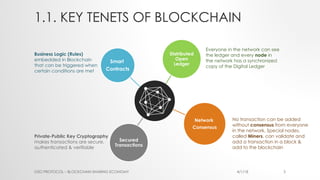
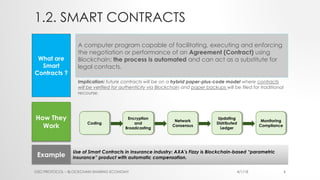
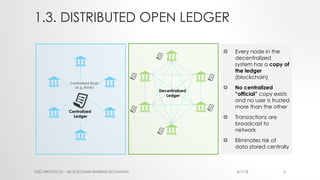
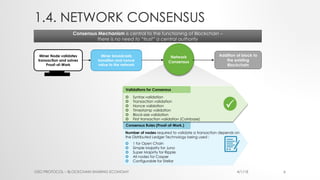
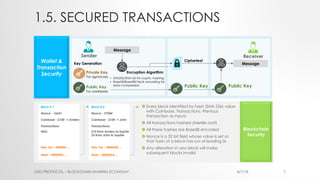
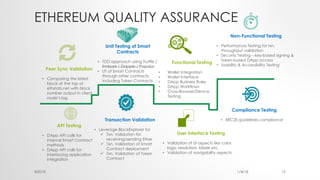
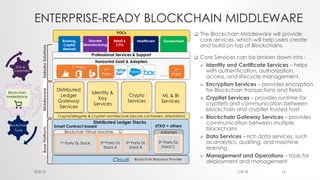
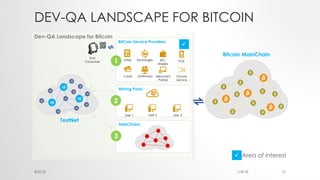
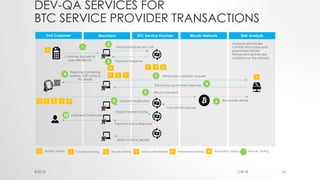
The document provides an introduction to Ethereum blockchain and smart contracts, outlining key concepts such as blockchain's distributed ledger, network consensus, and secured transactions. It discusses the functionality of smart contracts and their implications, particularly in industries such as insurance, and explains the advantages of decentralized systems. Additionally, it details the development and quality assurance of decentralized applications (dApps) on Ethereum, along with tools and methodologies involved in the blockchain ecosystem.