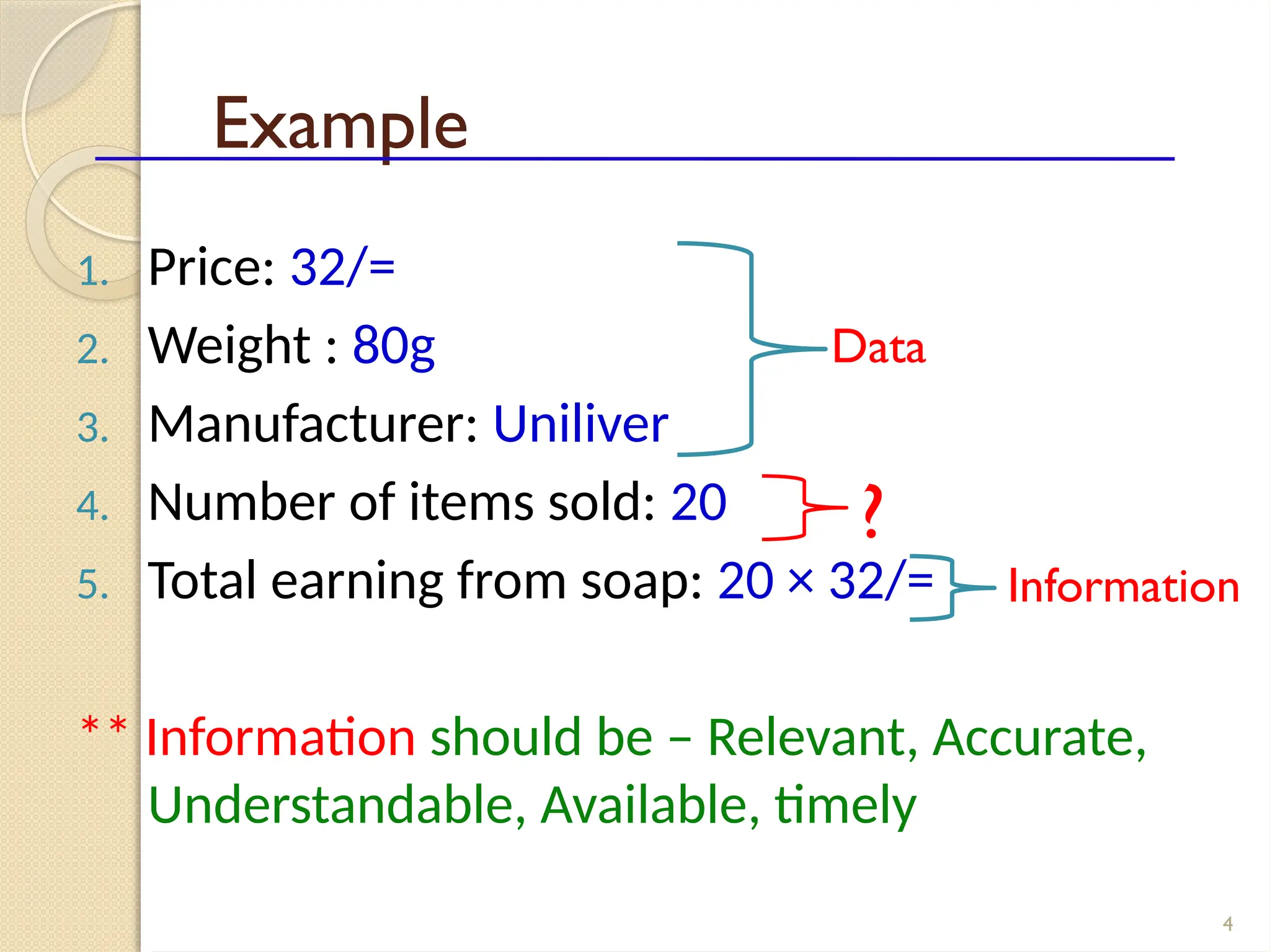
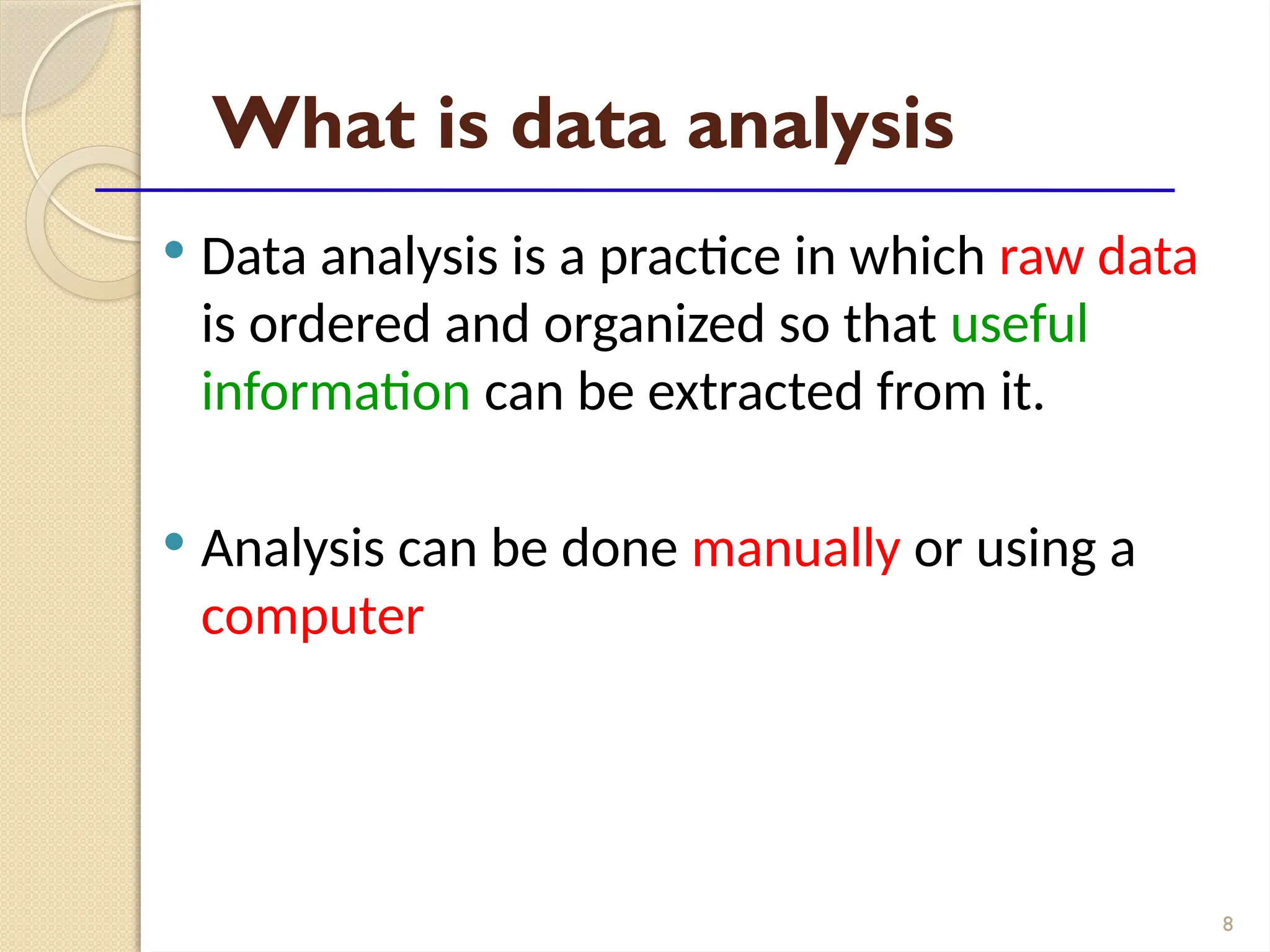
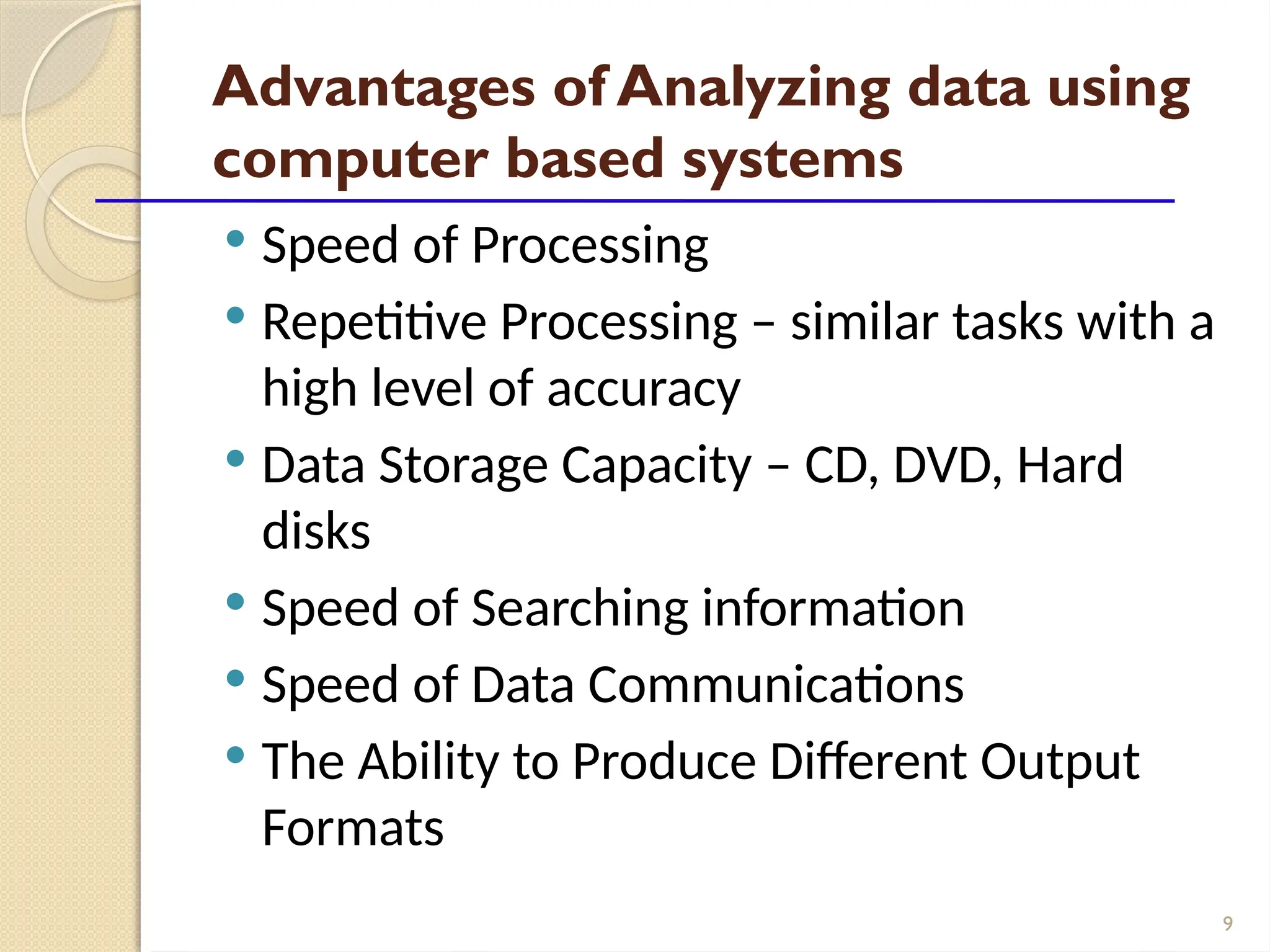
