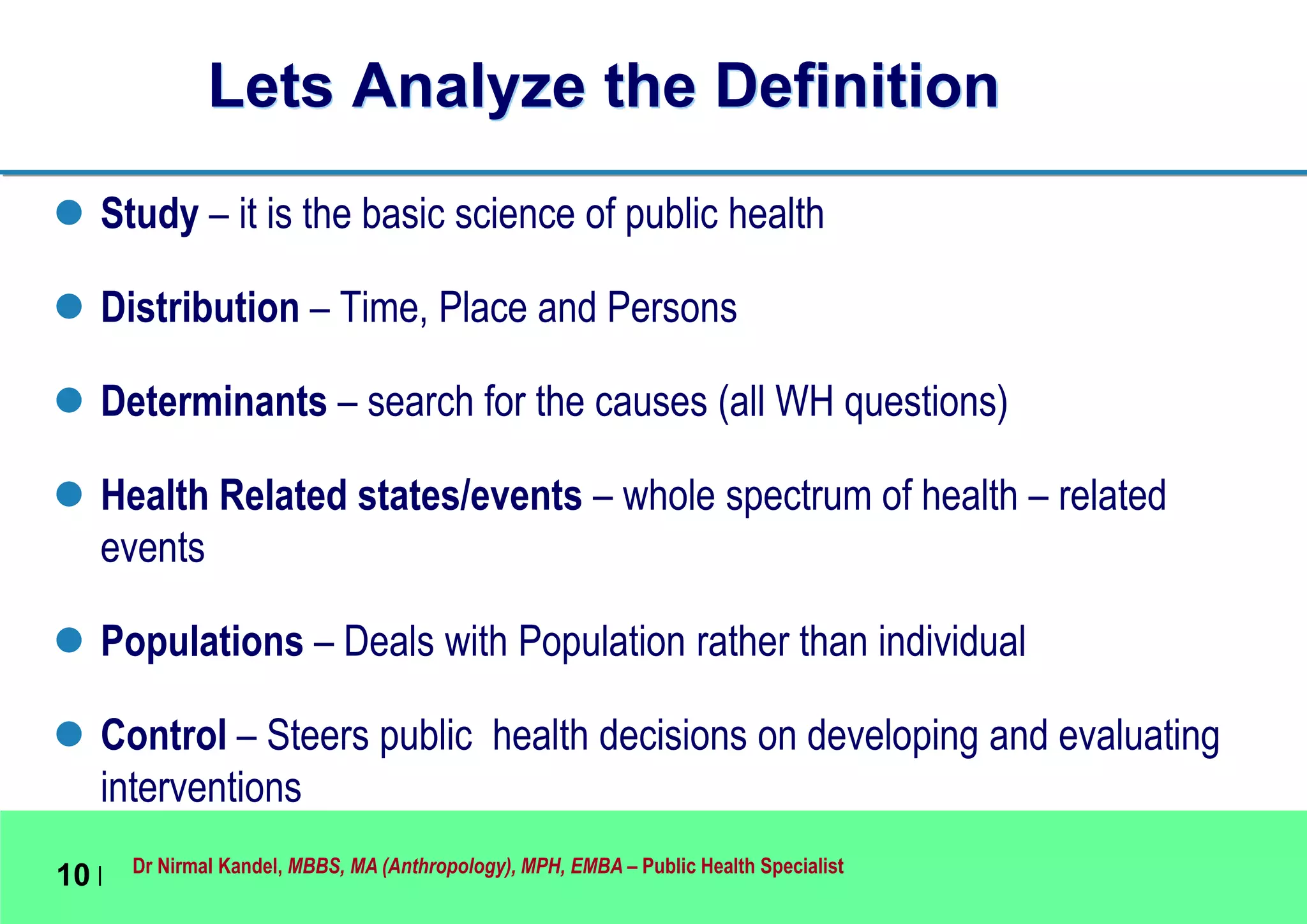
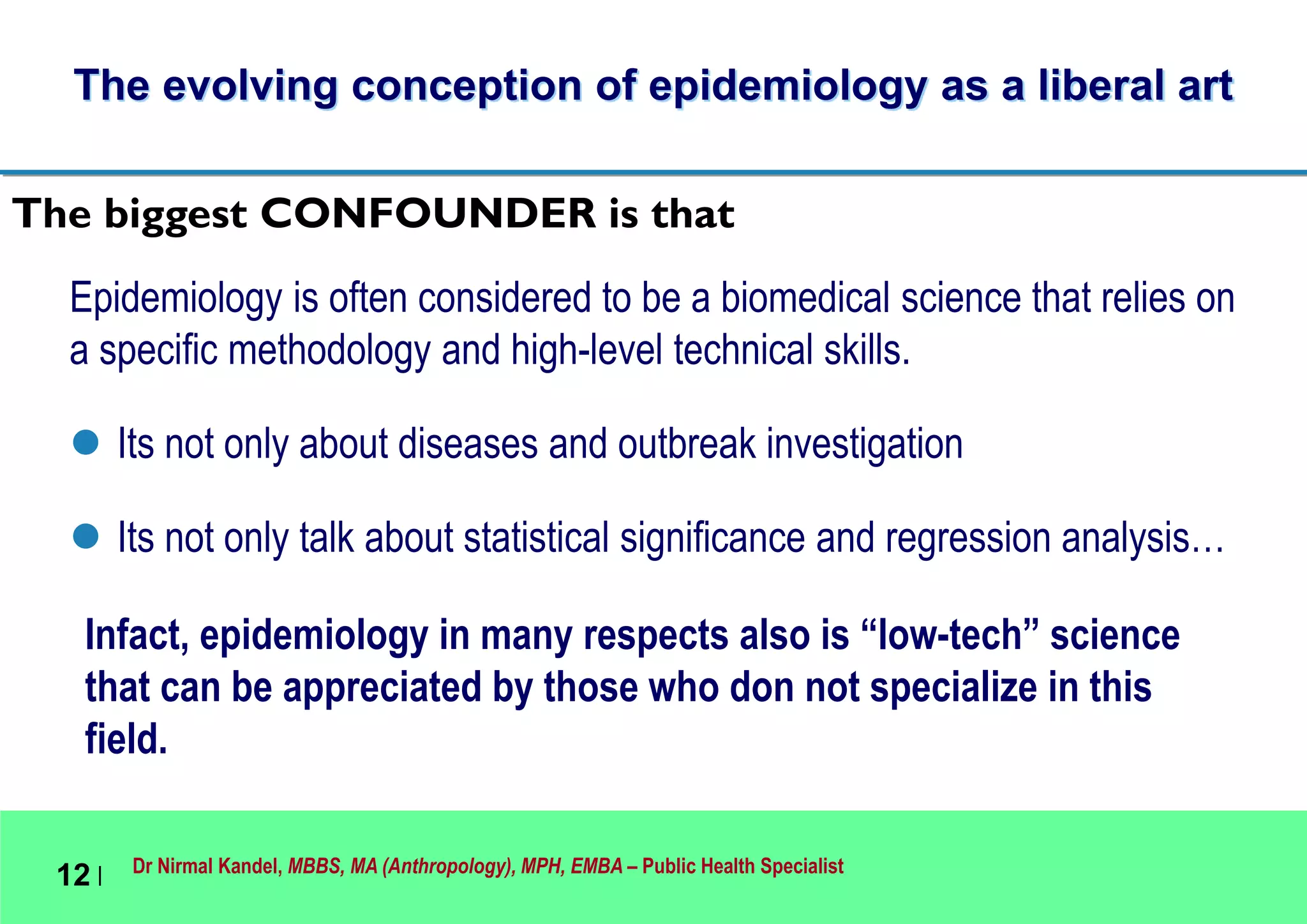
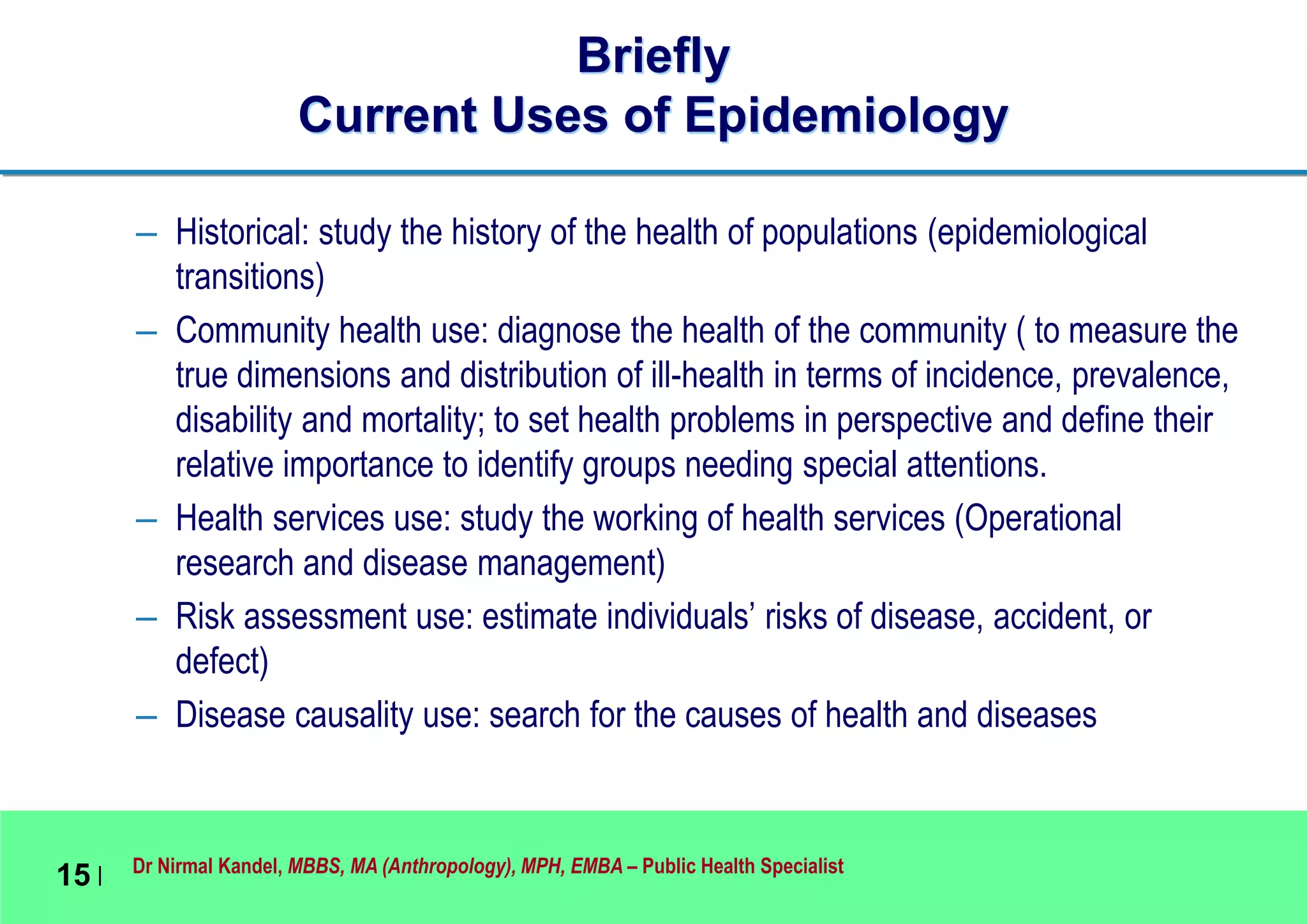
