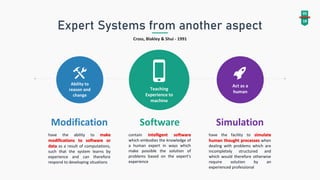
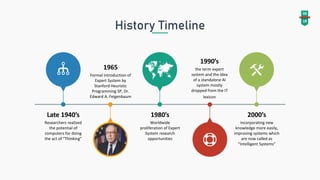
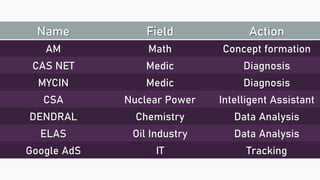
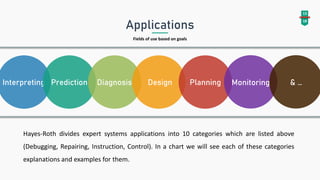
An expert system mimics human reasoning to solve problems and can learn from experience to adapt to new situations. The document outlines the architecture, components, and applications of expert systems across various fields such as medicine, engineering, and economics. It emphasizes the advantages of expert systems, including efficiency, reduced costs, and the ability to operate reliably in emergencies.