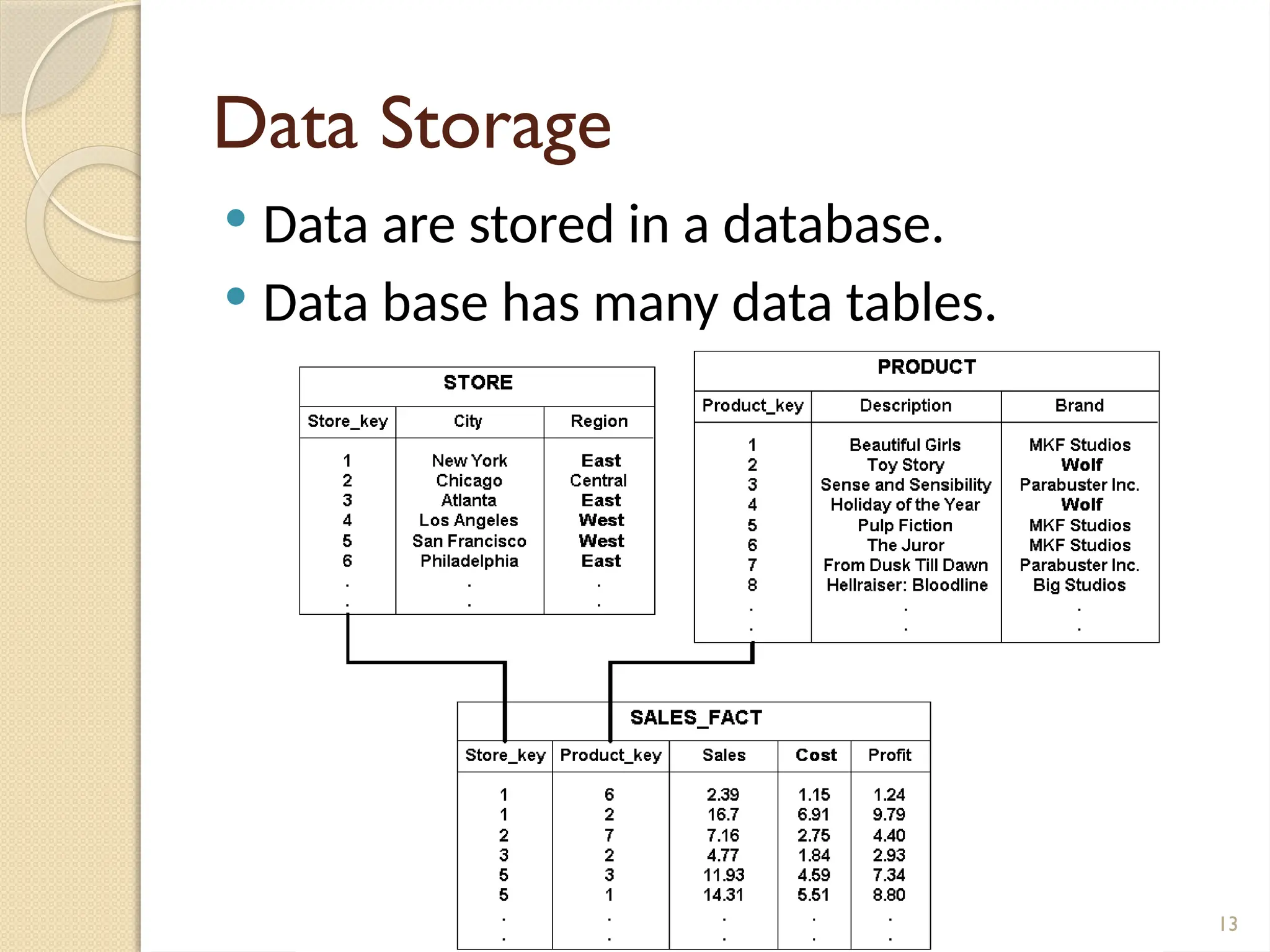
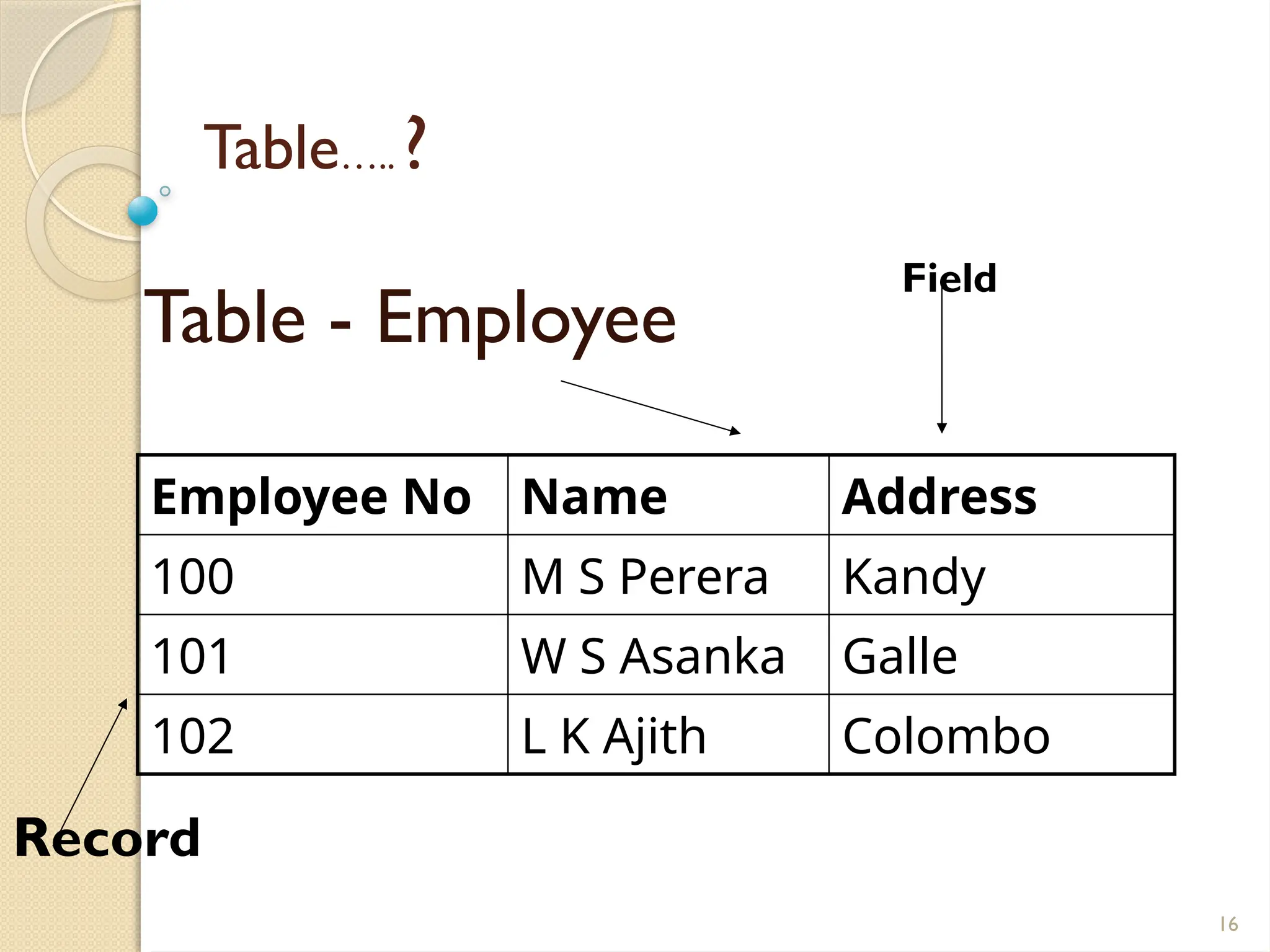
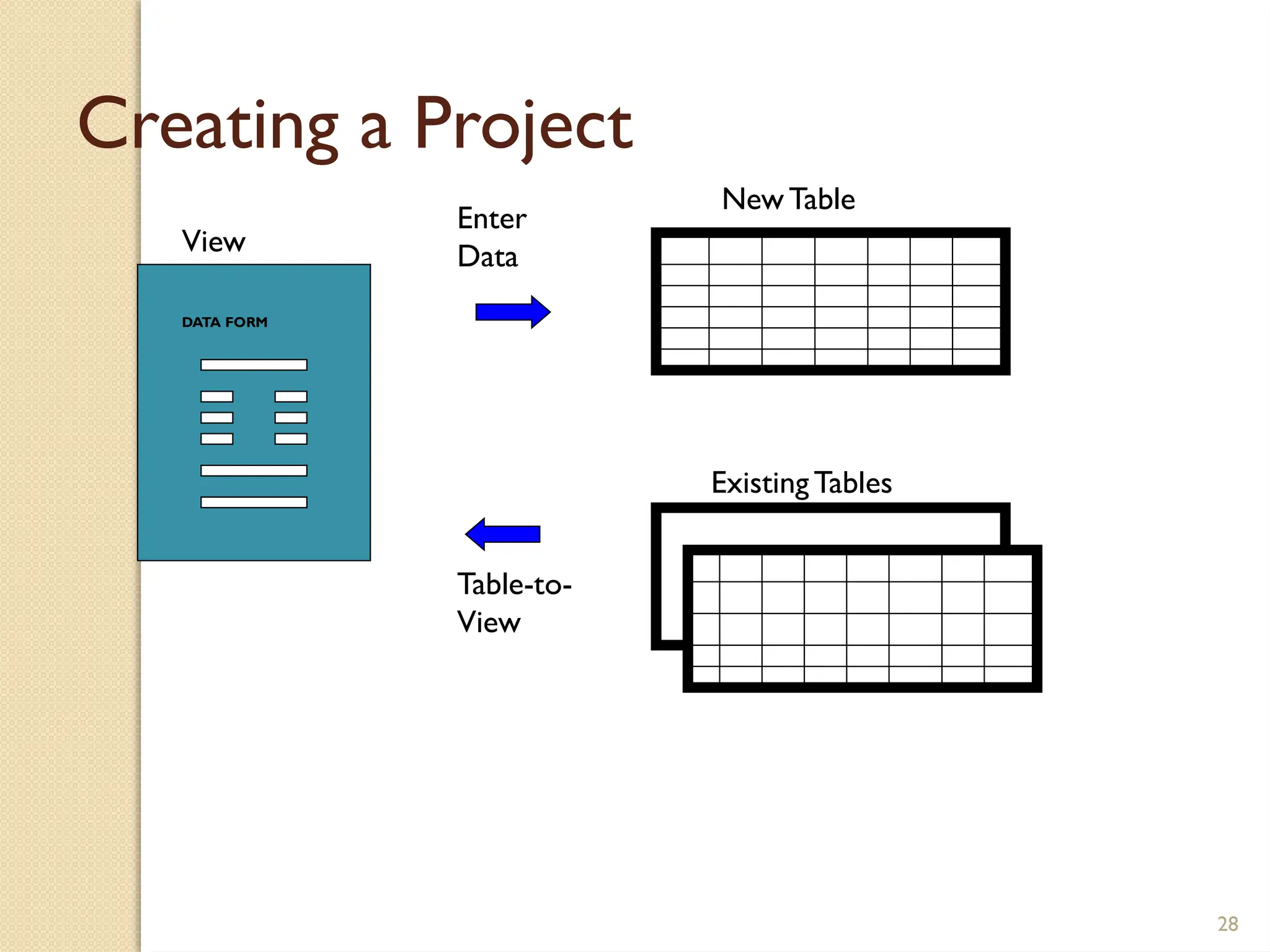