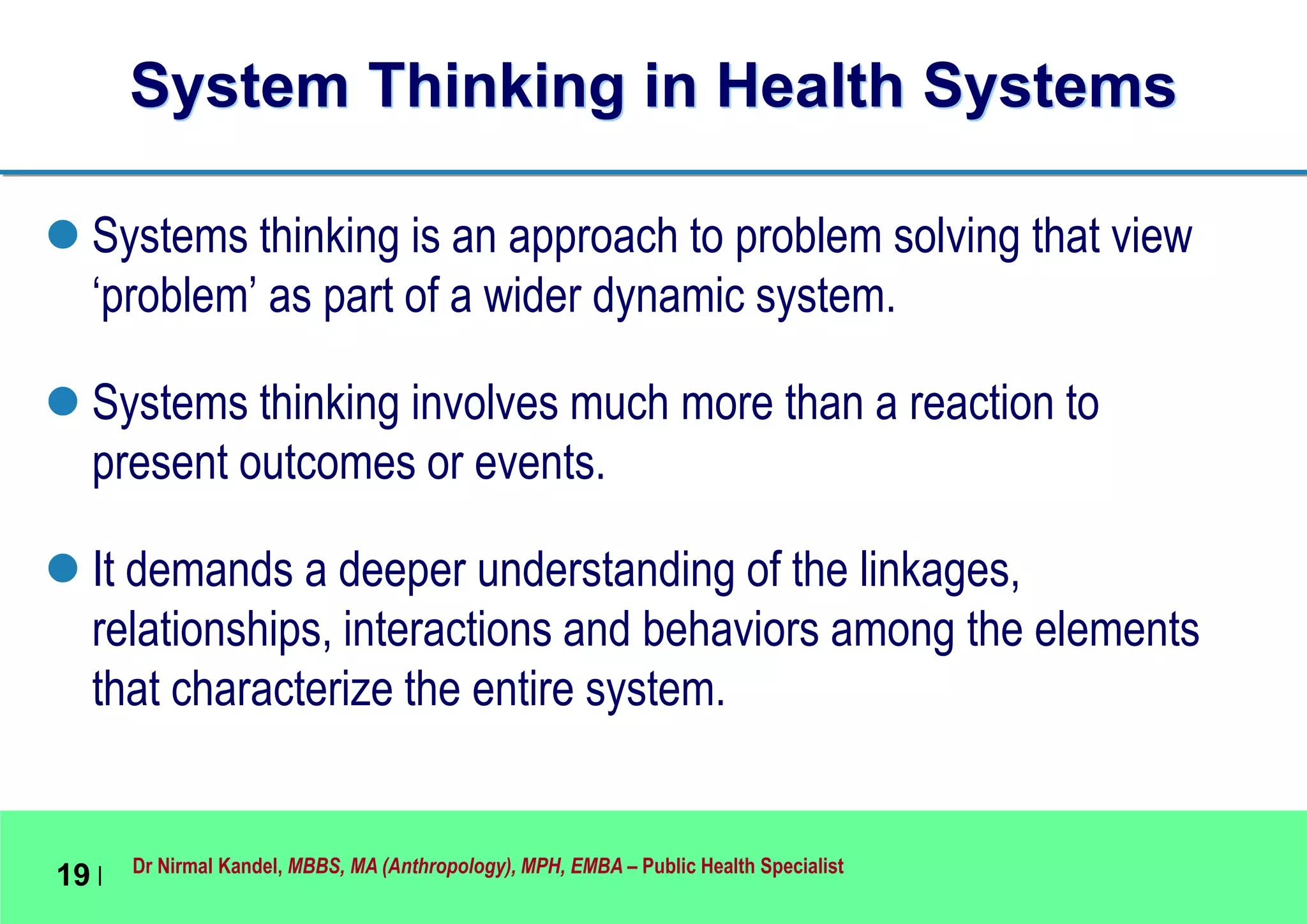
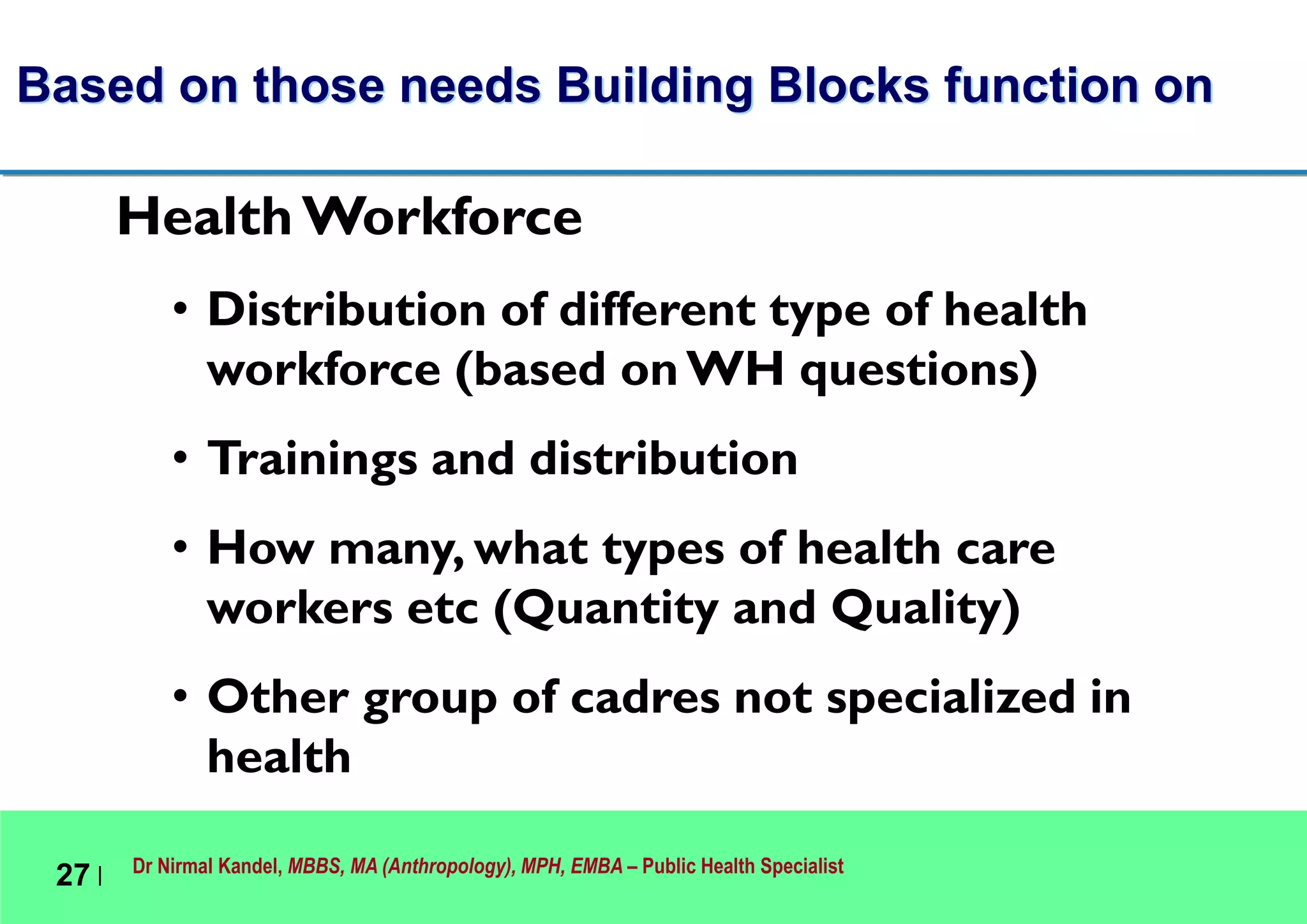
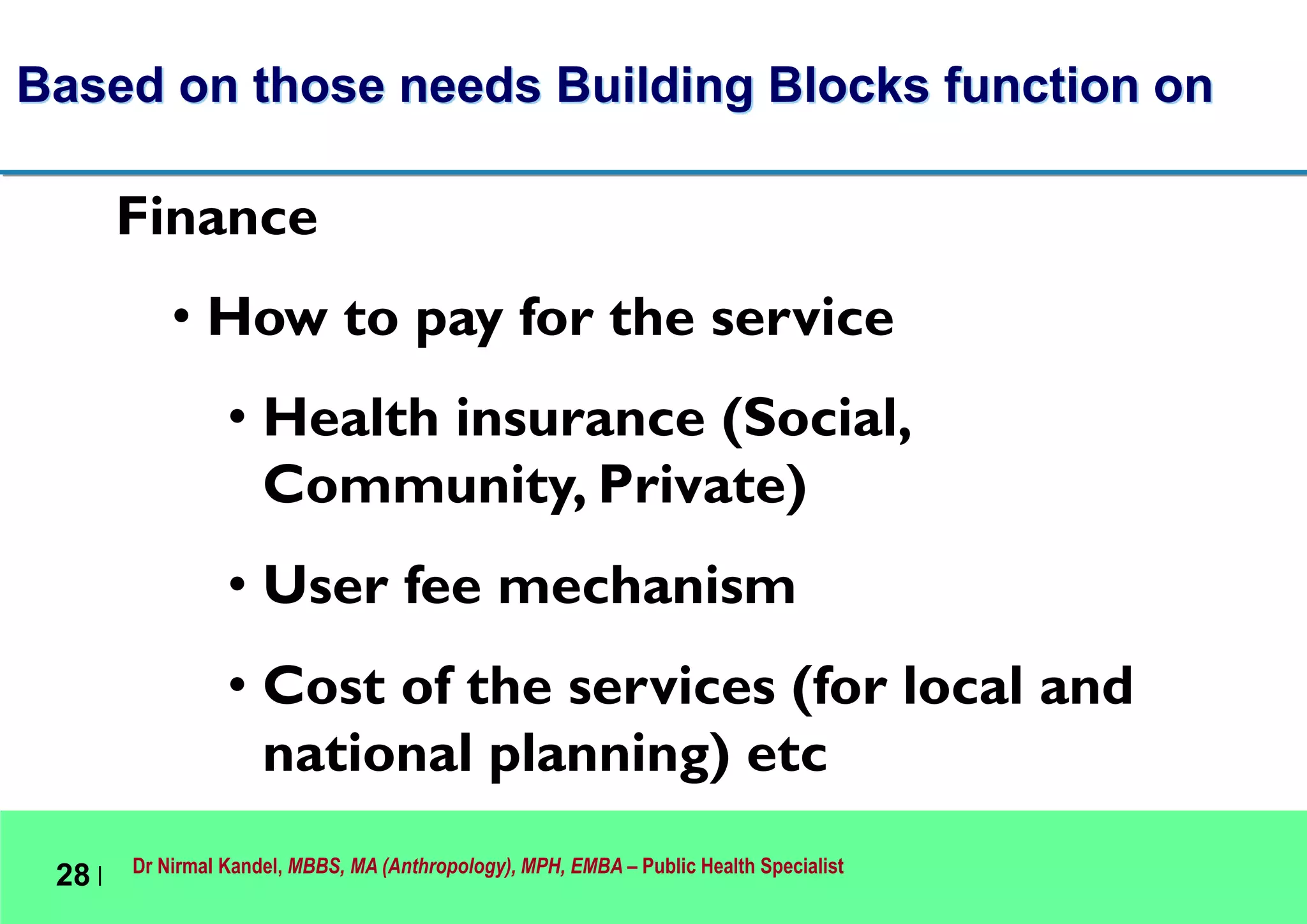
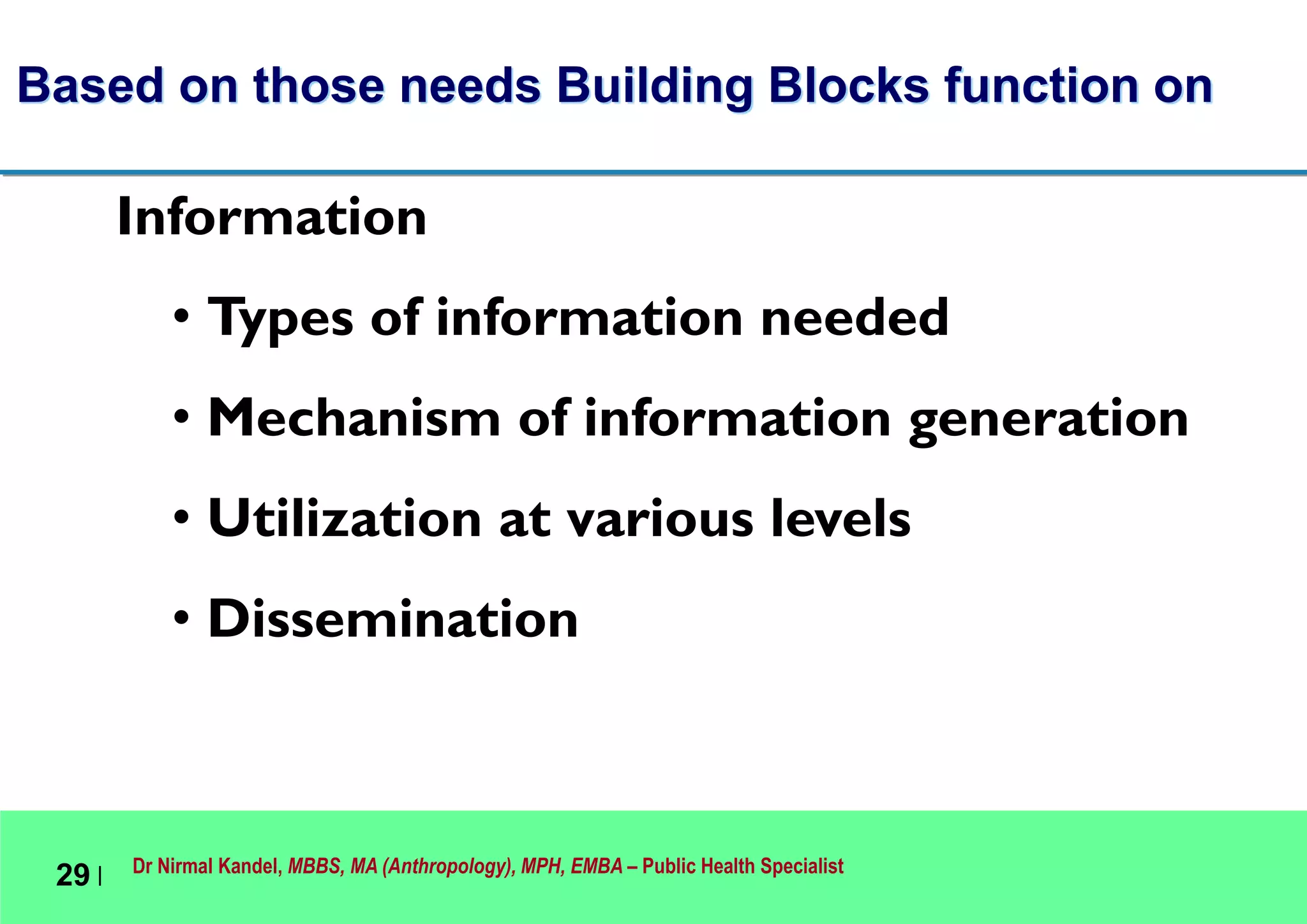
