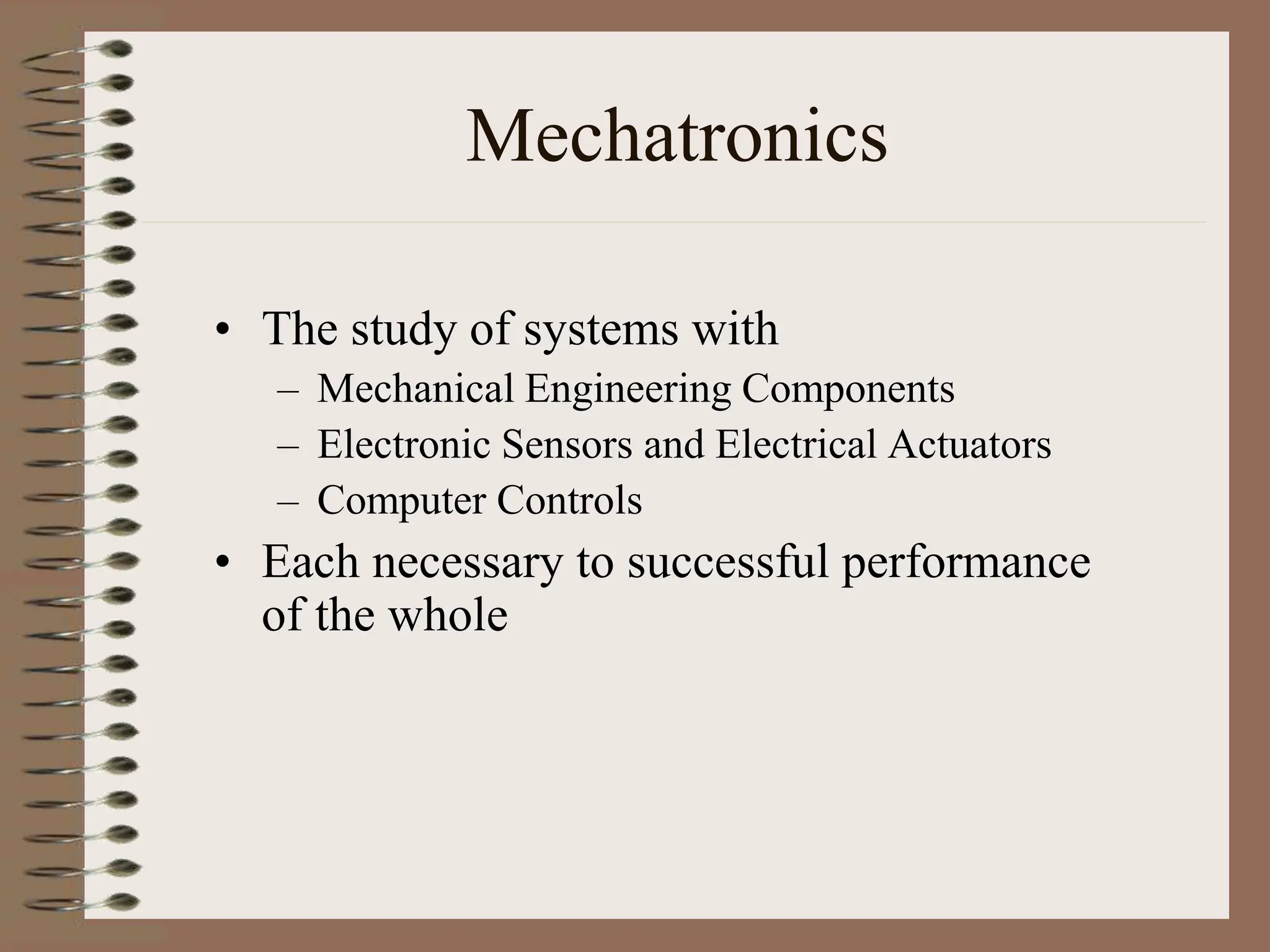
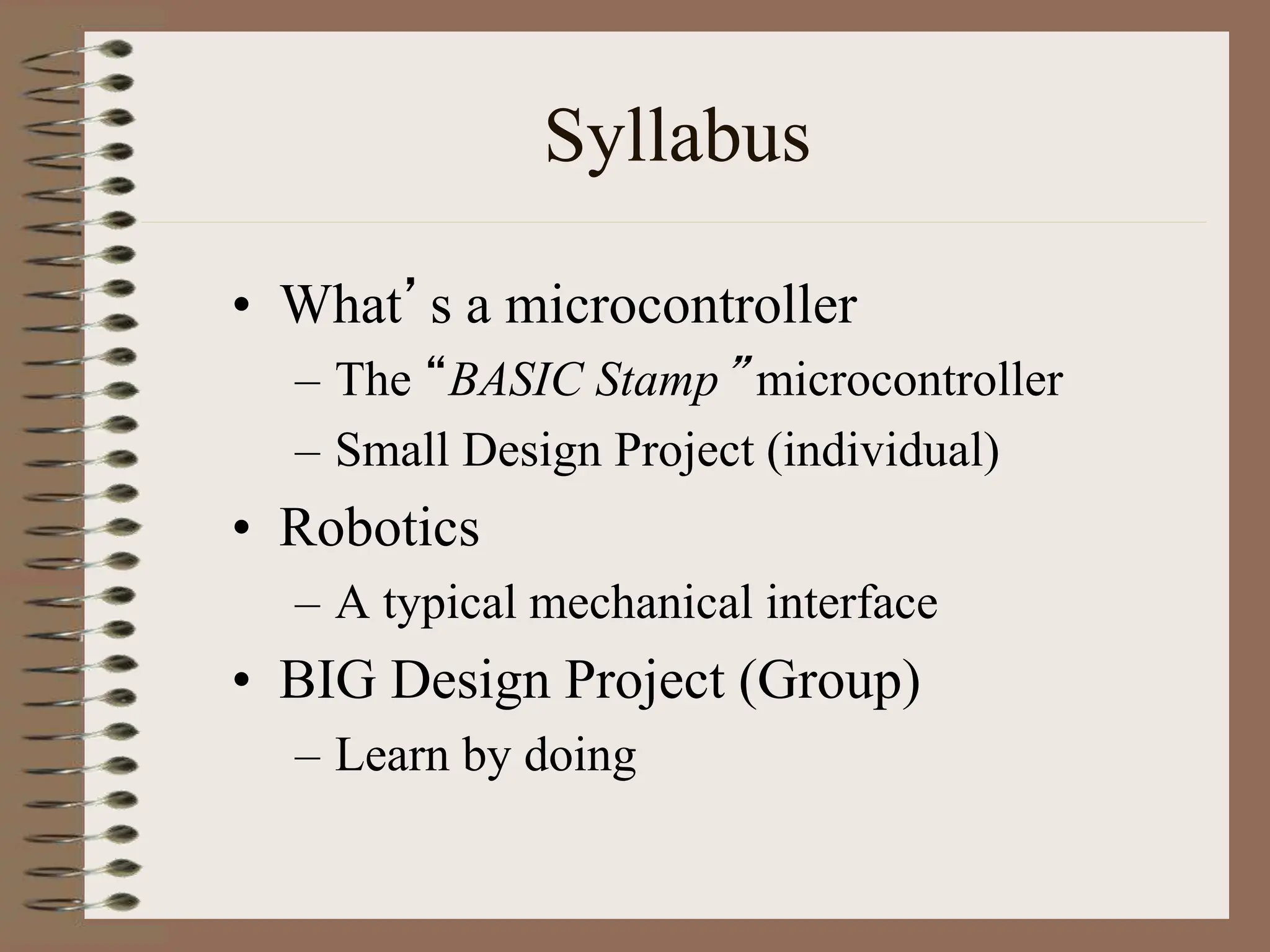
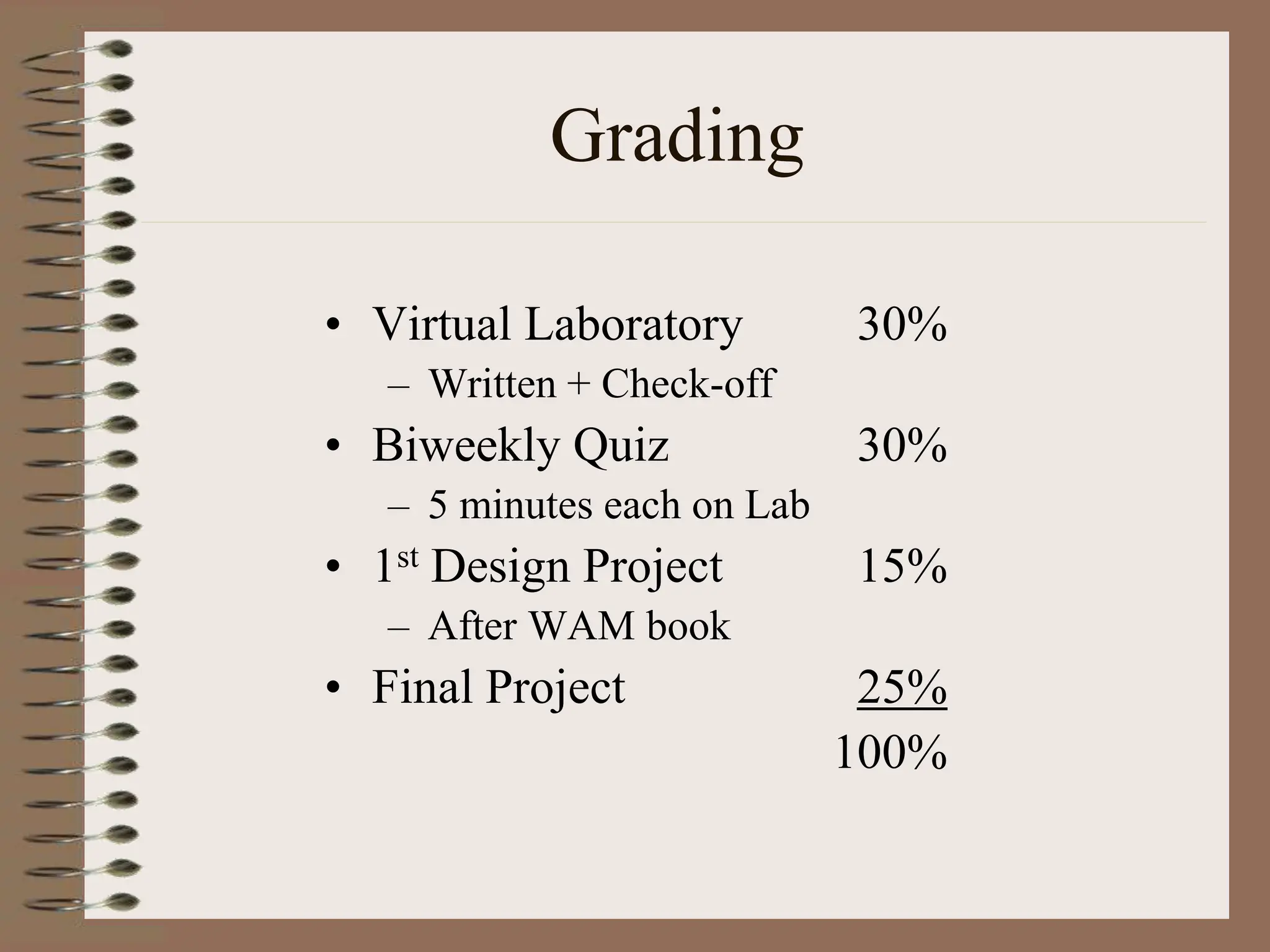
