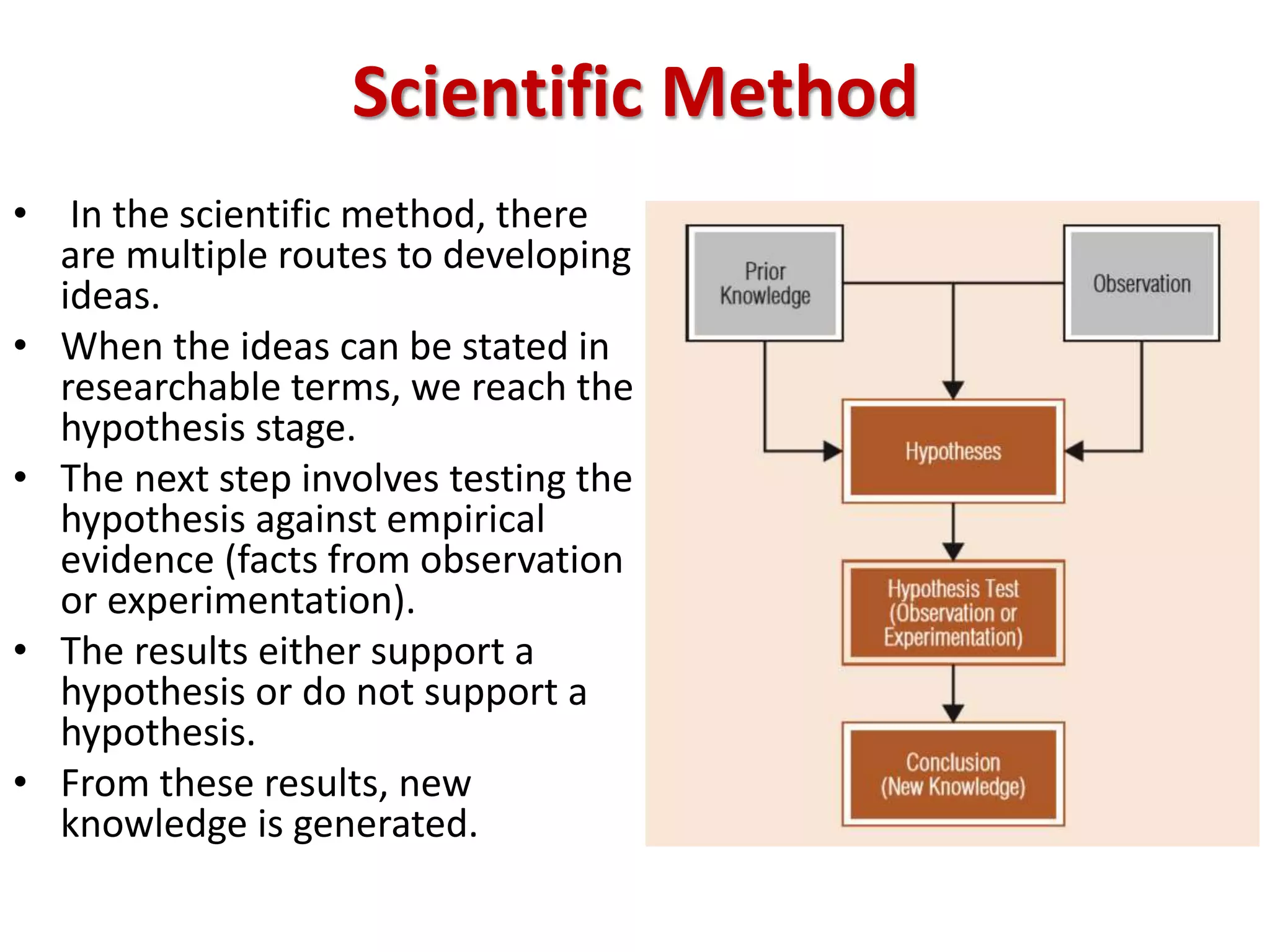
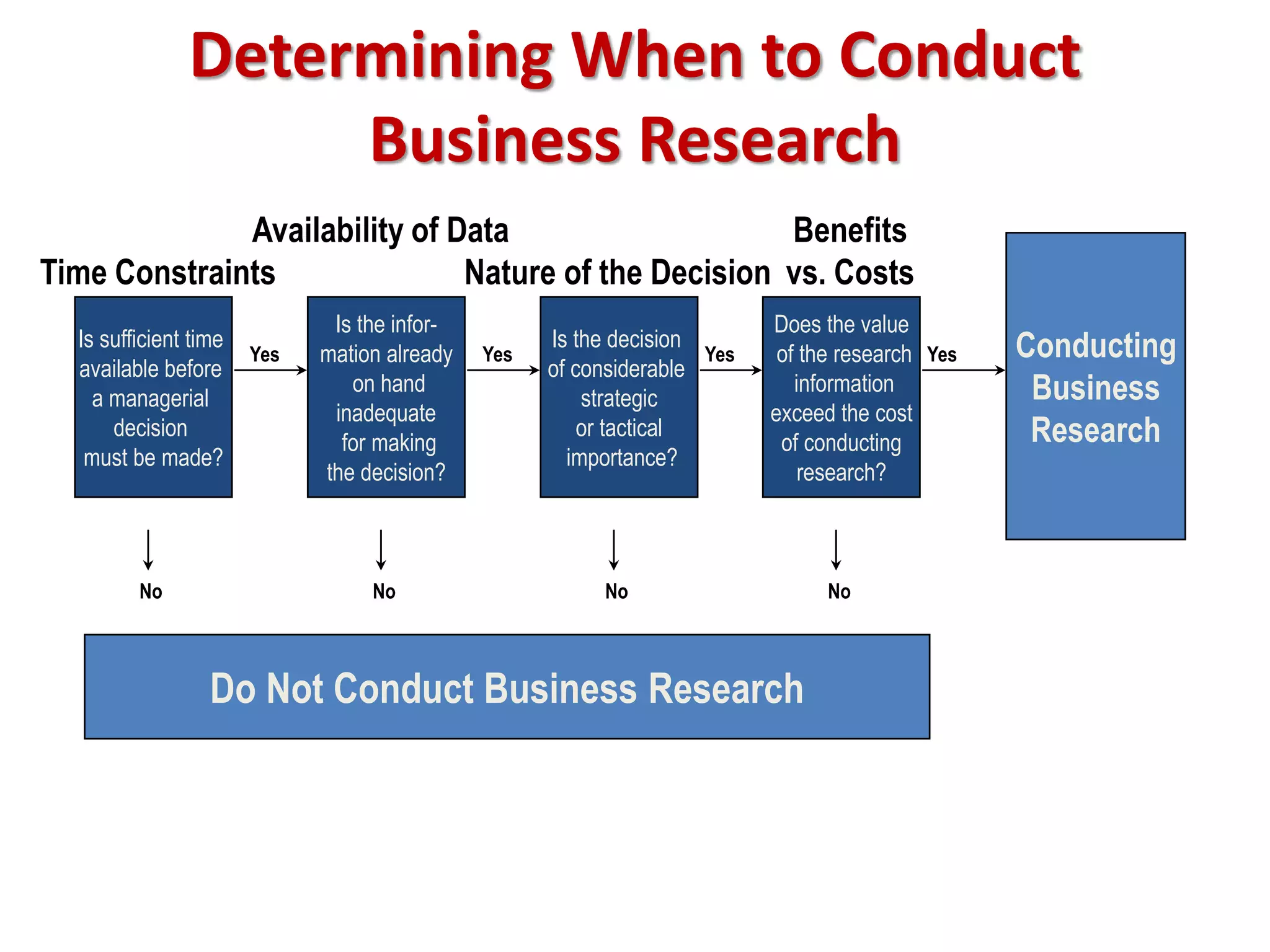
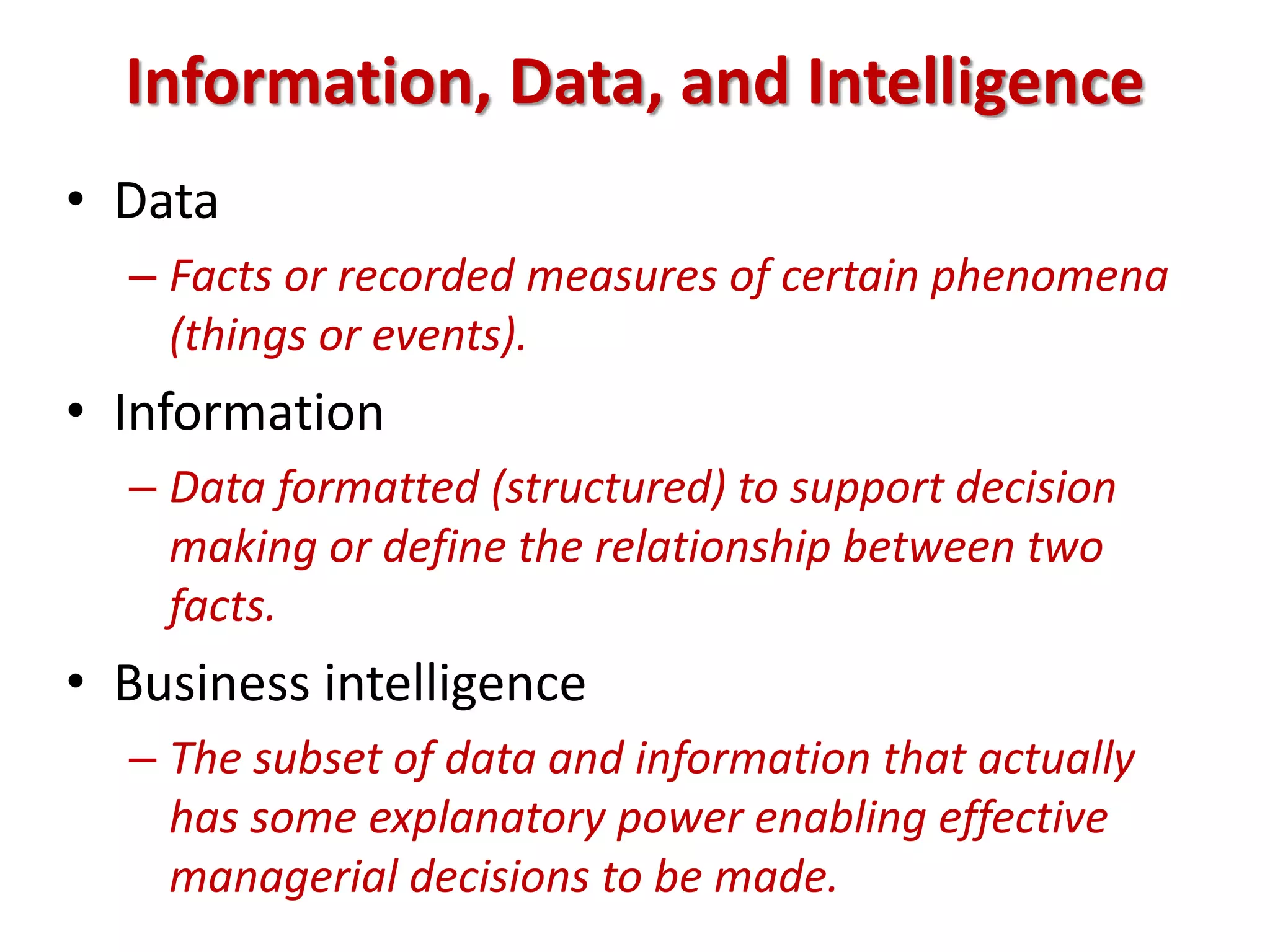
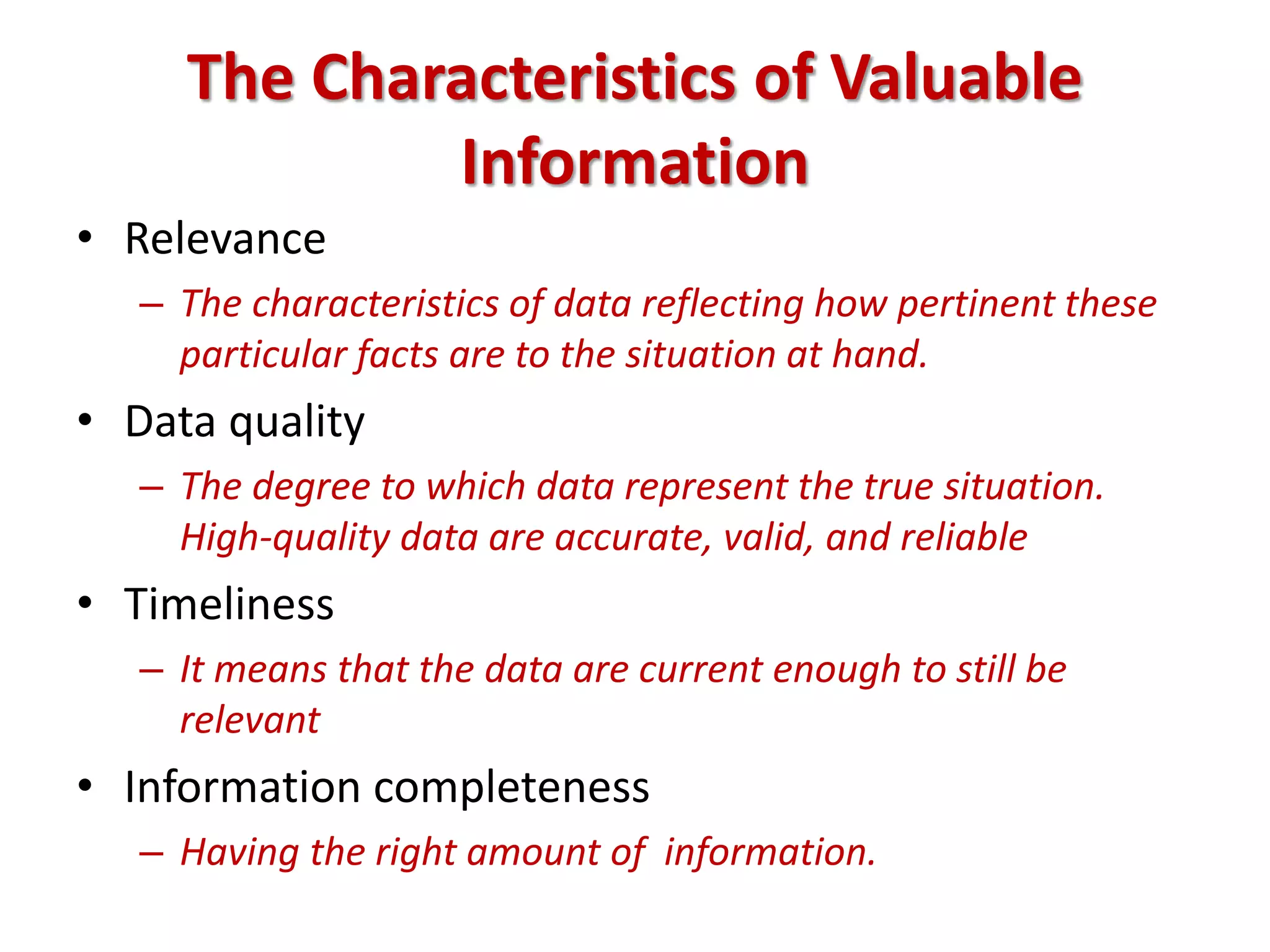
This document provides an overview of business research and information systems/knowledge management. It defines business research as the systematic process of generating objective information to aid decision-making. There are two main types: basic research expands general knowledge, while applied research addresses specific organizational problems. The scientific method involves testing hypotheses through empirical evidence. Key factors in determining when to conduct research include time constraints, data availability, the importance of the decision, and whether research benefits outweigh costs. Information systems and knowledge management are also discussed, including defining data, information, intelligence, and knowledge.