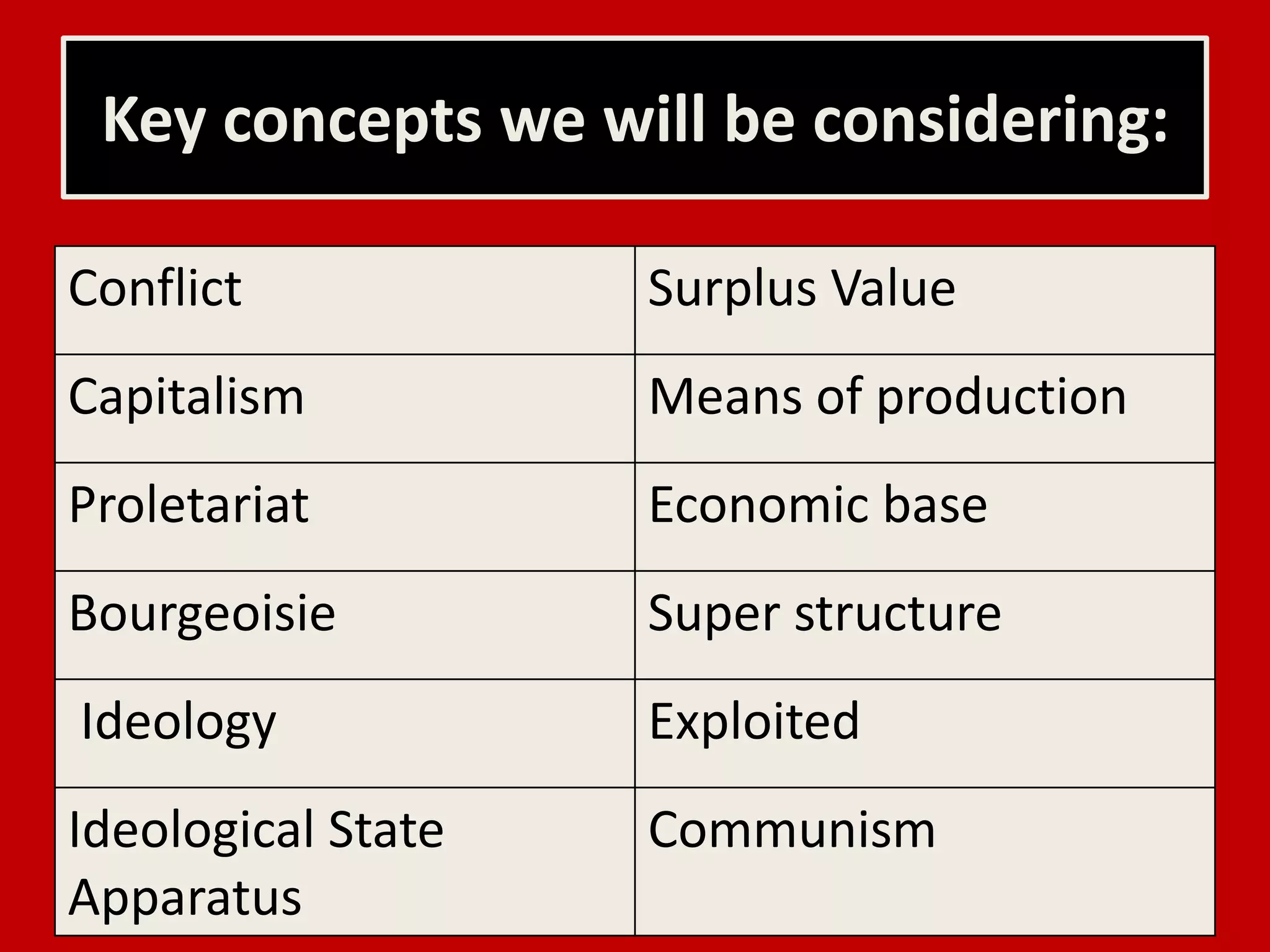
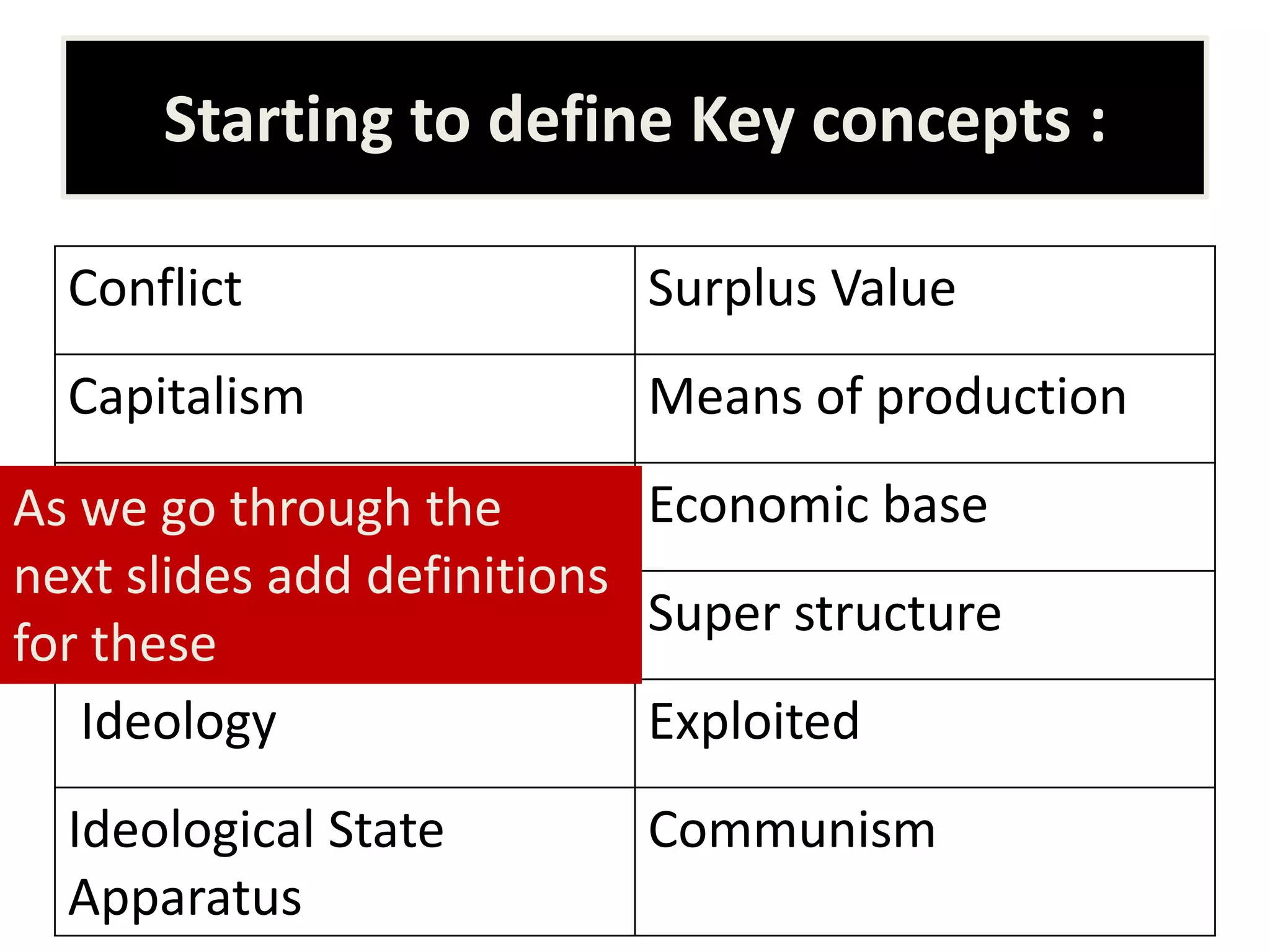
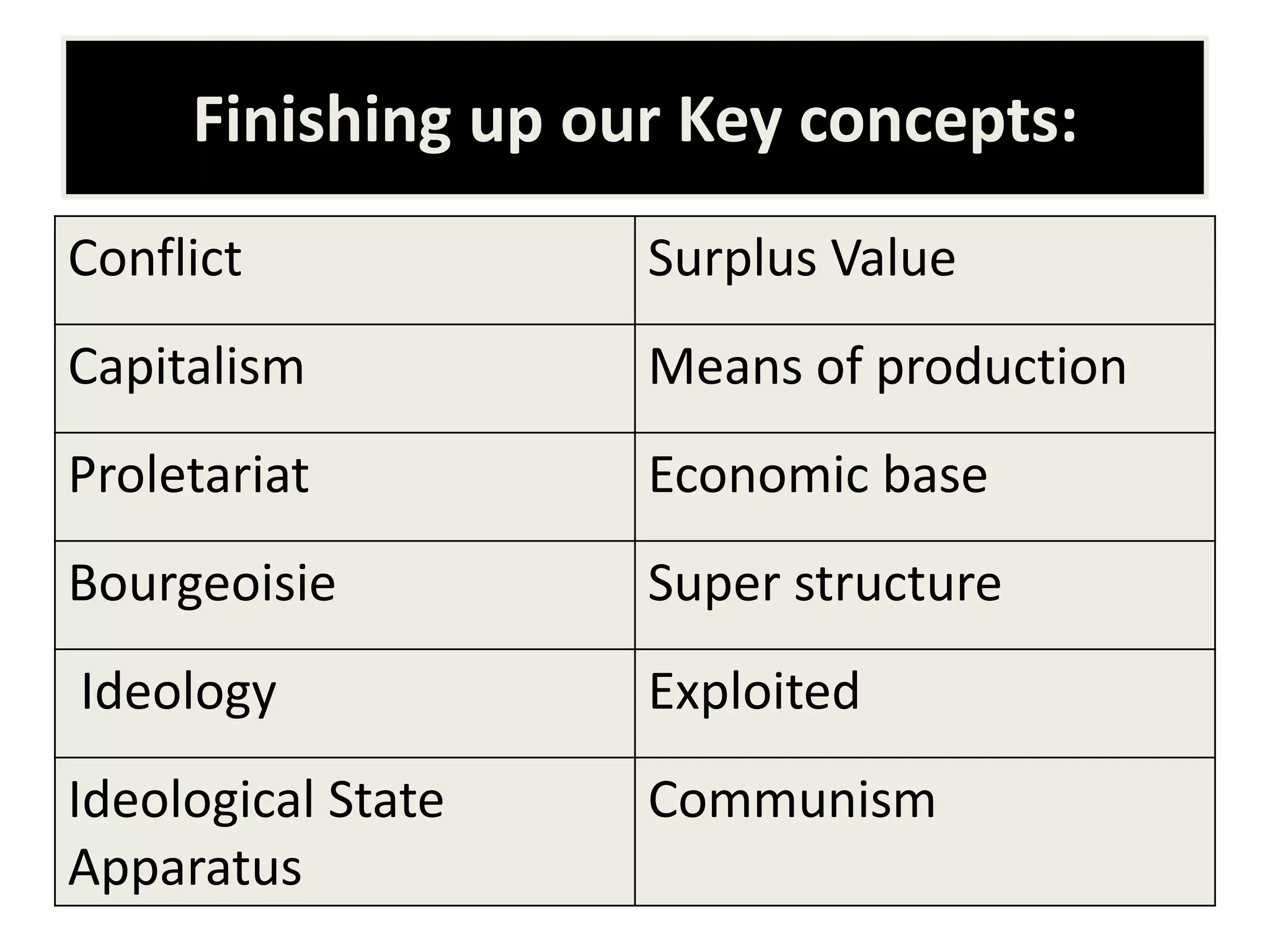
The document introduces Marxism and its key concepts. It aims to explain Marx's social theory and the Marxist perspective of capitalist society. Some of the key concepts discussed include the bourgeoisie and the proletariat, surplus value, means of production, ideology, and ideological state apparatuses. It asserts that society is based on conflict and exploitation between the rich and poor due to unequal power relations under capitalism. The document provides definitions for the key Marxist terms and concepts.