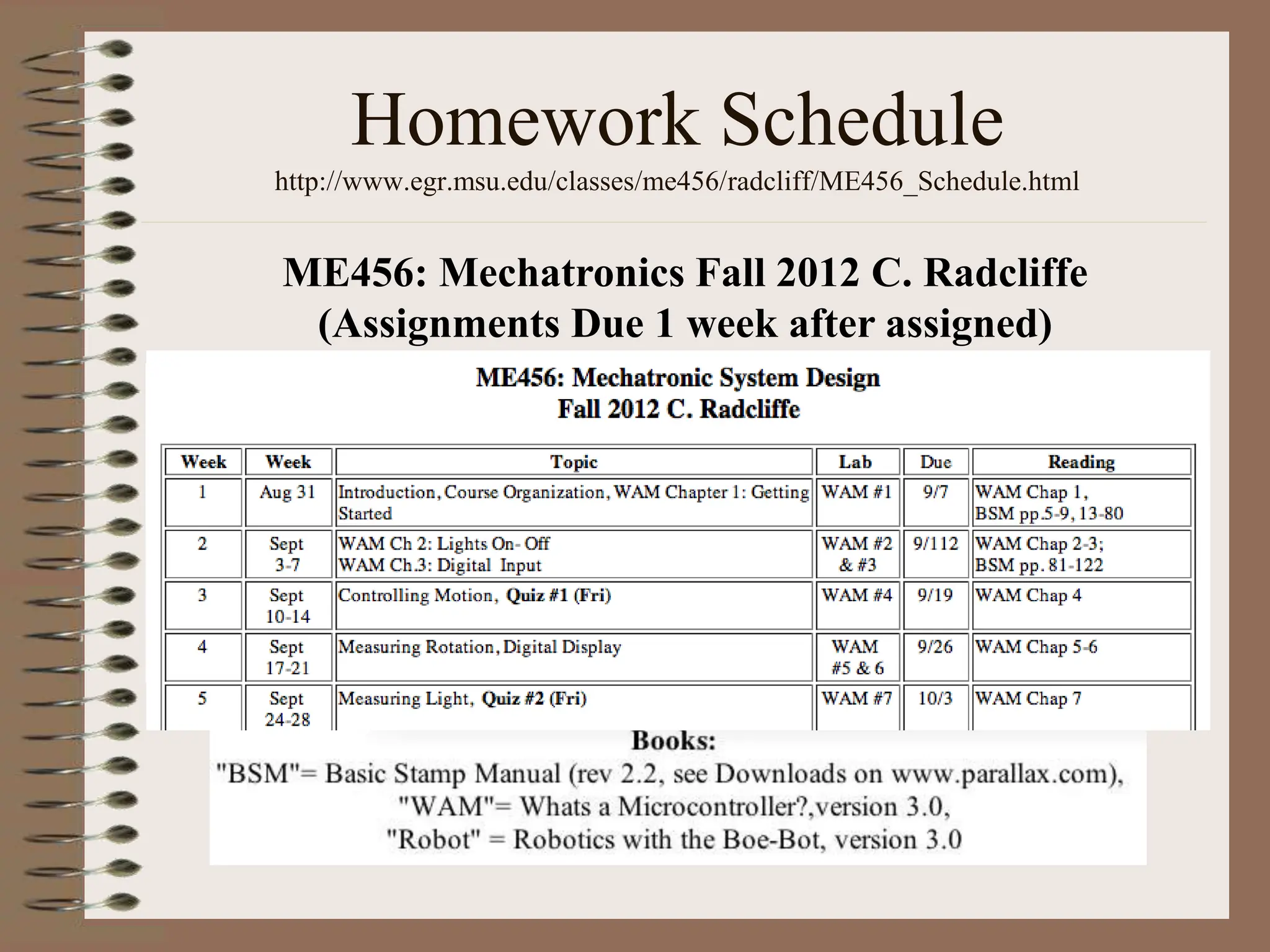
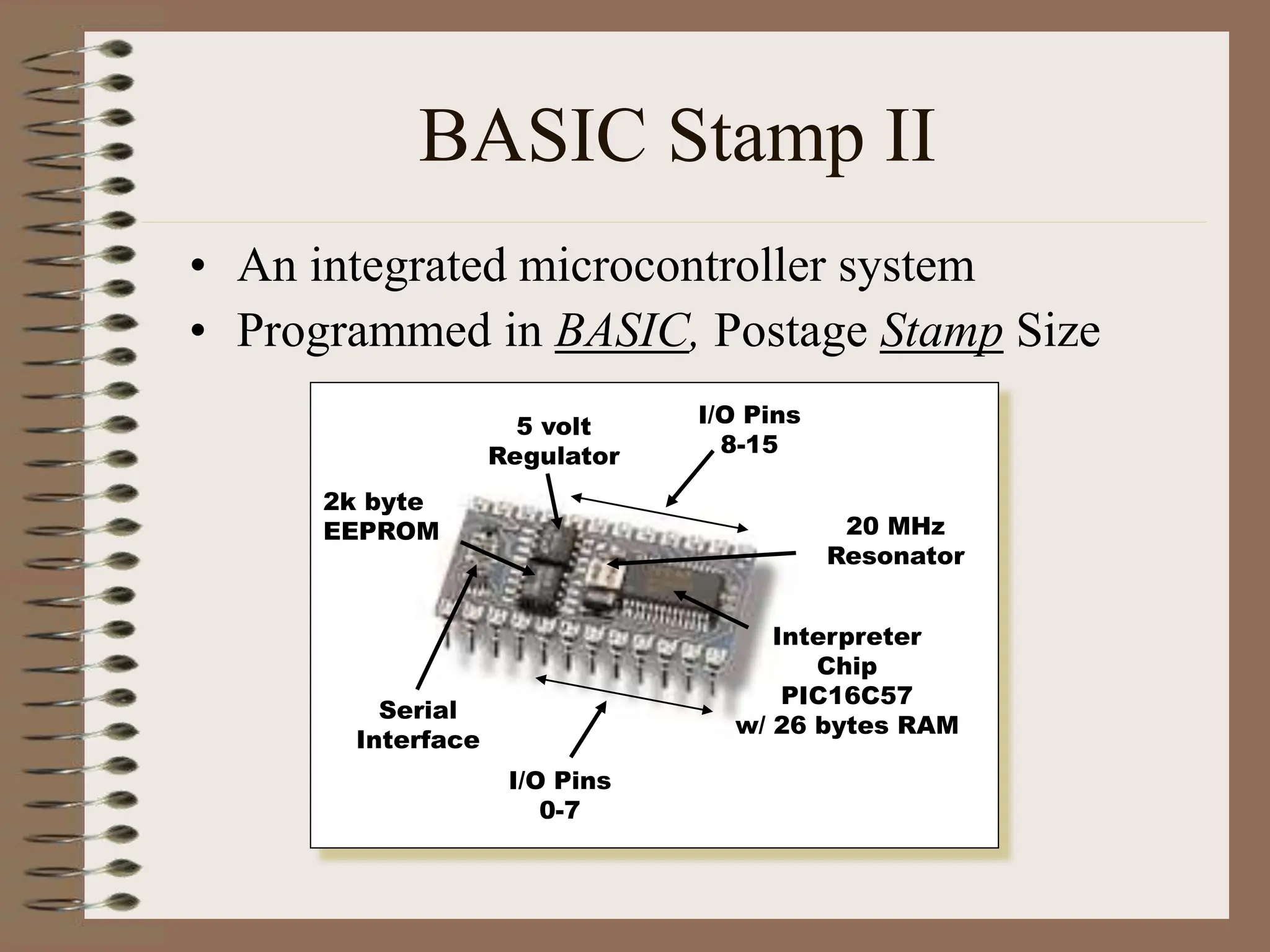
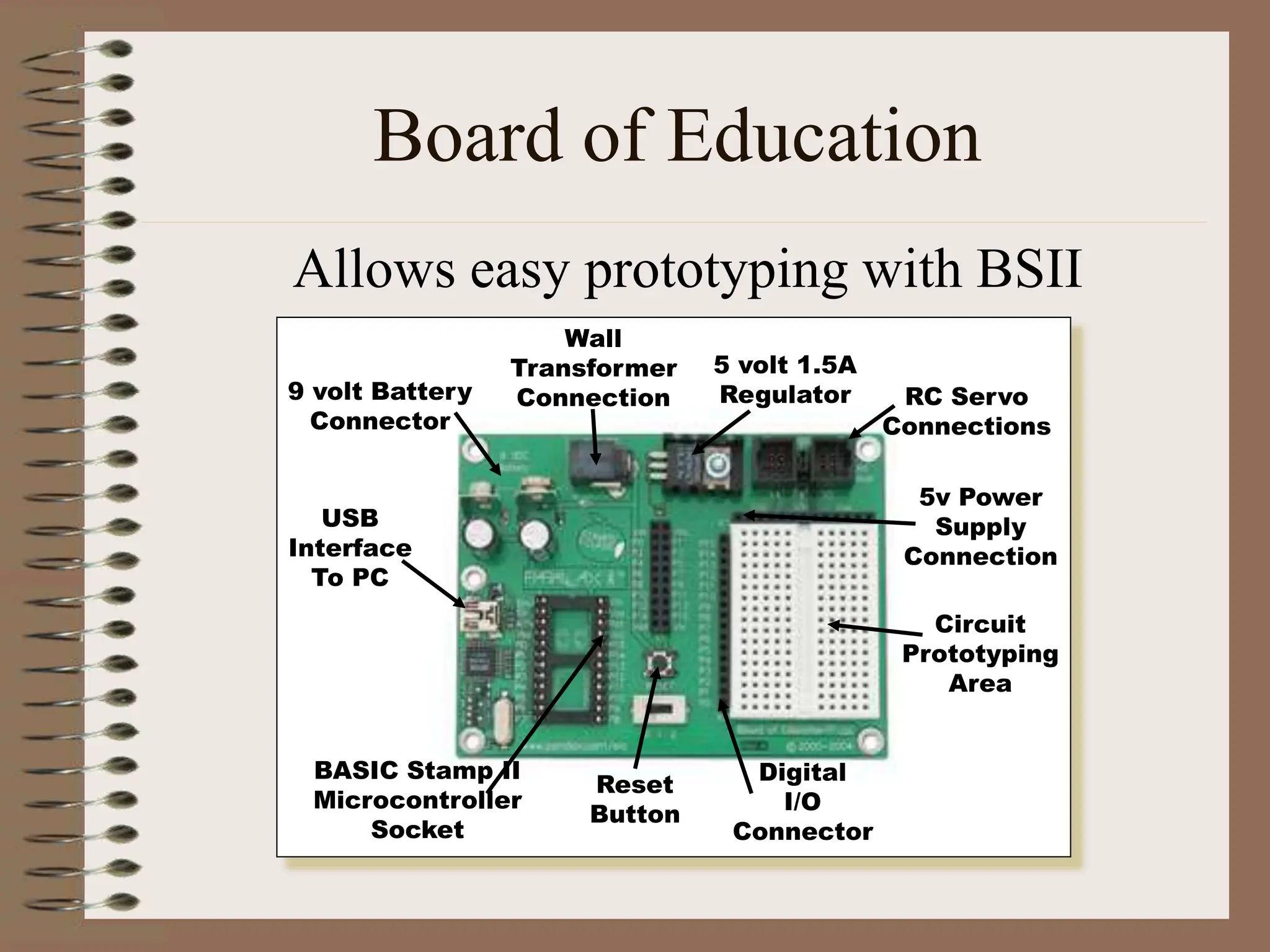
