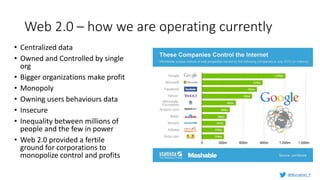
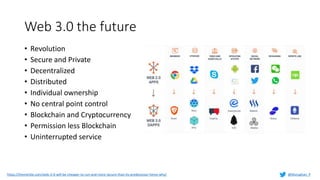
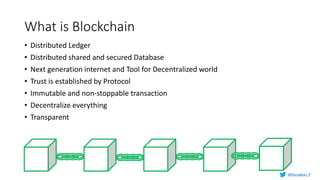
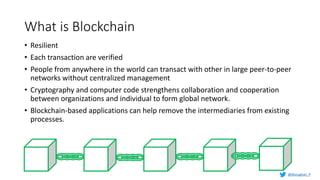
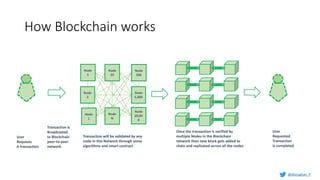
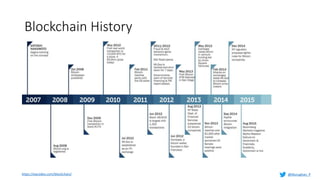
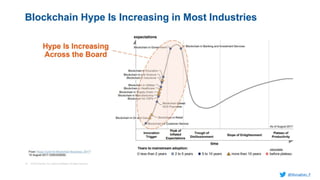
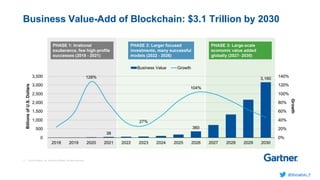
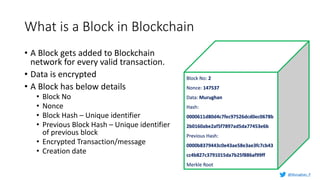
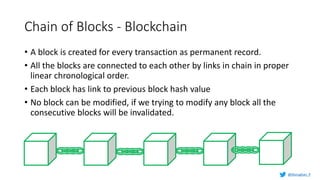
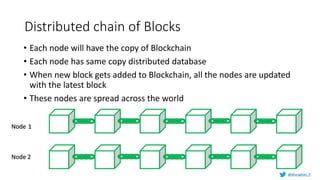
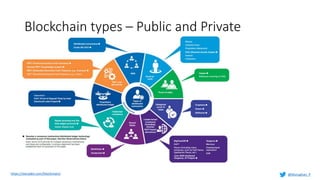
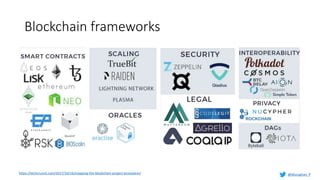
Murughan Palaniachari presents information on blockchain concepts. He discusses how blockchain enables a decentralized future (Web 3.0) with distributed and individual ownership of data. Blockchain uses distributed ledgers and cryptography to securely record transactions in an immutable, transparent and verifiable way without centralized control. Key concepts covered include how blockchain works, the structure of blocks and blockchains, consensus mechanisms, smart contracts, and examples of blockchain use cases.