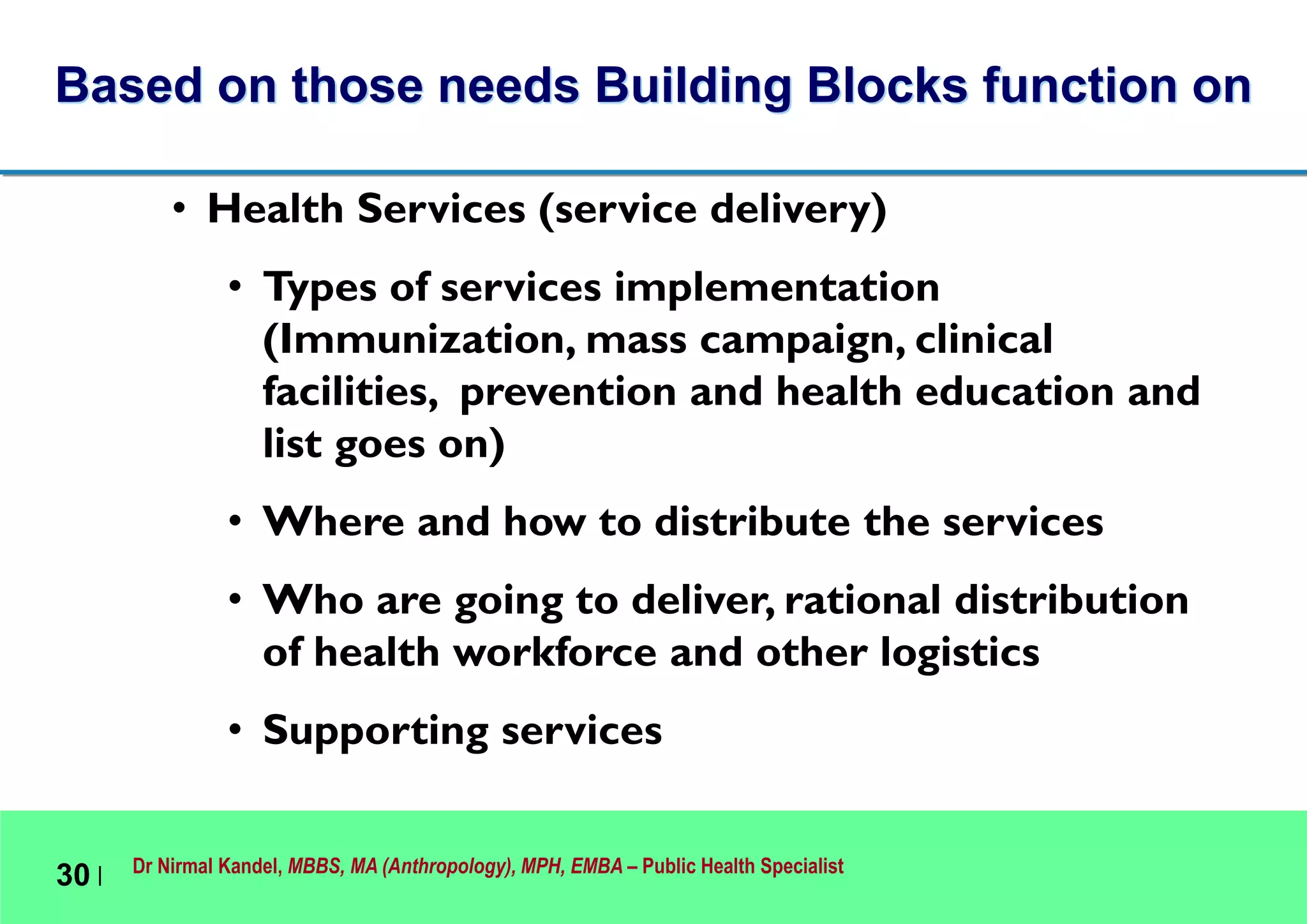
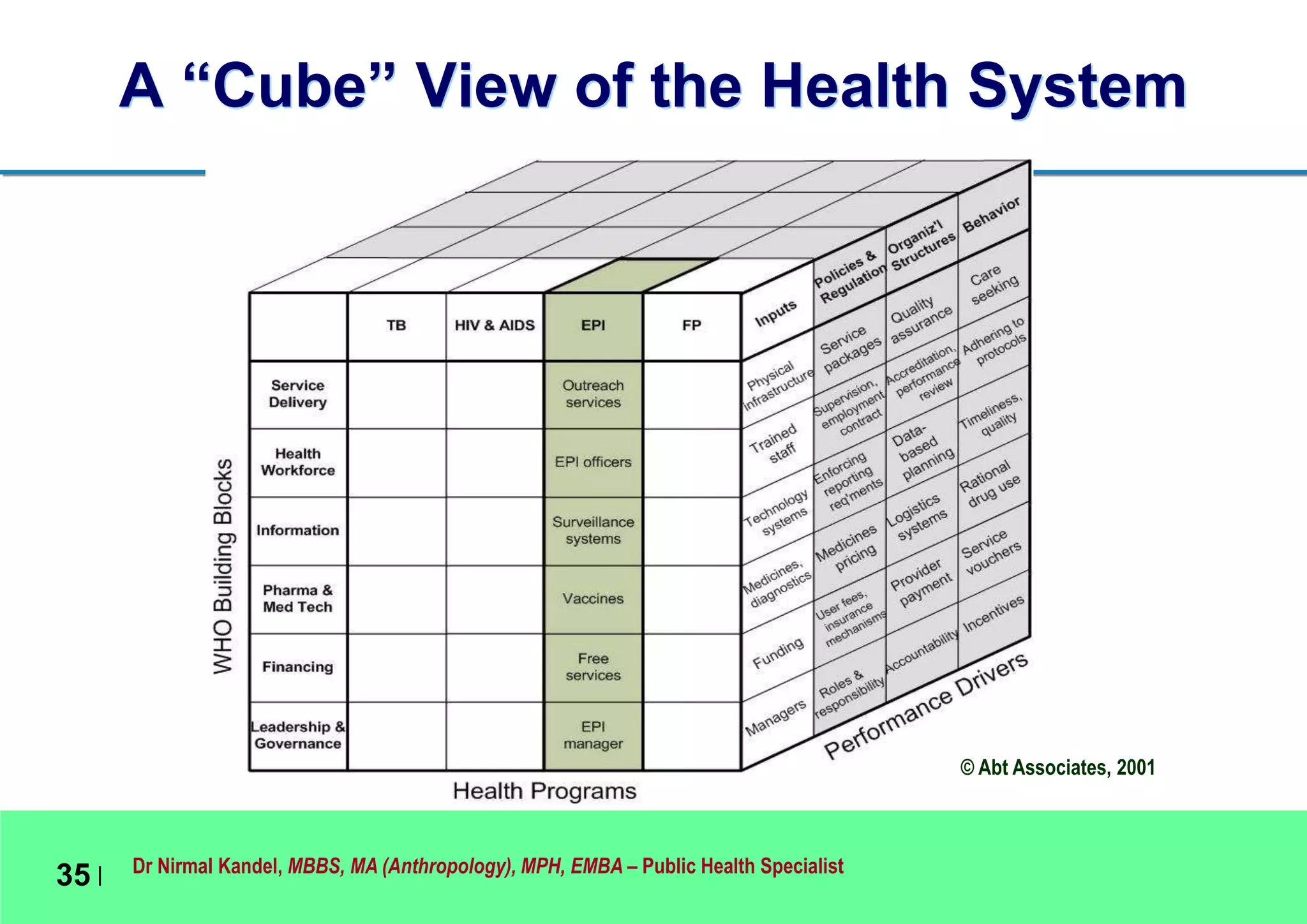
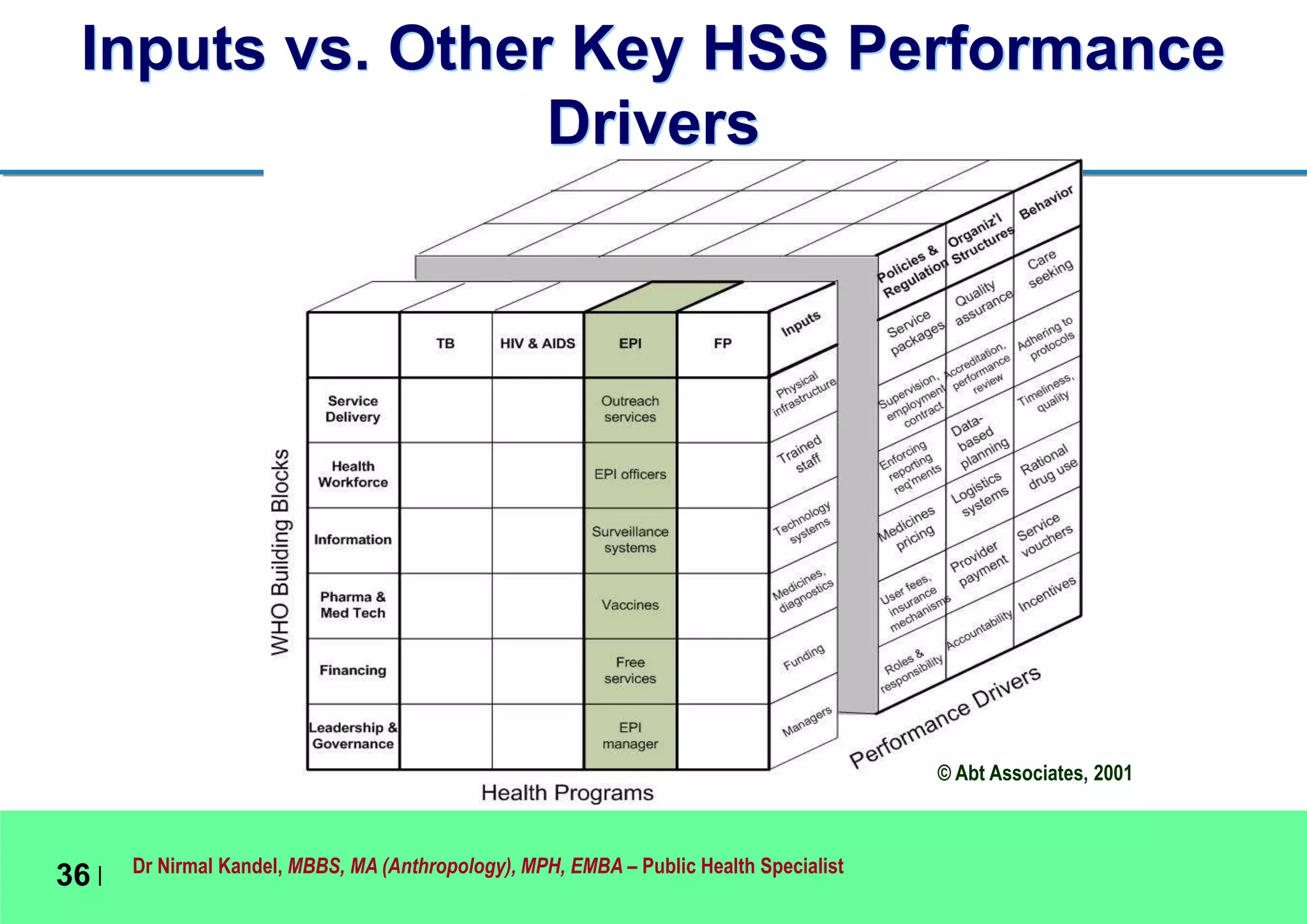
