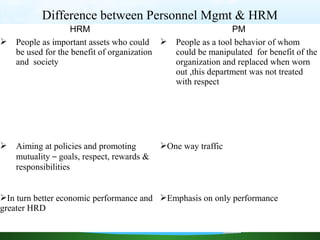
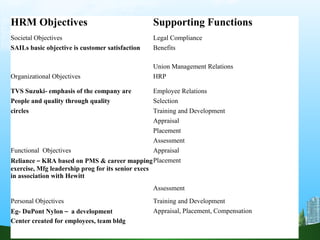
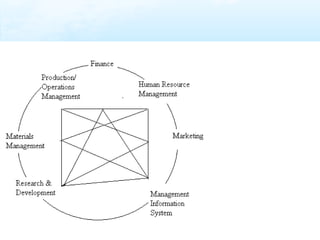
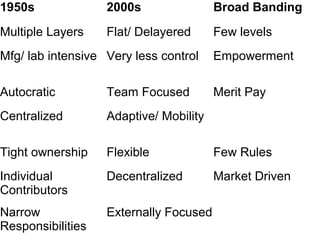
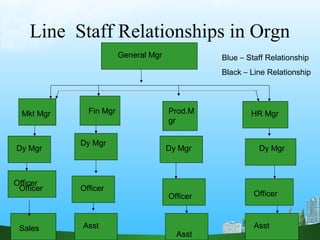
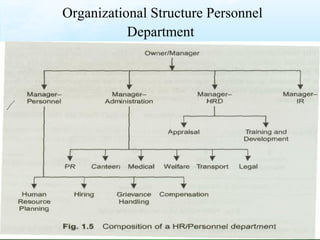
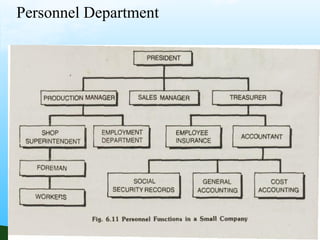
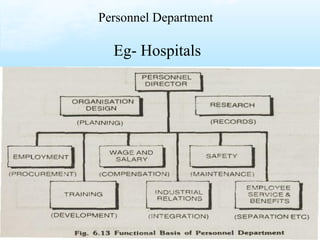
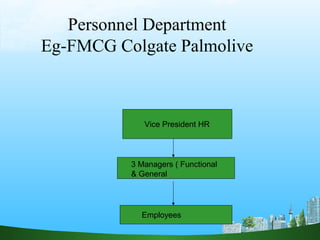
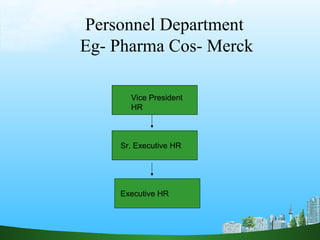
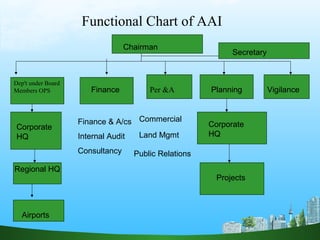
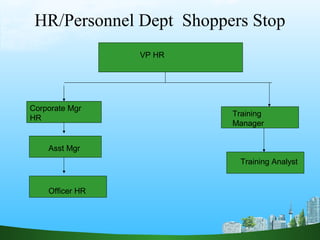
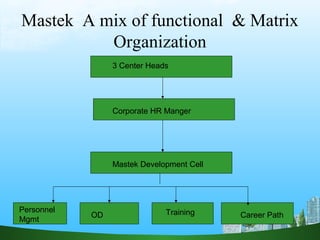
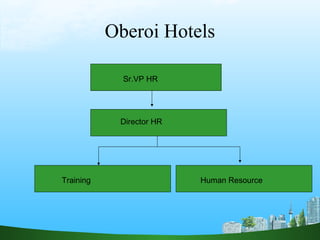
The document discusses key aspects of human resource management including definitions, core elements, objectives and functions. It describes HRM as integrating employment decisions to help organizations and employees achieve their goals. The core elements are organizations, people and management. Objectives include societal, organizational and personal goals. Functions involve planning, staffing, directing and controlling human resources from recruitment to retirement. It also outlines the scope, role and challenges of HRM in modern organizations.