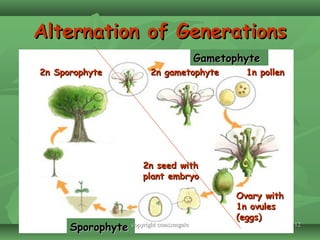
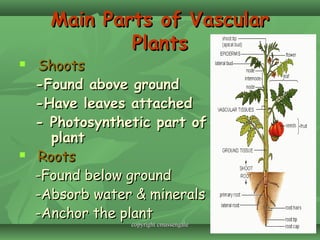
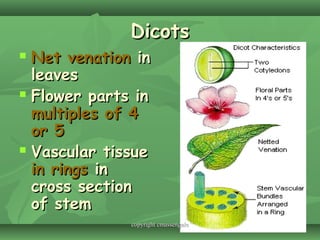
Plants evolved from aquatic algae to colonize land. They developed vascular tissue to transport water and nutrients throughout the plant. Plants are divided into two kingdoms - nonvascular bryophytes and vascular plants. Vascular plants are further divided into seedless plants like ferns and seed-producing plants like gymnosperms and angiosperms. Angiosperms, which include monocots and dicots, are the most diverse and economically important group of plants.