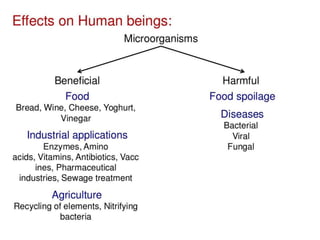
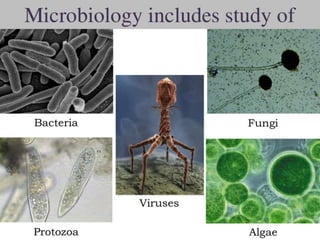
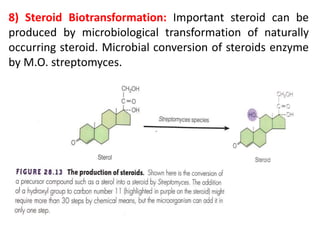
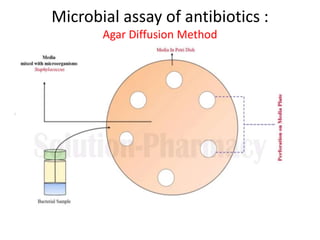
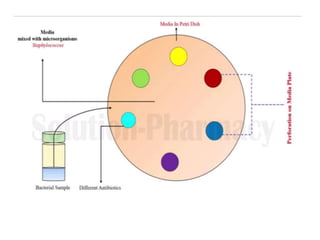
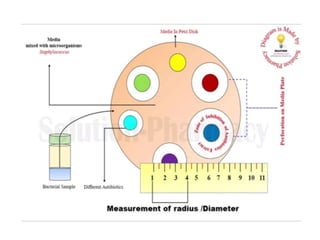
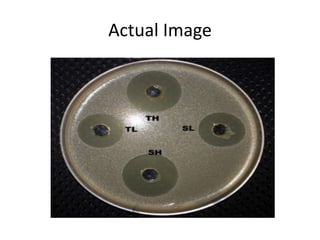
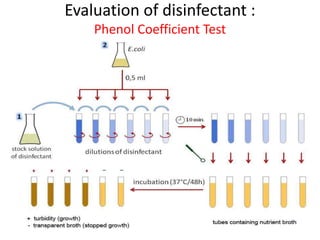
The document outlines the field of microbiology, highlighting its definition, branches, and applications. It details the role of microorganisms in antibiotic production, disease diagnosis, enzyme and vaccine development, and environmental applications such as waste treatment and plant growth promotion. Additionally, it discusses methods for testing pharmaceuticals and ensuring sterility in medical products.