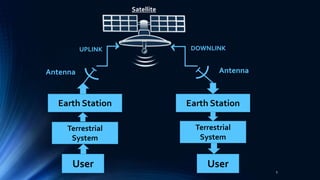
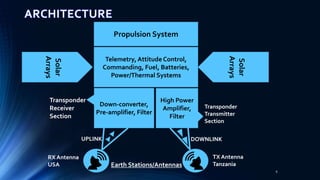
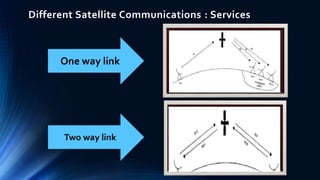
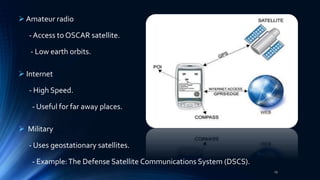
Satellite communication plays a vital role in global telecommunications. A satellite is an object that revolves around another object due to gravitational forces. There are two types of satellites: passive satellites that simply reflect signals, like the Moon, and active satellites that have onboard processing equipment to act as repeaters. The first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched in 1957. Key components of satellite communication systems are the space segment including the satellite, and the ground segment including earth stations. Satellites can be in either geostationary orbit or non-geostationary orbits, and provide important one-way and two-way communication services with many advantages.