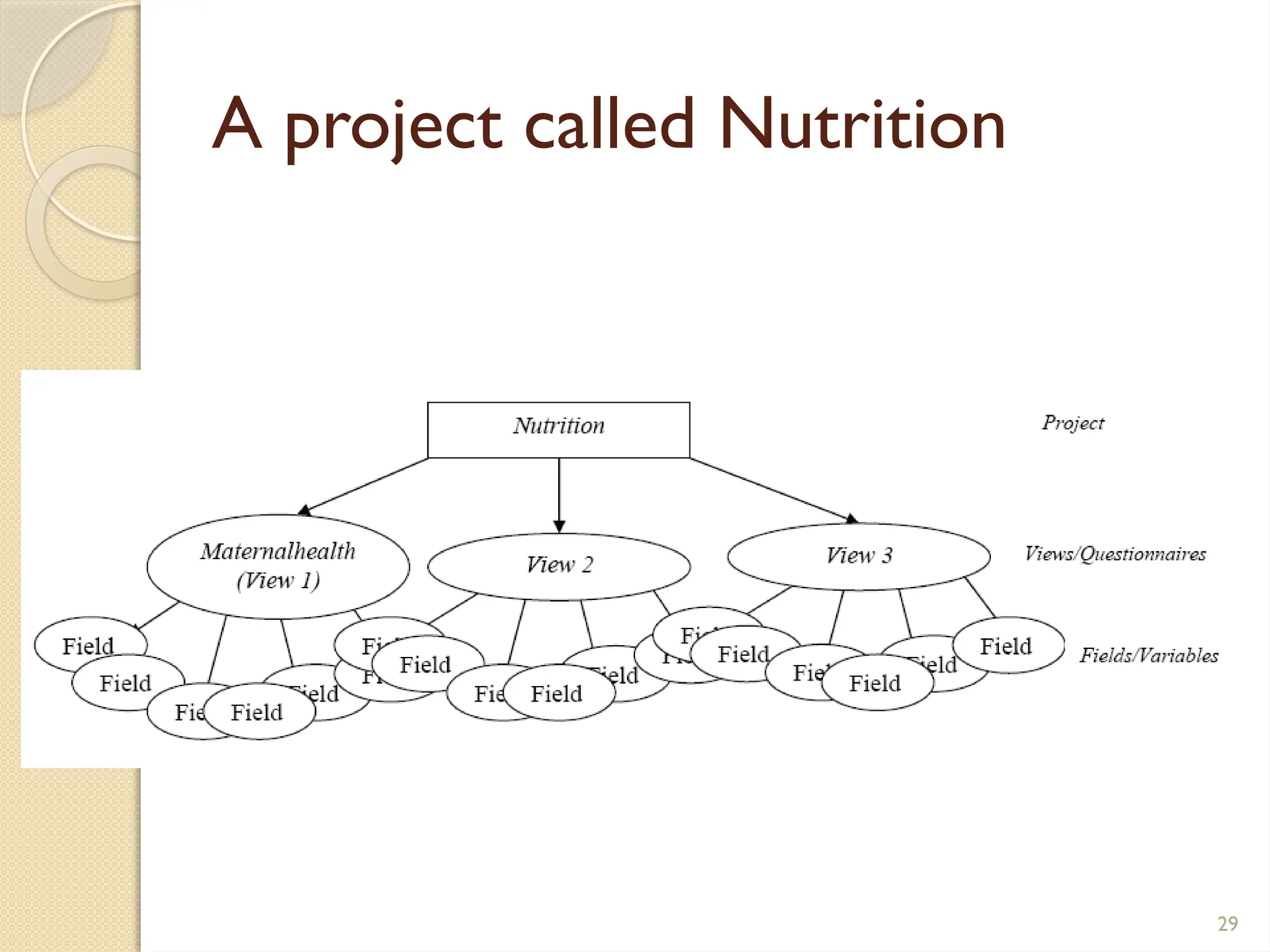
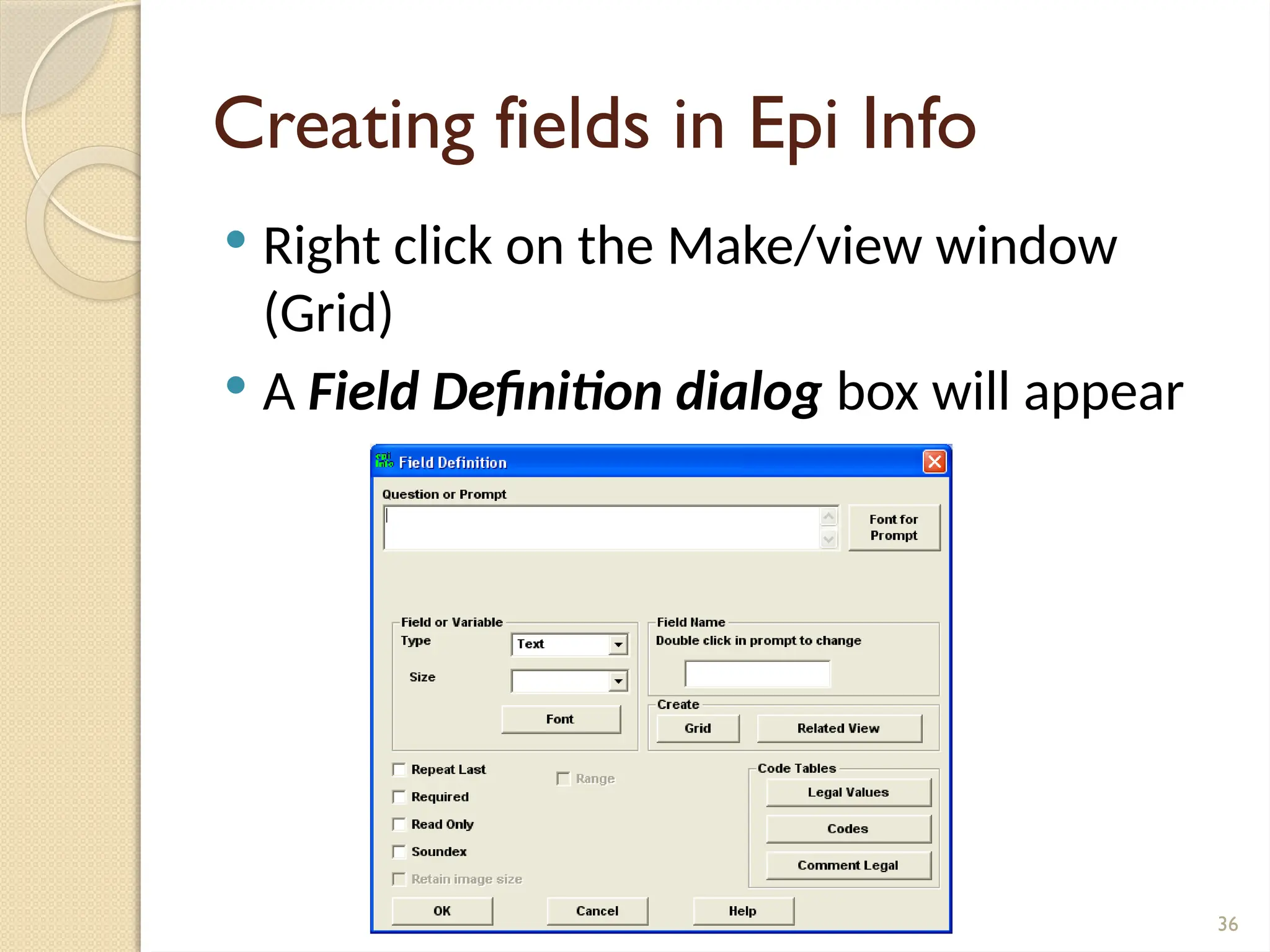
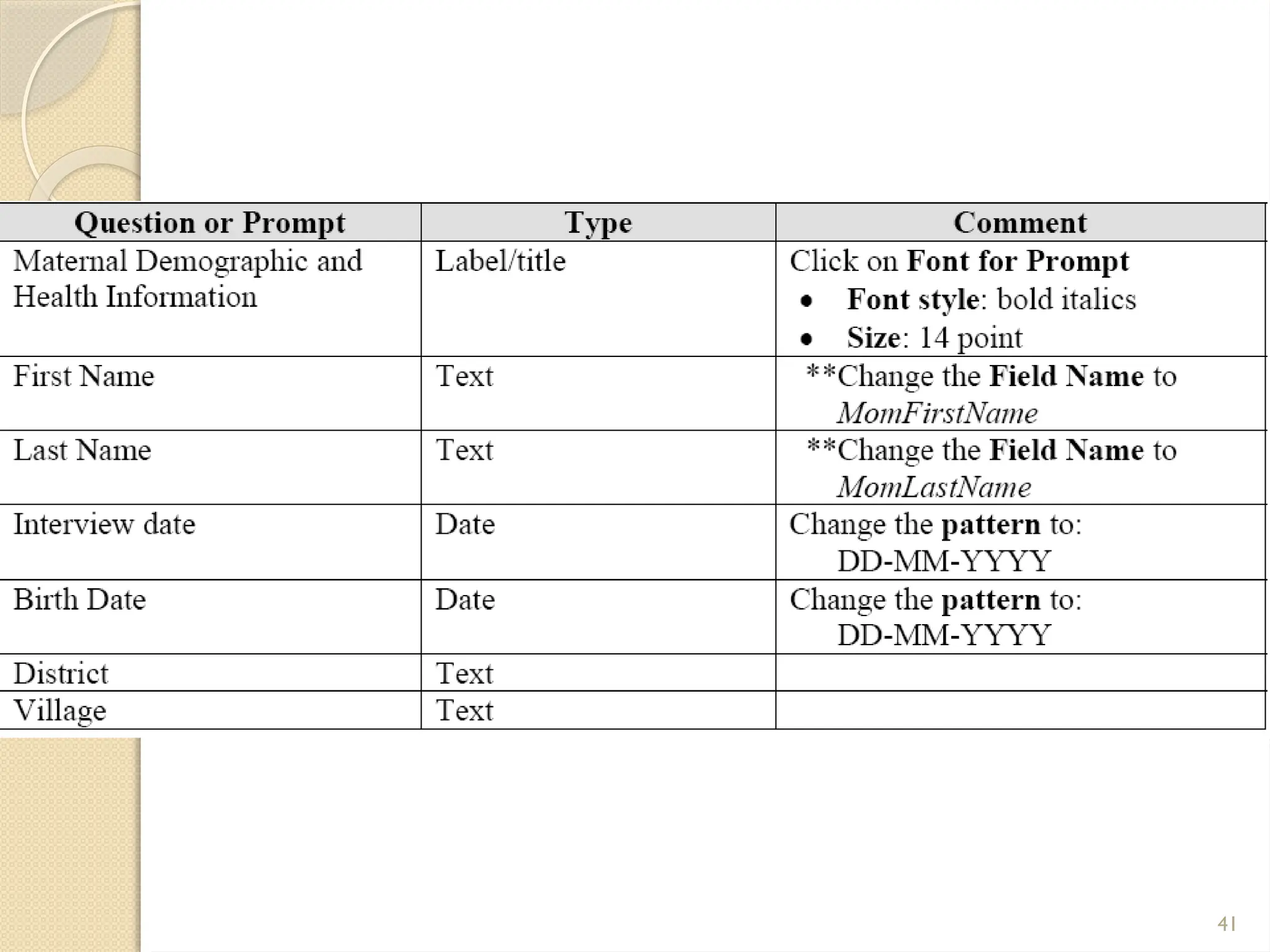
