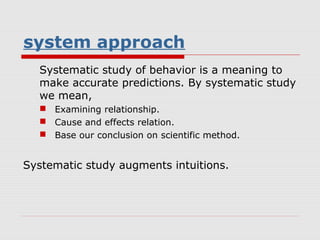
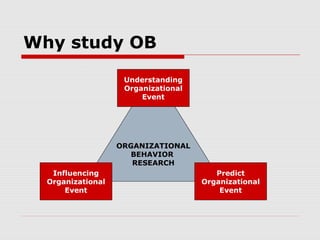
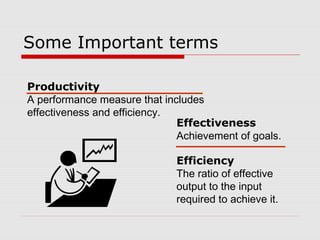
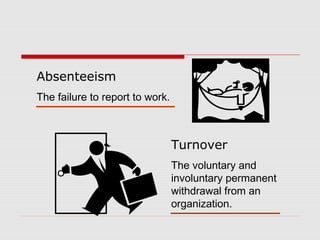
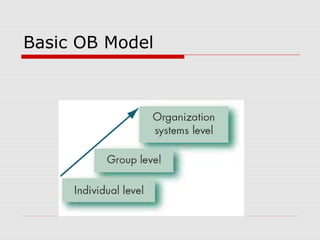
The document outlines key concepts in organizational behavior including:
1. The objectives of studying organizational behavior which are to define OB, discuss its historical perspective and multi-disciplinary nature, and why managers require OB knowledge.
2. A summary of the seminal Hawthorne Studies from the 1920s-30s which examined how various working conditions impacted productivity. The studies found that productivity increased regardless of changes, likely due to the social dynamics within the work group.
3. An overview of challenges and opportunities for applying OB concepts like responding to globalization, diversity, innovation, and improving customer service and ethics. Knowledge management, which involves acquiring, sharing and using knowledge, is also discussed.