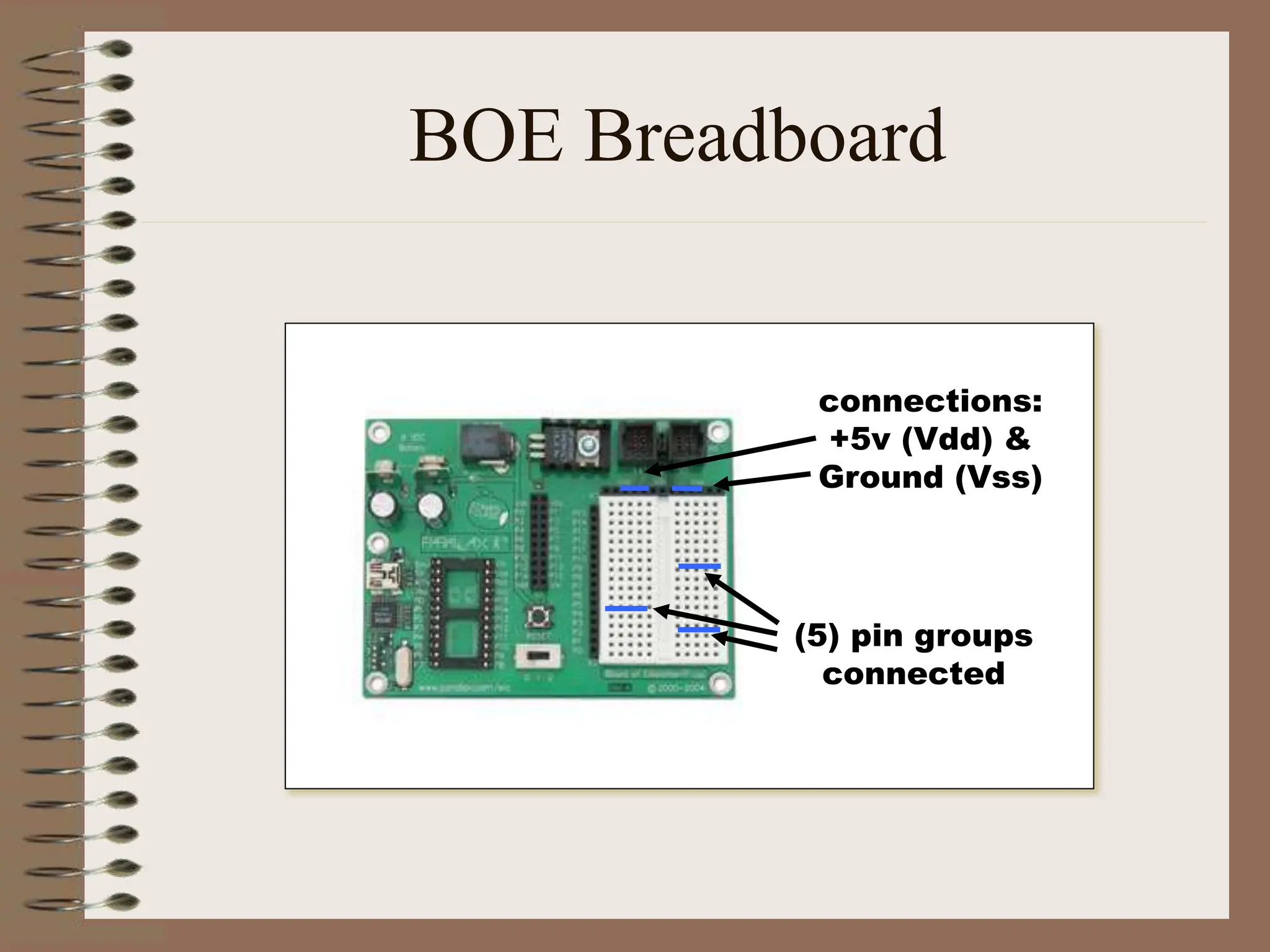
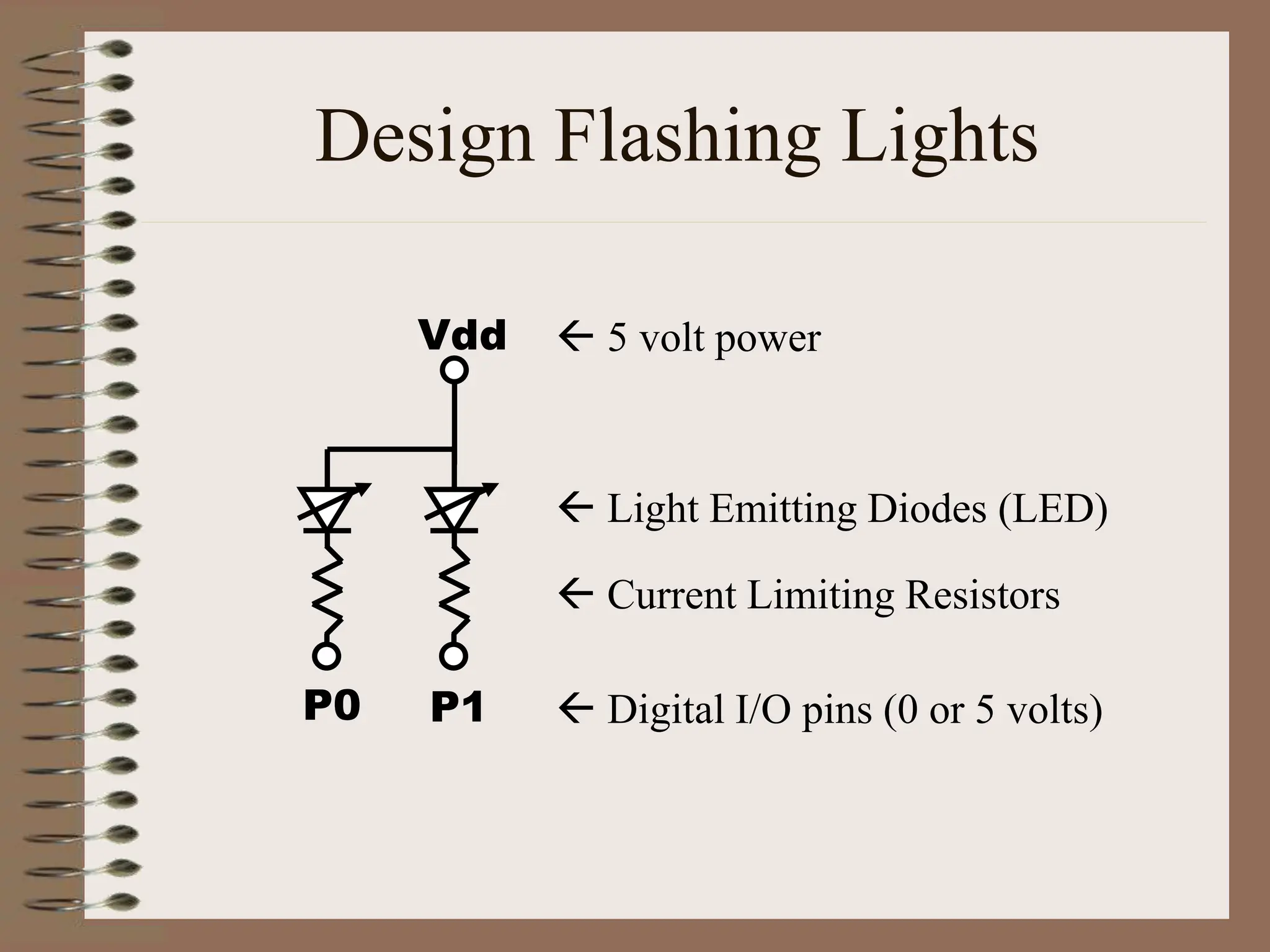
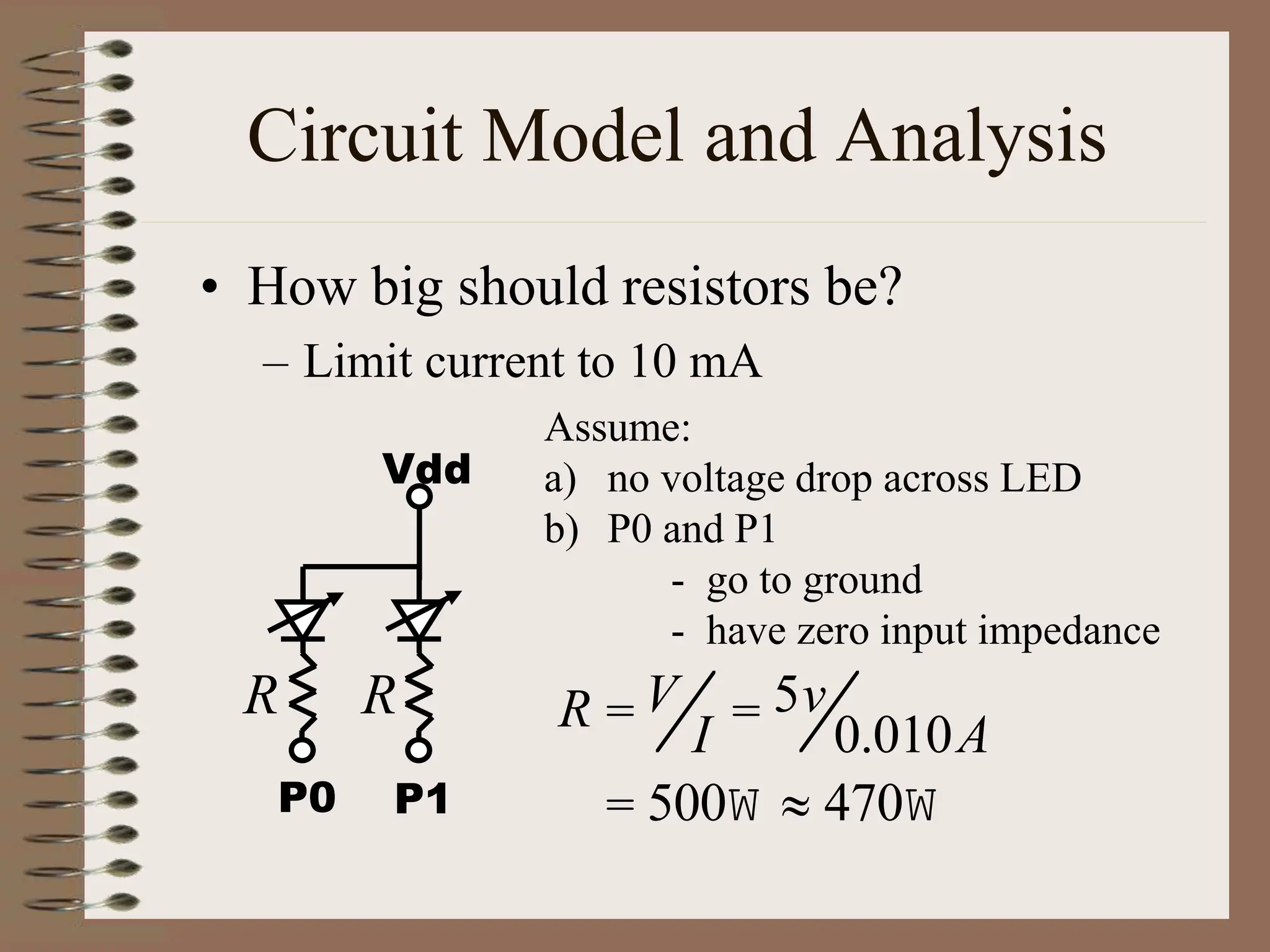