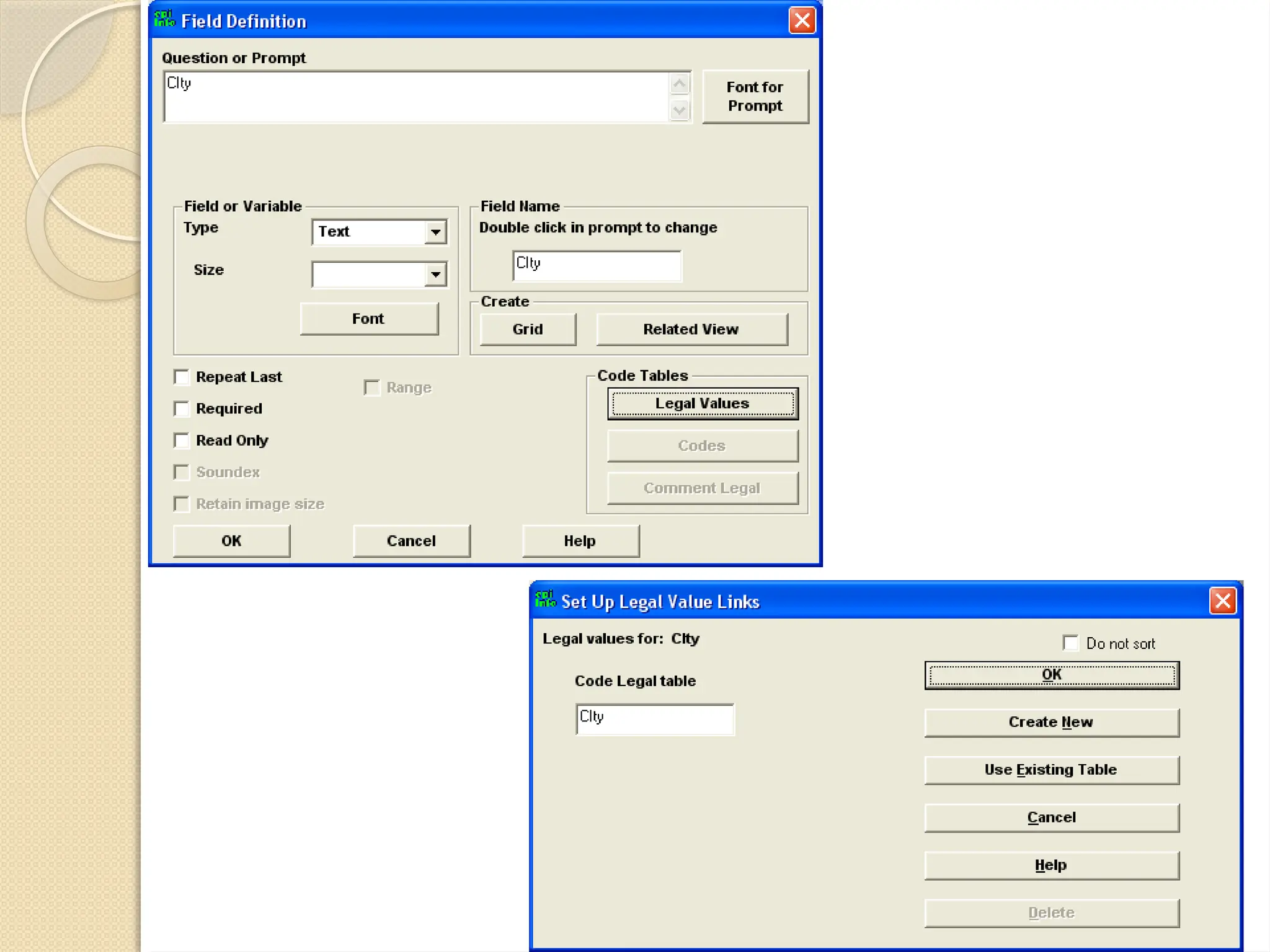
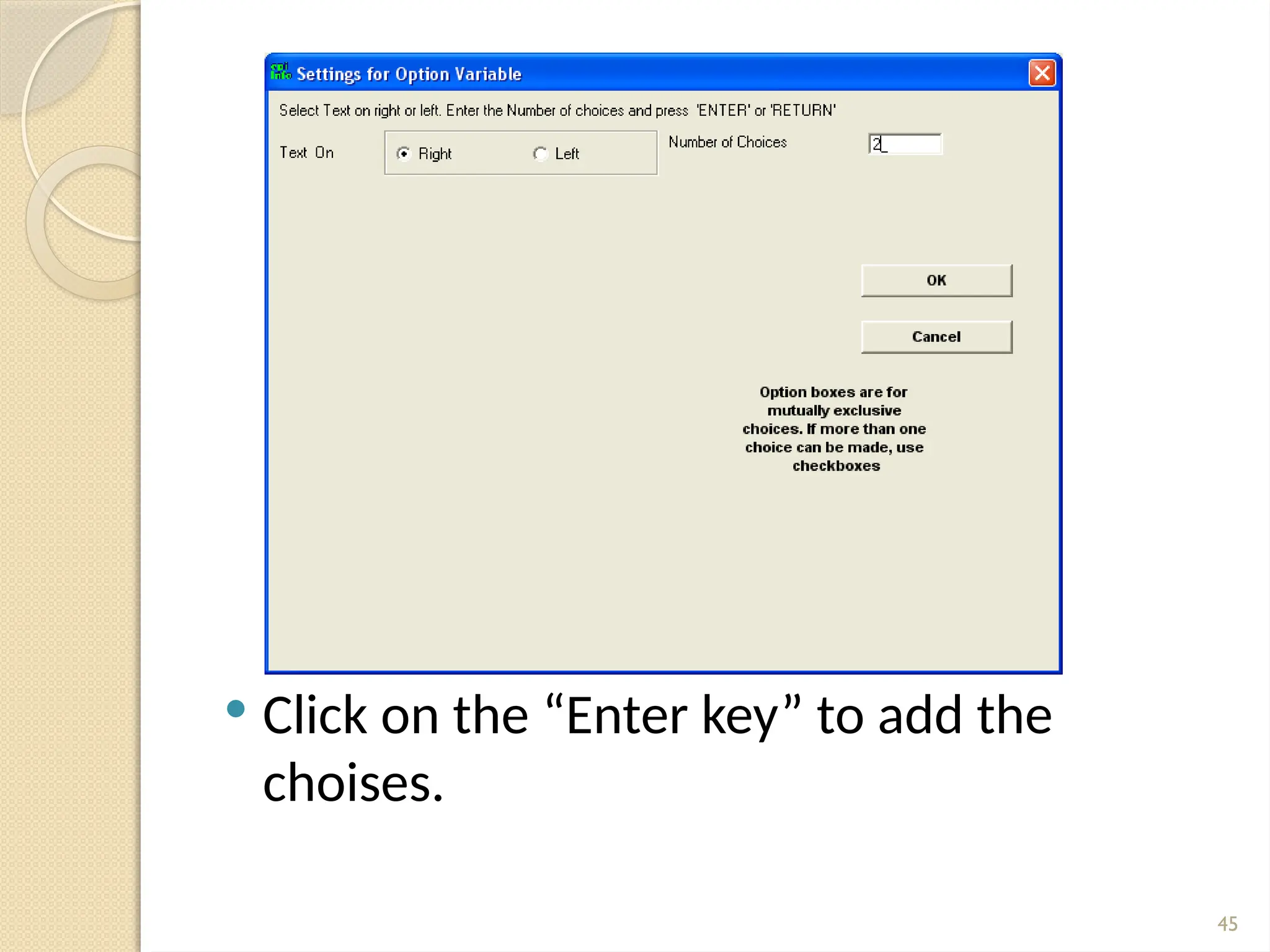
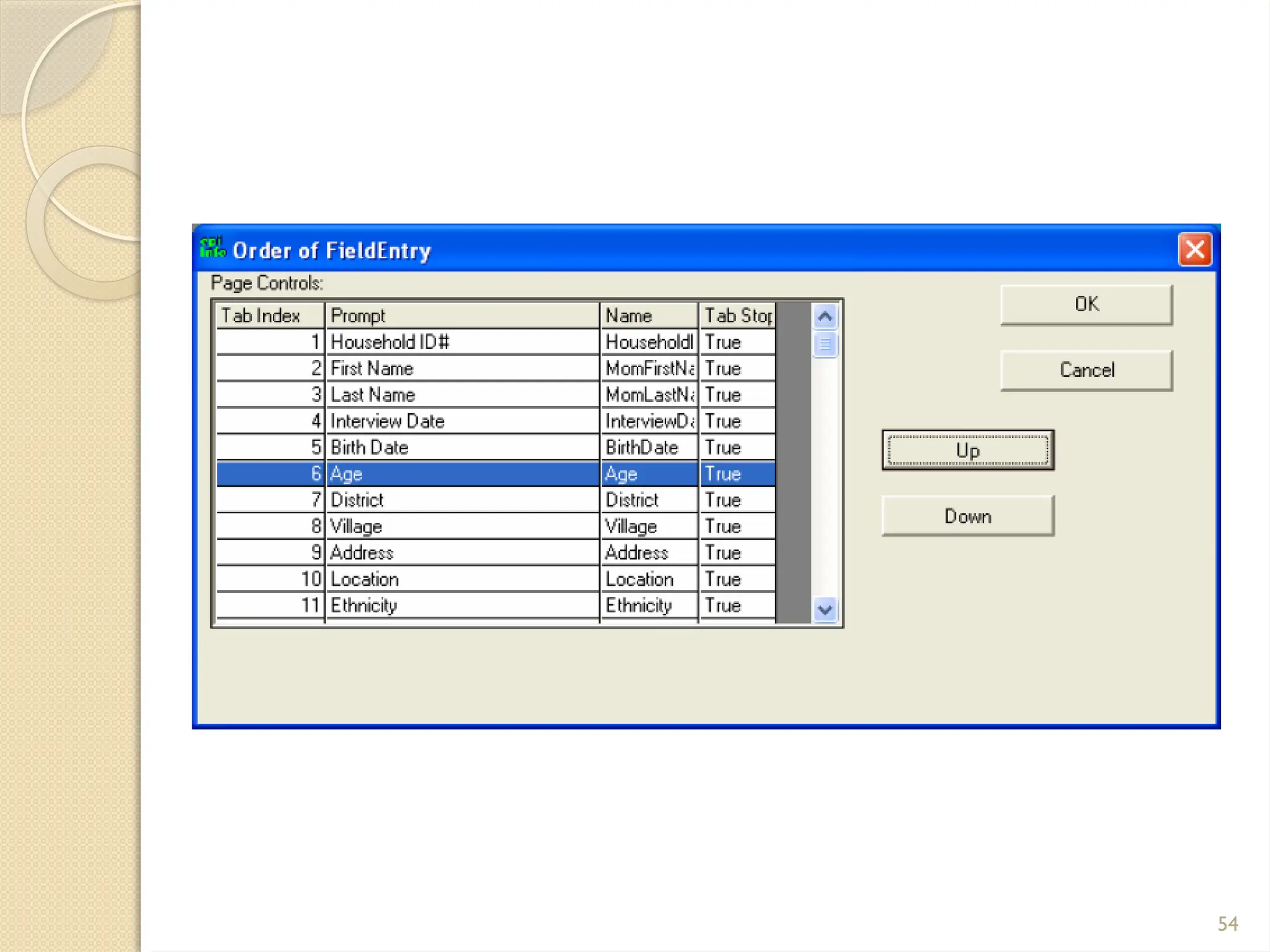
The document details data handling and analysis through the software Epi Info, developed by the CDC, which facilitates the creation, collection, and reporting of data. It compares manual and computer-based information systems, highlighting the advantages of the latter, such as speed and accuracy in data processing. Additionally, the document covers the structure of databases, including primary and foreign keys, and outlines the functionalities of Epi Info for designing questionnaires and analyzing data.