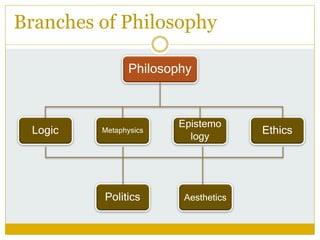
This document provides an introduction and overview of philosophy. It defines philosophy as the systematic study of fundamental human knowledge and the pursuit of wisdom. The document traces the origin of the term "philosophy" to ancient Greek roots meaning "love of wisdom". It outlines the main goals of philosophy as discovering the nature of truth and knowledge. The document also describes the scope and key branches of philosophy, and emphasizes philosophy's importance in clarifying beliefs, stimulating thinking, and developing analytical abilities.