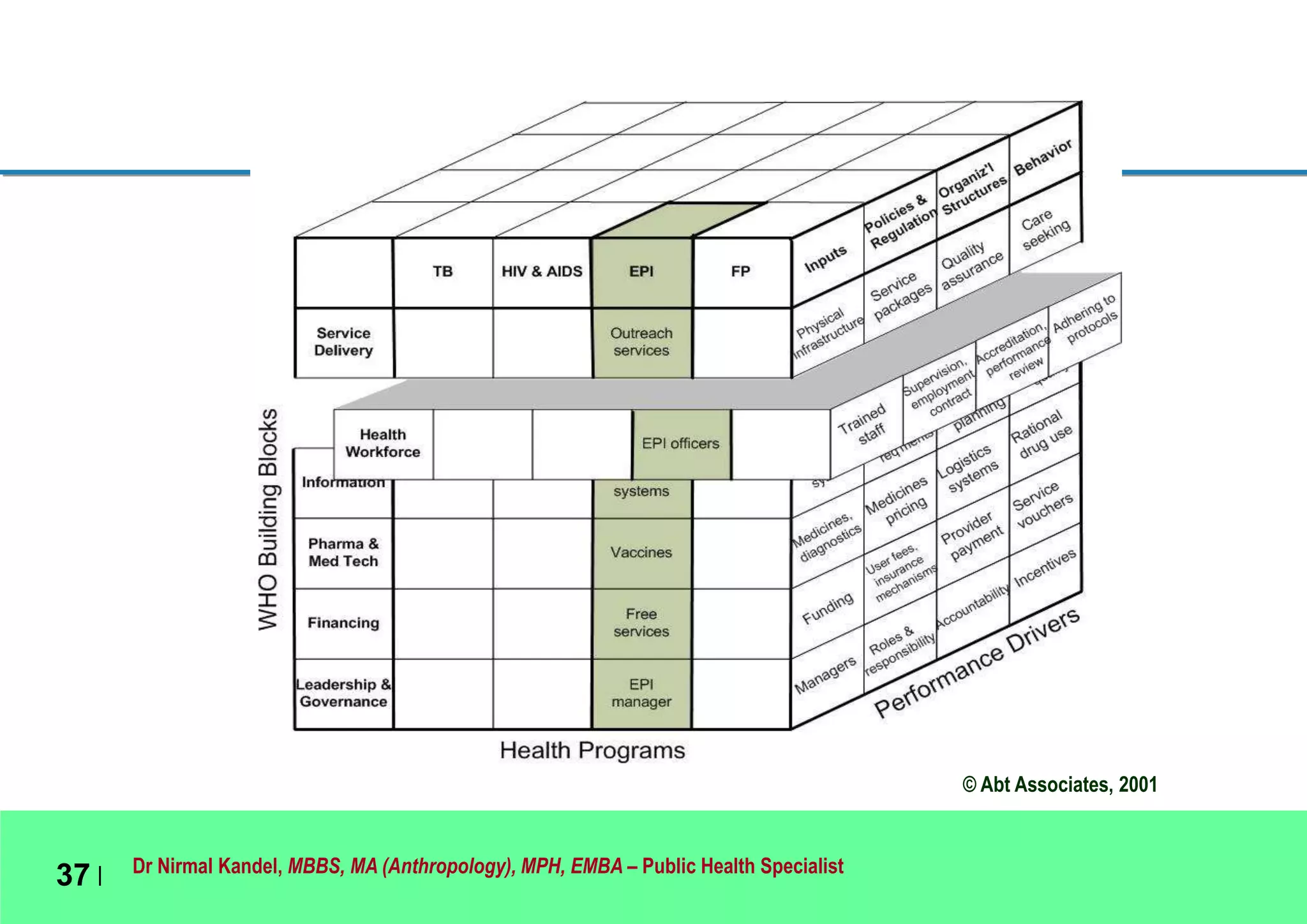
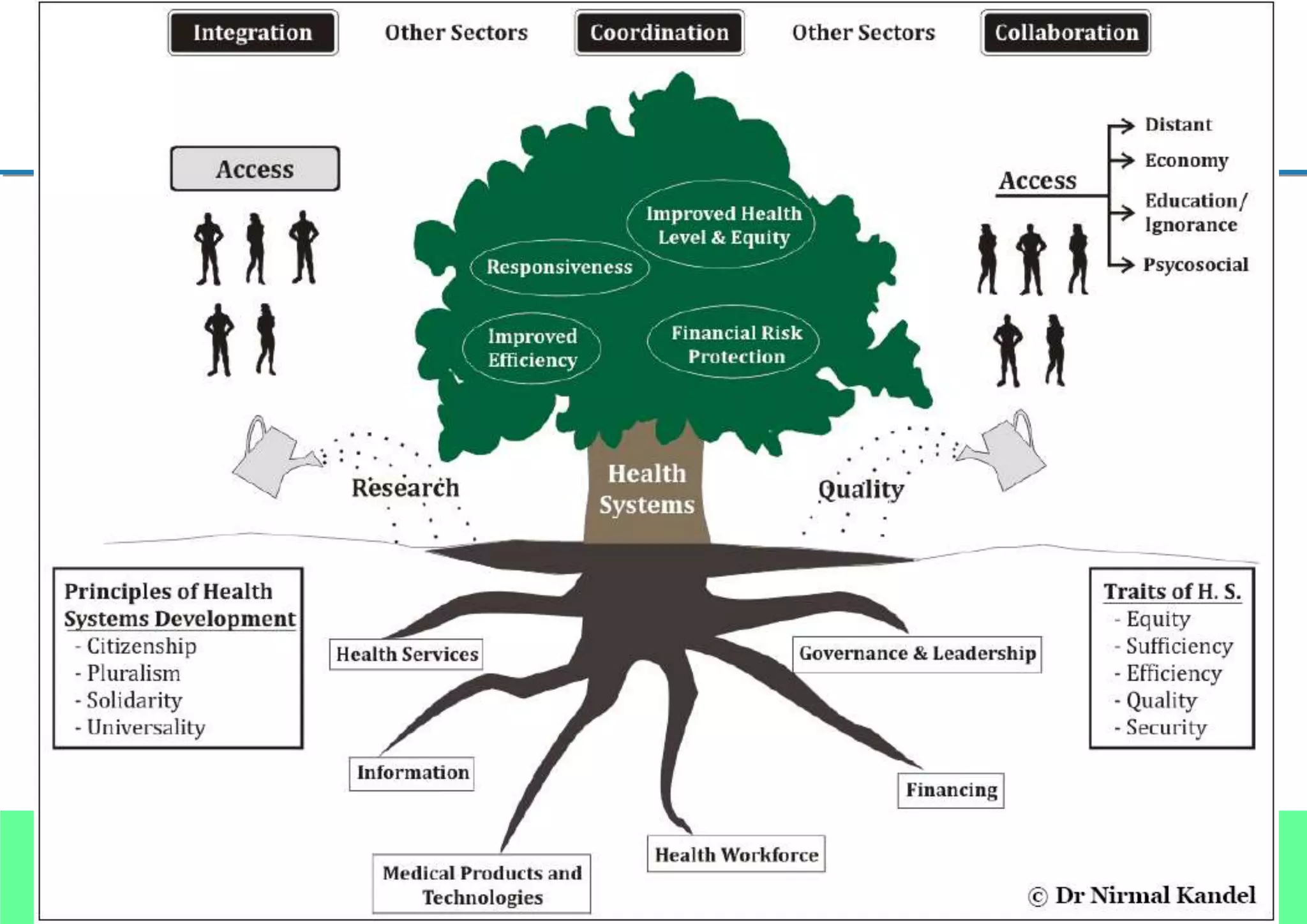
This document outlines Dr. Nirmal Kandel's presentation on epidemiology and health systems at the 2nd National Scientific Conference on Epidemiology in Bandung, Indonesia. The presentation covers definitions of epidemiology, skills gained through epidemiology training, current uses of epidemiology, applying epidemiology to health system development, and developing an epidemiological model for health systems. Dr. Kandel emphasizes using epidemiology to understand population health needs and inform how different components of health systems, such as workforce, finance, and information, should function based on those needs.