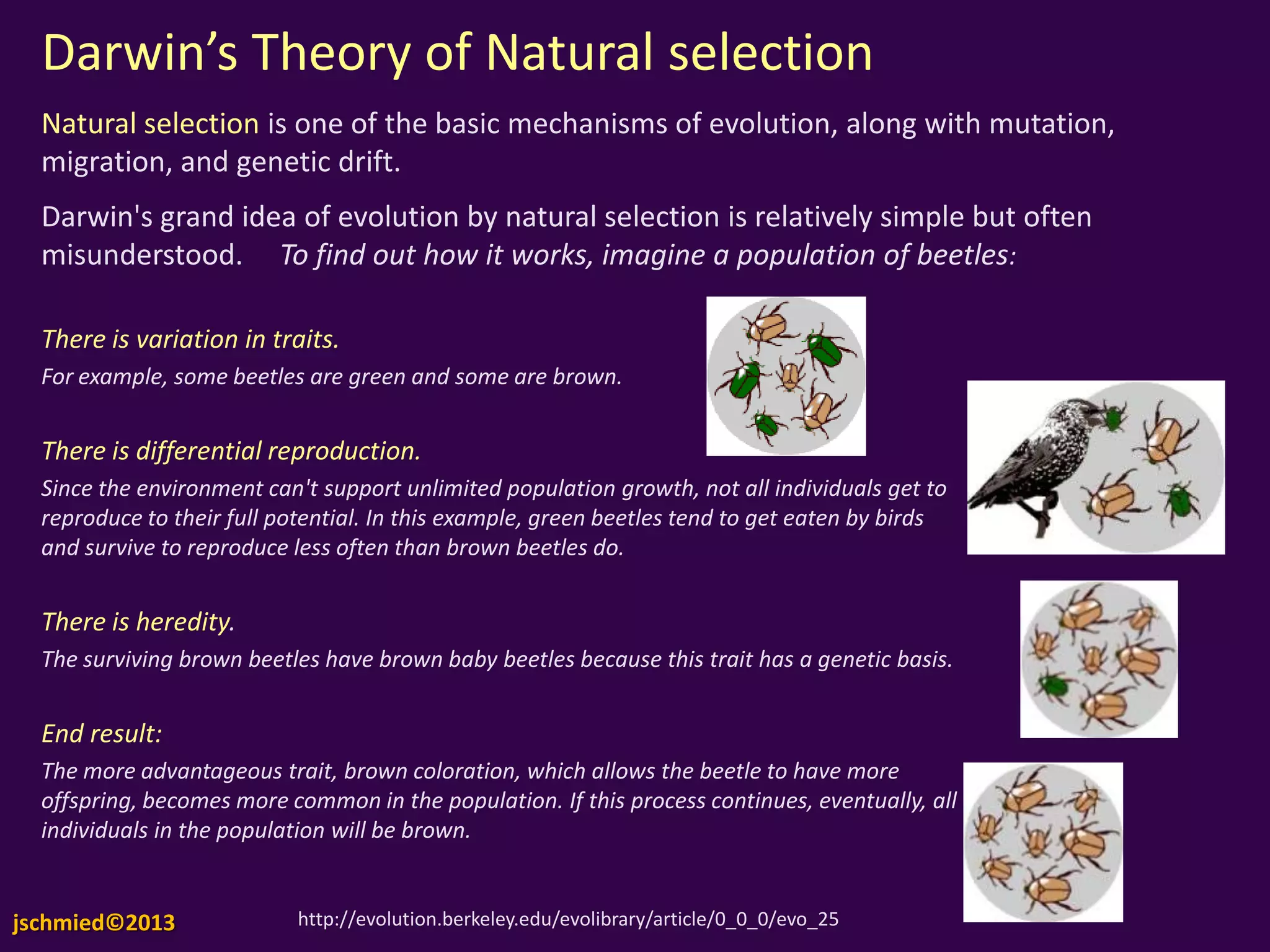
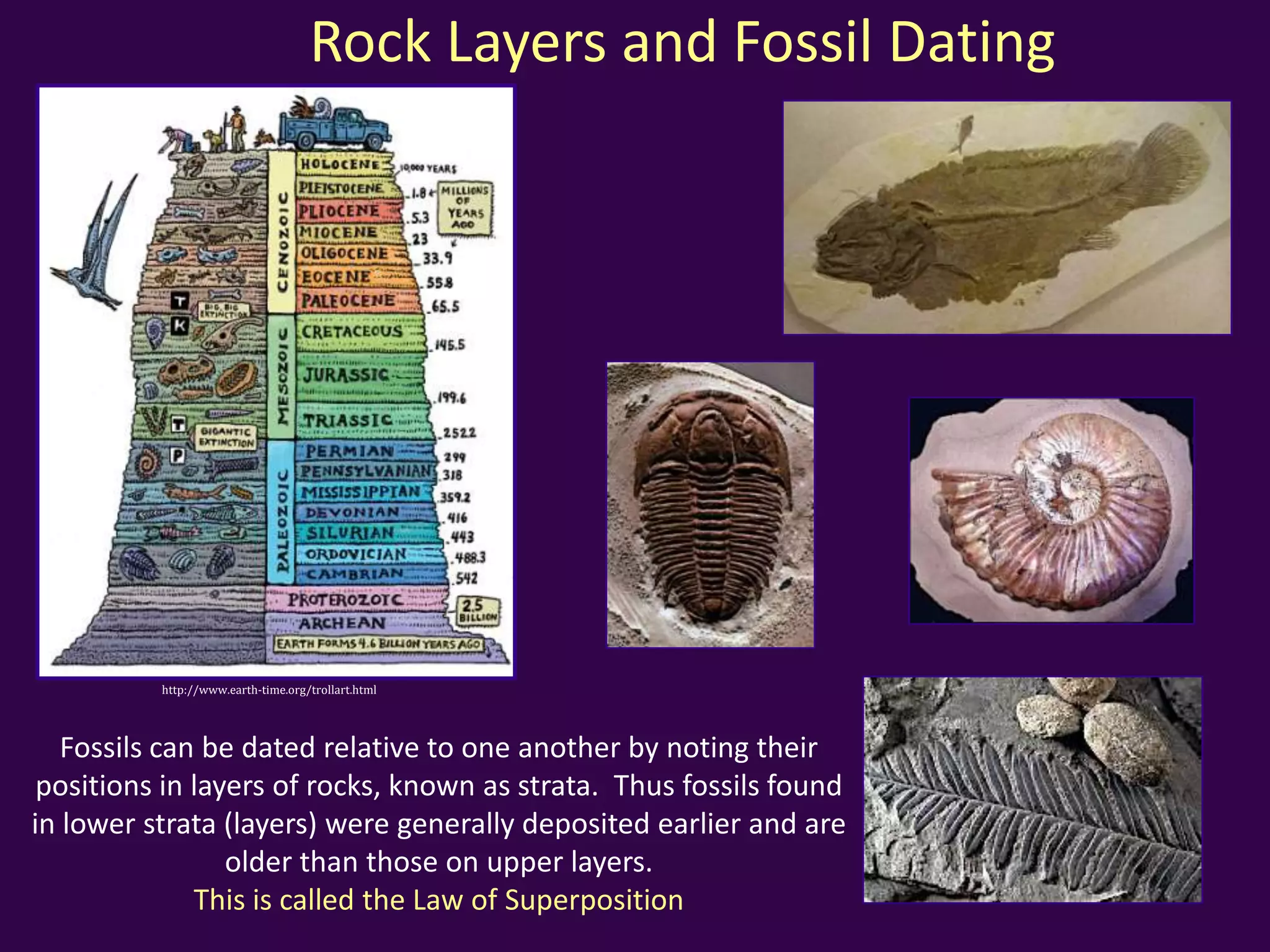
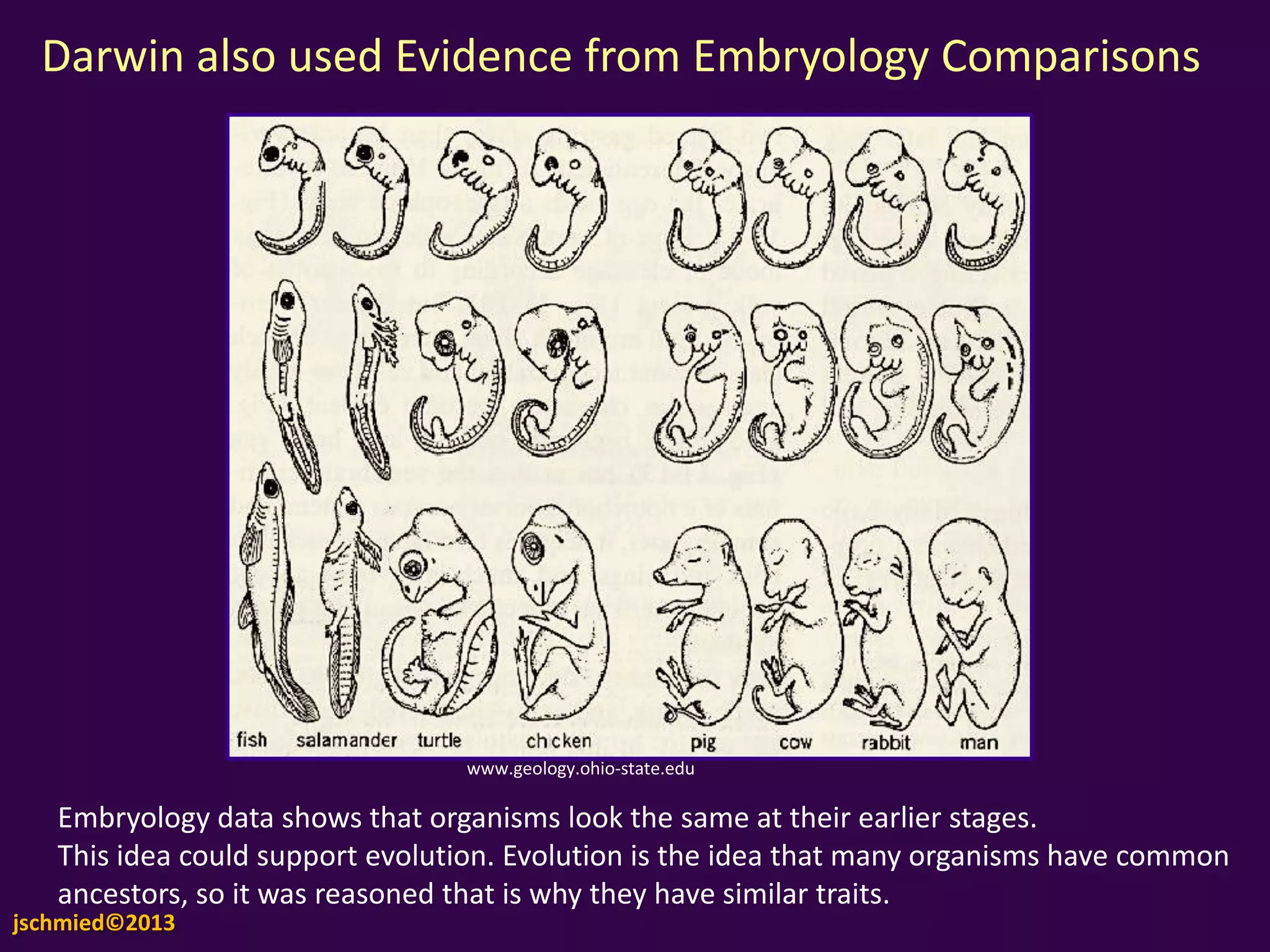
This document contains unit notes on evolution from Charles Darwin's voyage of the Beagle to Jean-Baptiste Lamarck's theory of evolution. It summarizes Darwin's theory of natural selection, noting that there is variation in traits, differential reproduction depending on environmental pressures, and heredity of advantageous traits. Lamarck's theory proposed that use and disuse of organs during an organism's lifetime could influence evolution, and that nature drove organisms to greater complexity over time. The document also discusses using fossil records and comparative anatomy to infer relatedness between species.