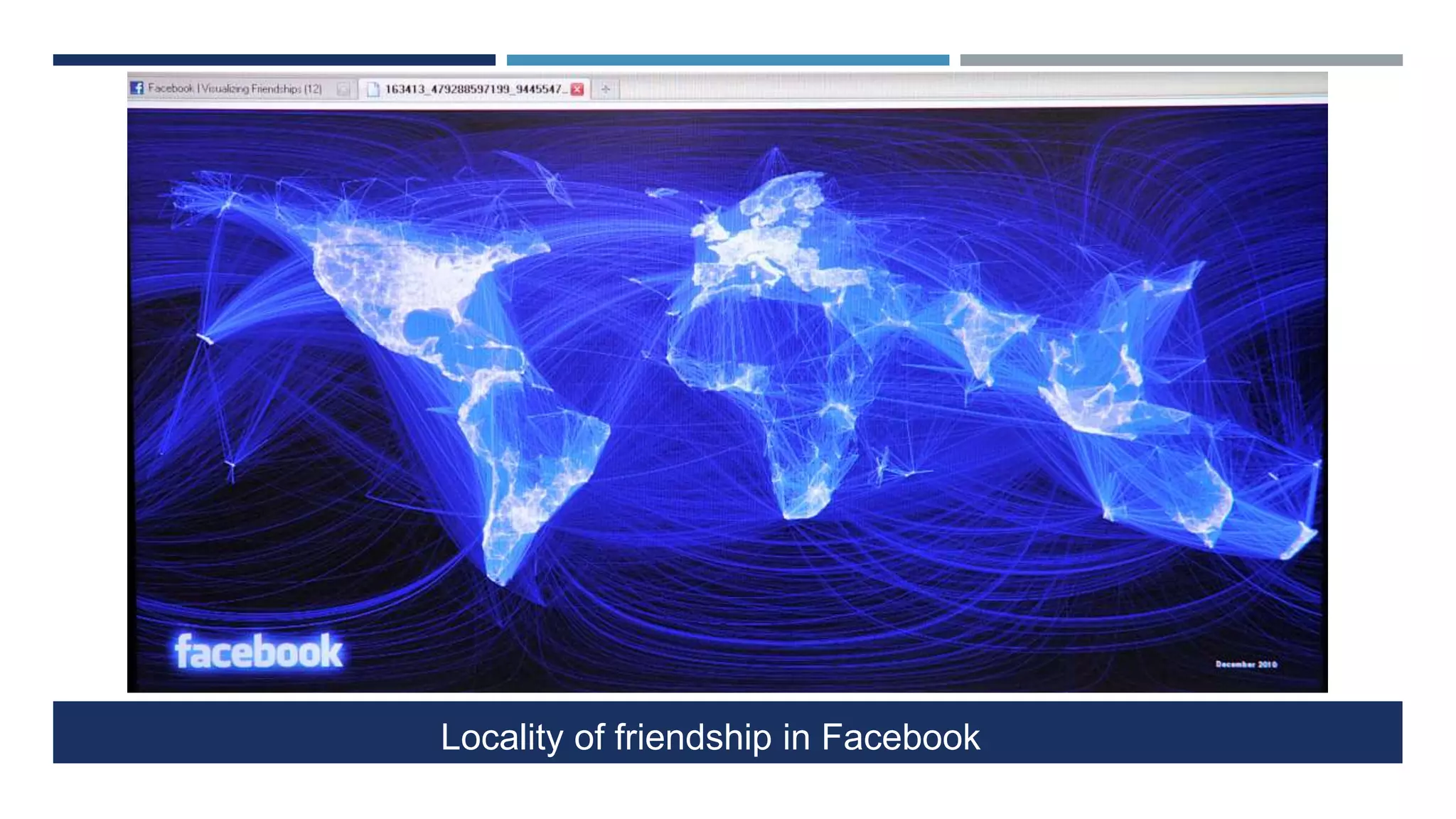
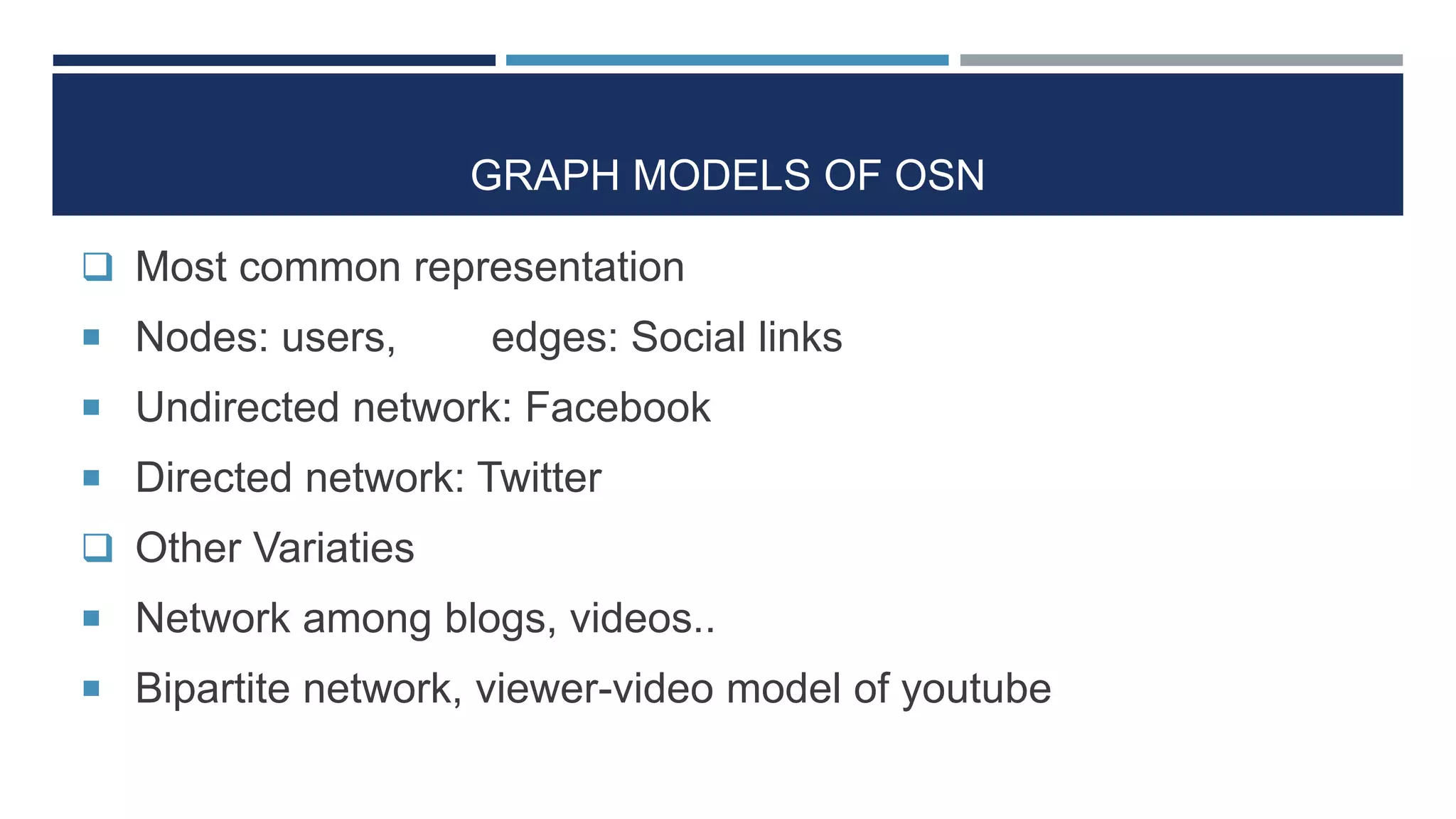
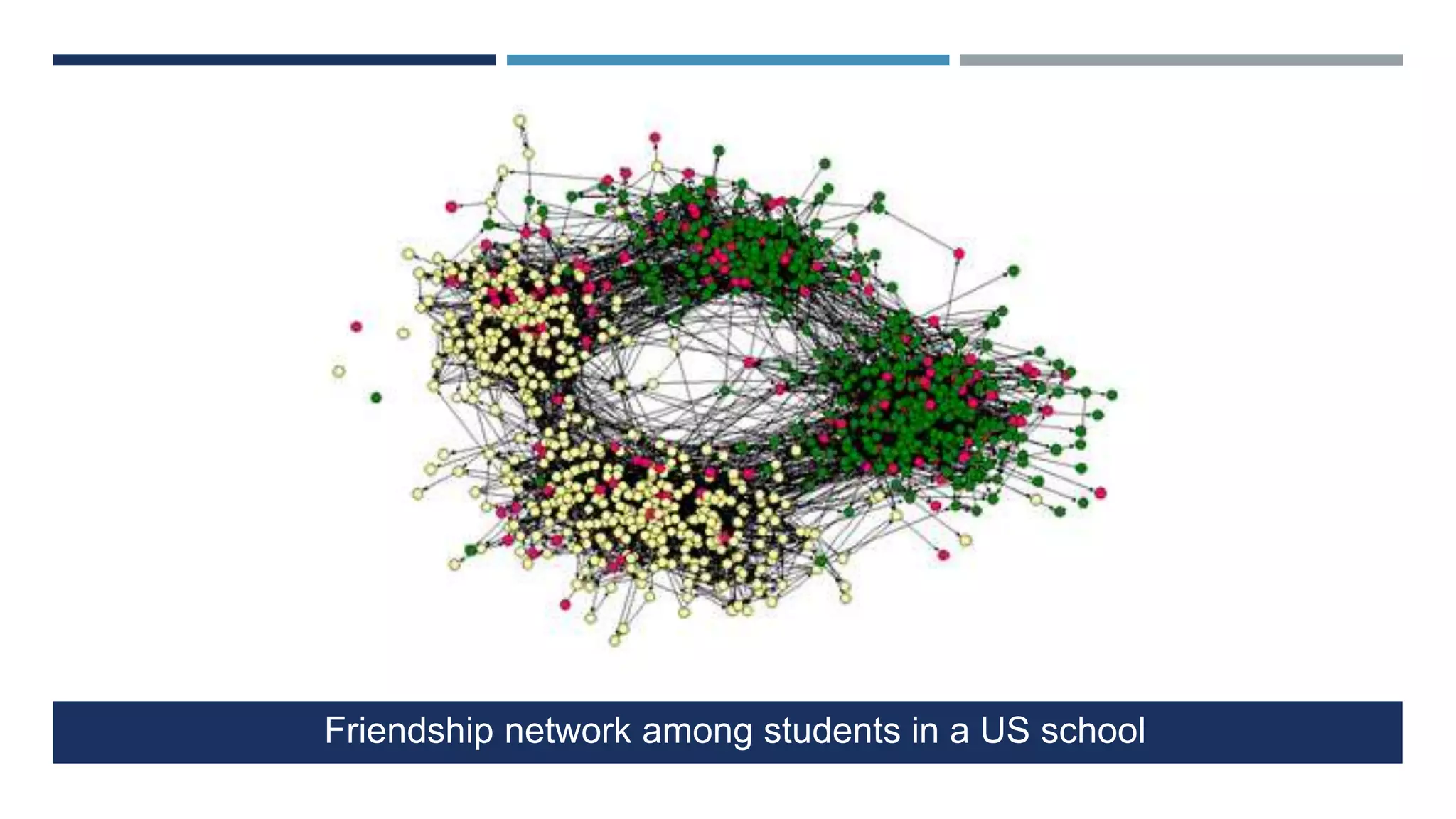
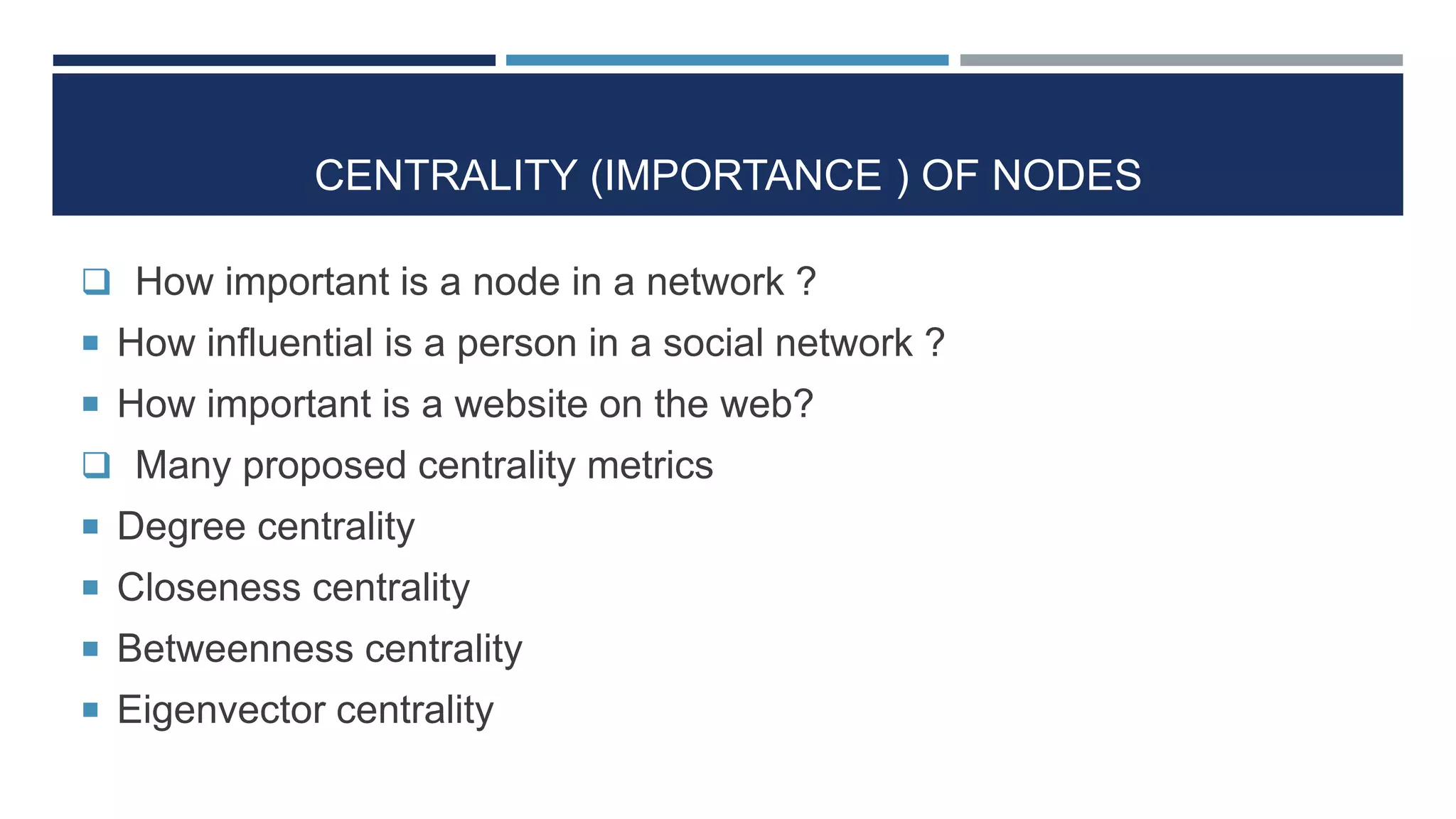
