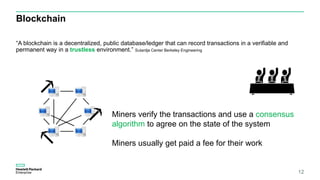
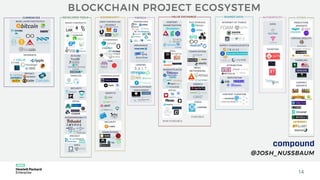
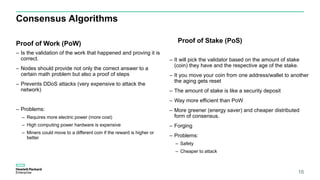
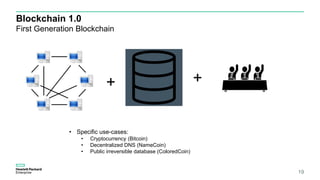
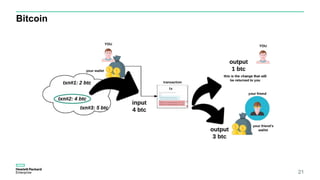
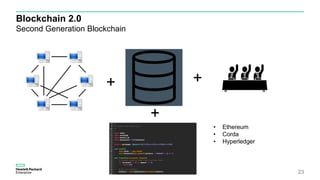
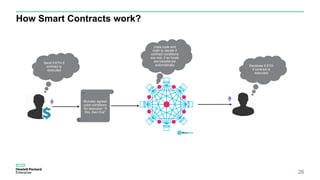
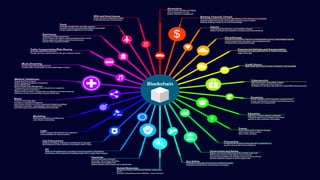
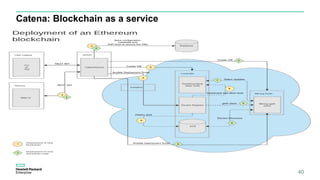
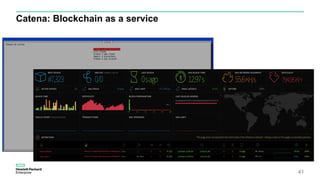
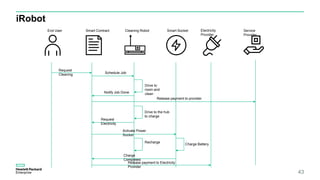
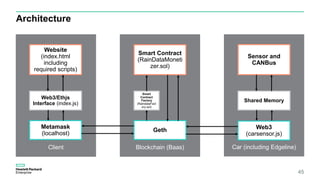
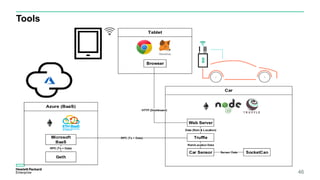
Blockchain & Smart Contracts! This document provides an introduction to blockchain and smart contracts. It discusses what a blockchain is, why many blockchains exist, consensus algorithms like proof of work and proof of stake, public versus private blockchains, smart contracts and how they work, examples of successful smart contracts, potential use cases, and CIT blockchain projects including Catena which provides blockchain as a service and an iRobot proof of concept.