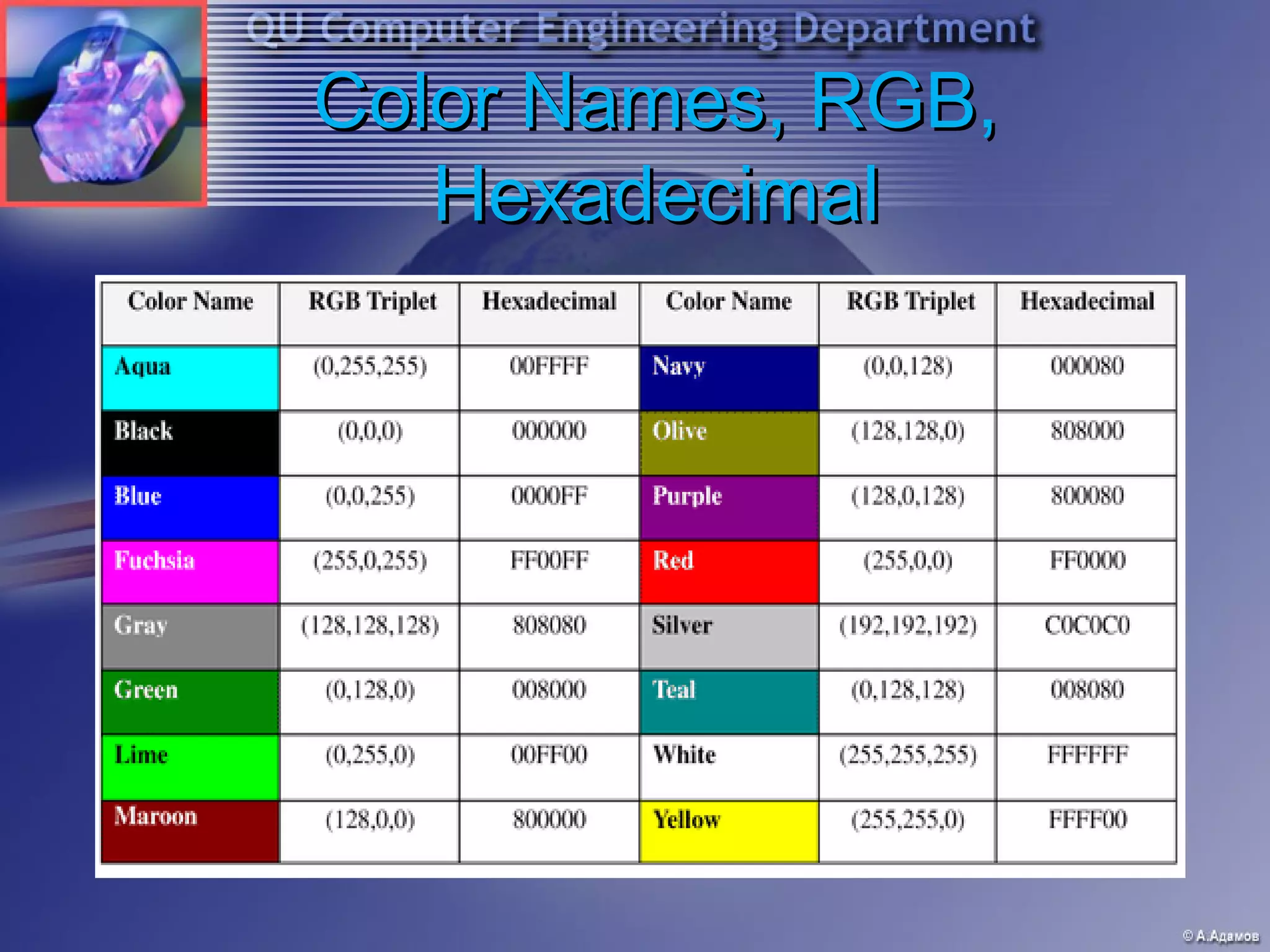
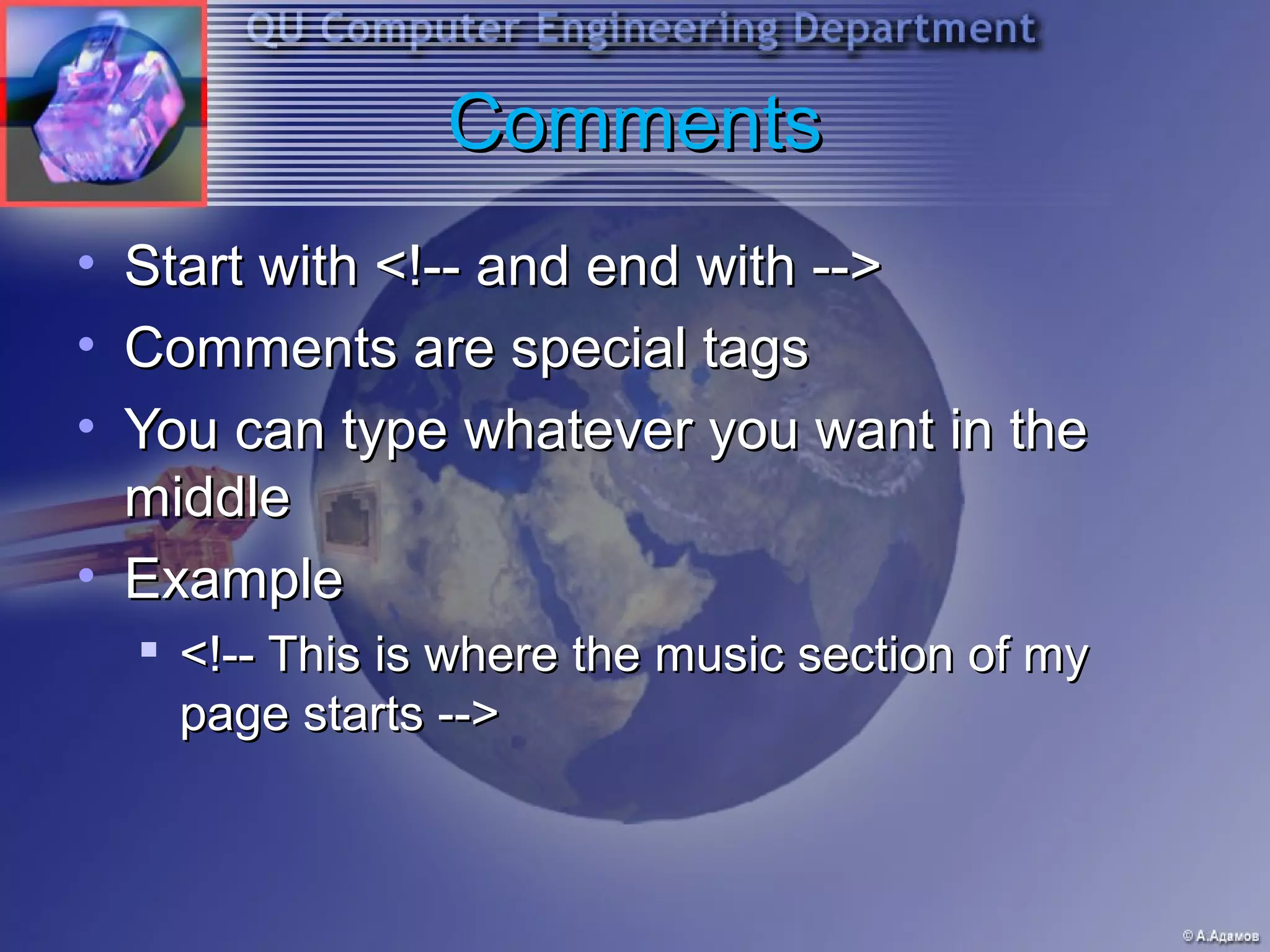
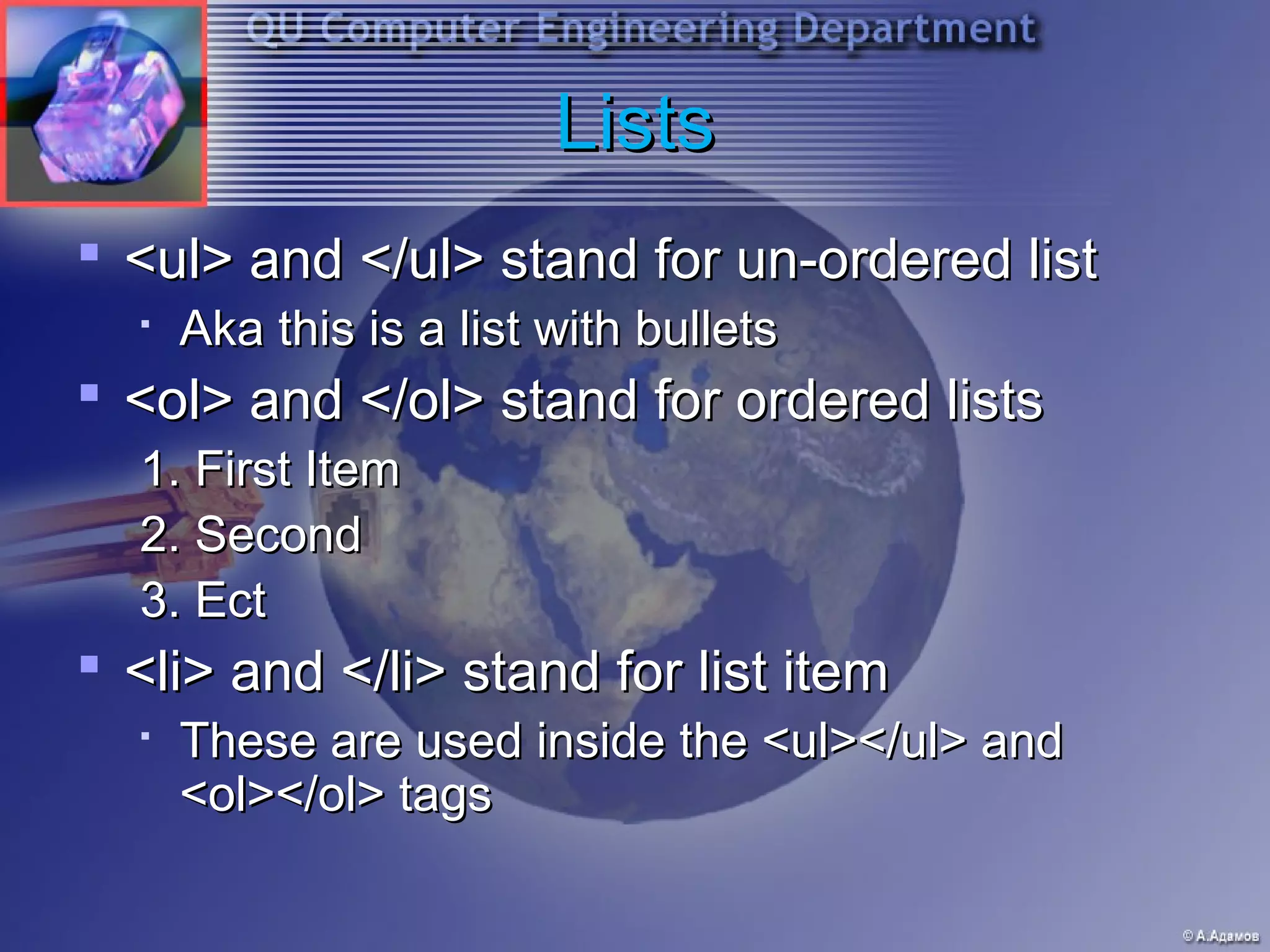
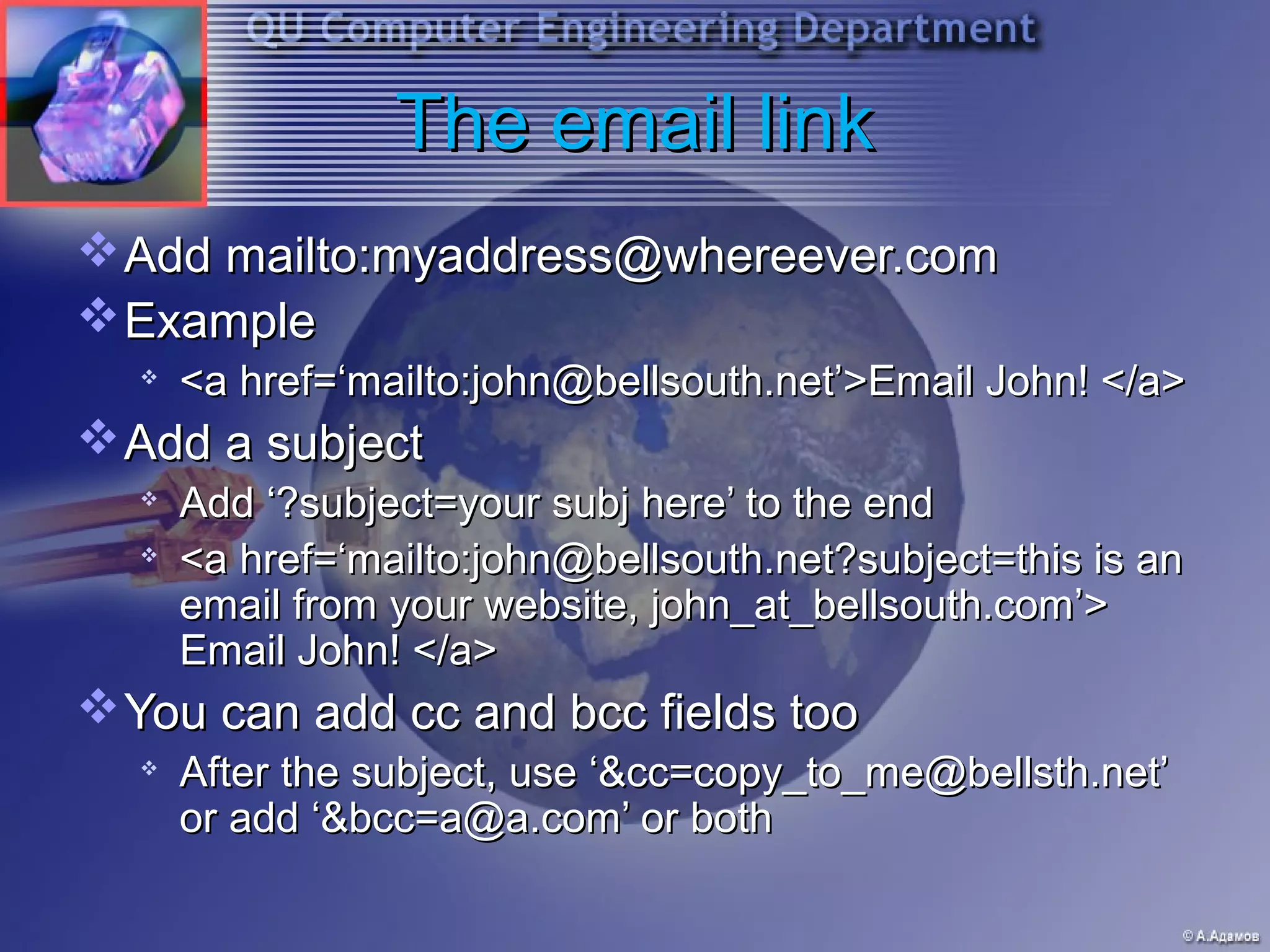
This document provides an introduction and overview of HTML and web programming. It discusses the basic tools and software needed, including a text editor and web browser. It covers fundamental HTML tags and structures, such as the <head> and <body> sections, headings, paragraphs, lists, links, and images. It also explains how to add comments, horizontal rules, and meta tags. The document is intended to teach beginners the essential elements of HTML and building basic web pages.