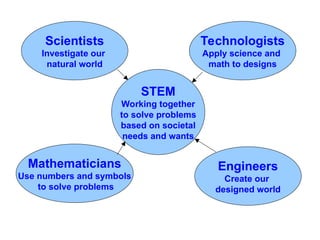
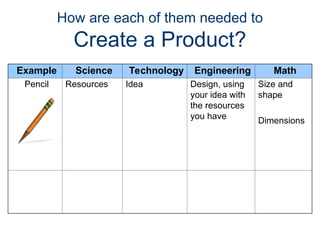
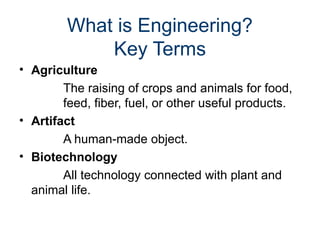
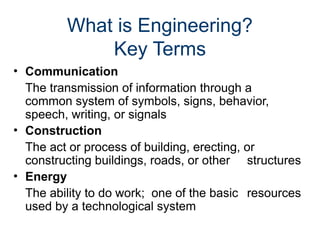
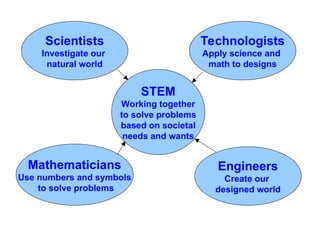
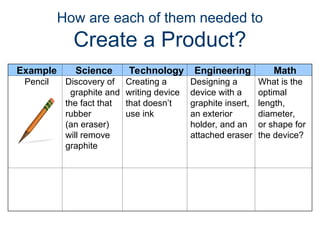
The document outlines the roles of scientists, engineers, mathematicians, and technologists in creating products to meet societal needs, emphasizing collaboration in STEM fields. It differentiates between science and technology, illustrating how each contributes to engineering and problem-solving, with examples like the development of a pencil. Additionally, it discusses essential questions related to engineering practices, the importance of documentation, and the distinctions between inventions and innovations.