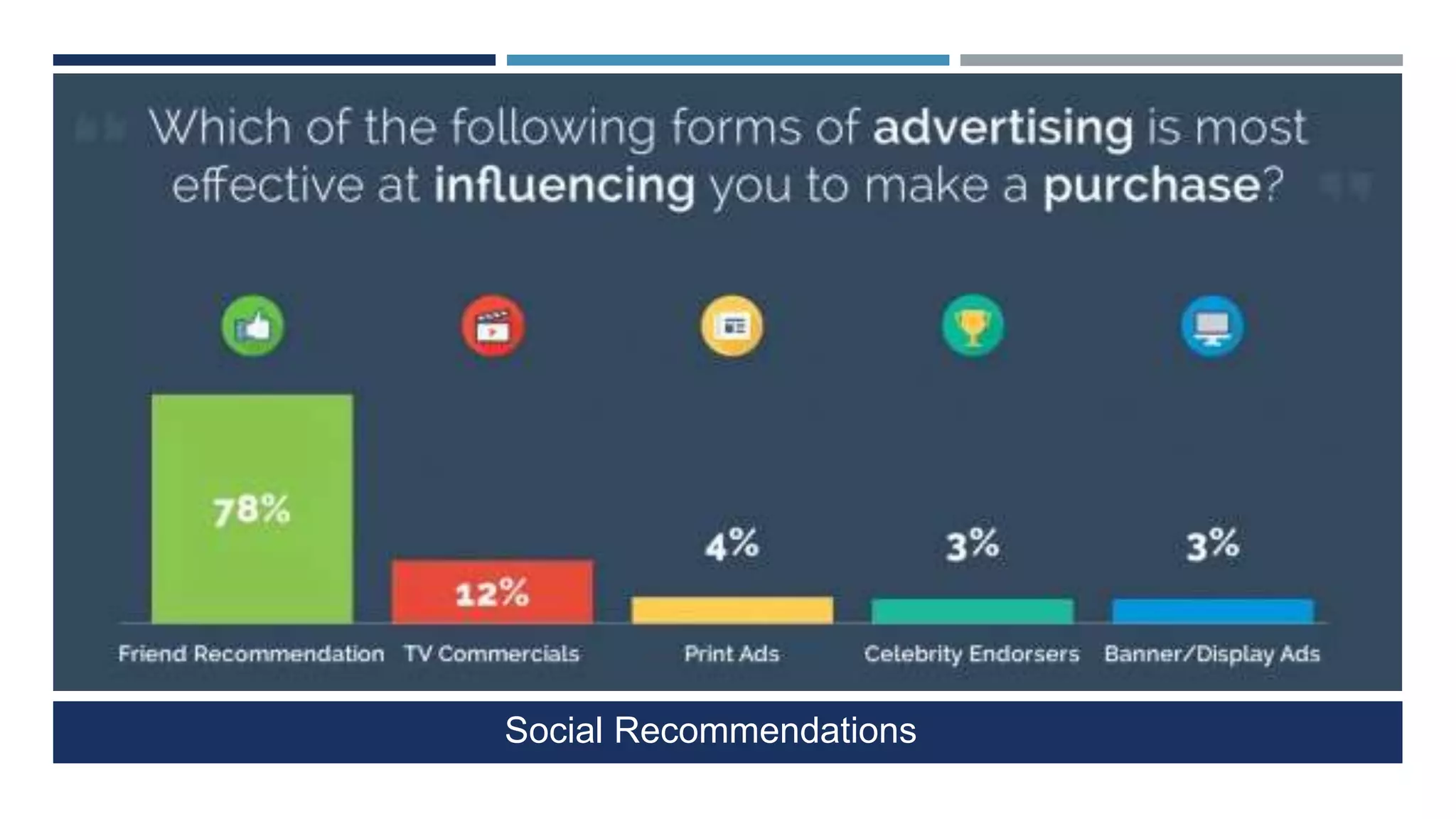
The document discusses social network analysis (SNA) as a method for examining relationships among actors in various fields such as sociology, biology, and computer science. It highlights key sociological theories, the significance of online social networks (OSNs), and tools used to analyze these networks, along with various metrics for assessing the centrality and strength of connections. Additionally, it outlines the implications of SNA in understanding data-driven phenomena like information diffusion and social governance.