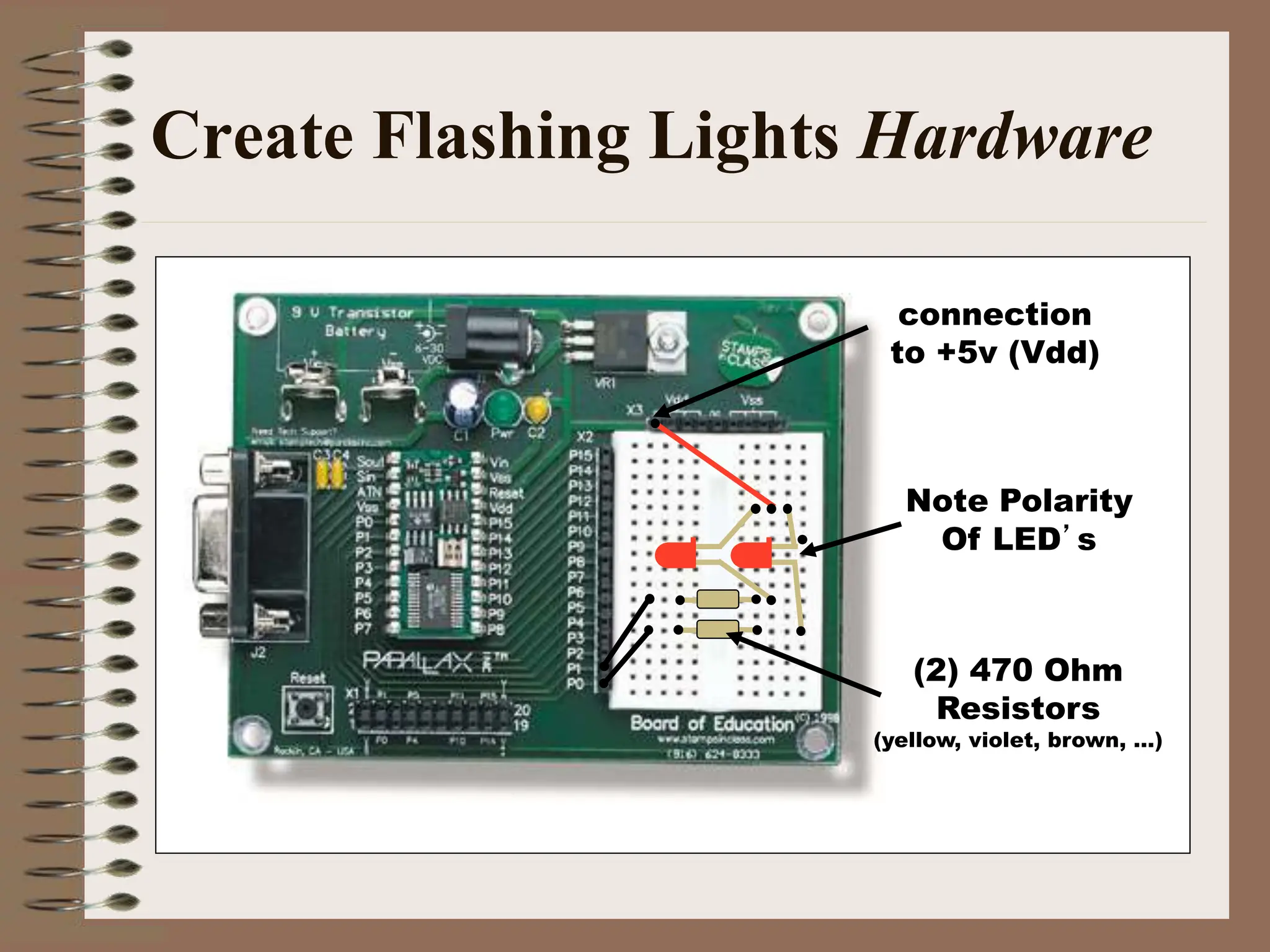
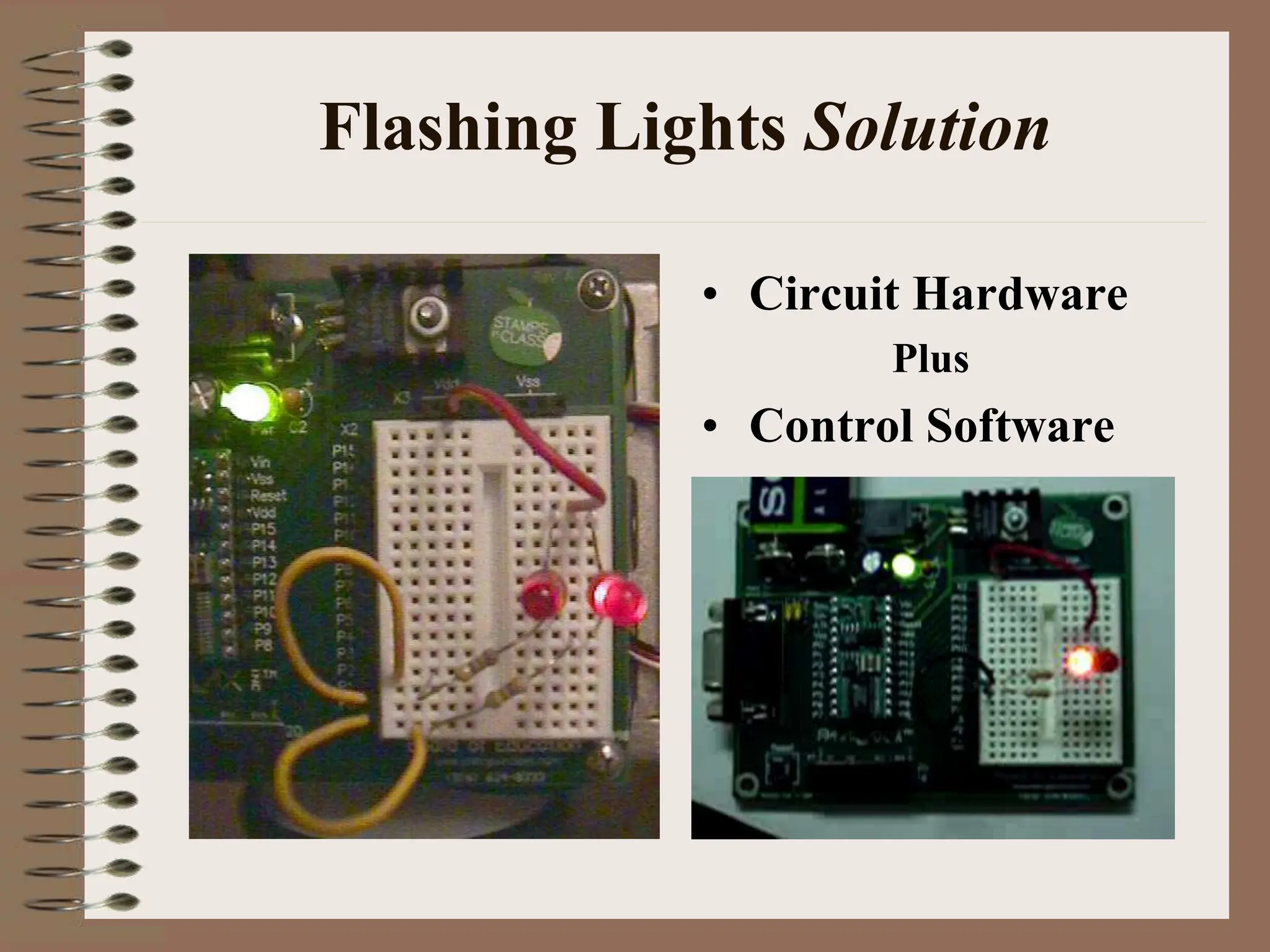
The document outlines the ME456 Mechatronics course led by Professor Clark J. Radcliffe at Michigan State University, detailing office hours, contact information, and course scheduling. It highlights key aspects of mechatronics, including the integration of mechanical and electronic systems with computer controls, as well as practical projects focusing on microcontrollers. The grading system and initial assignments, including hands-on lab work and design projects, are also described.