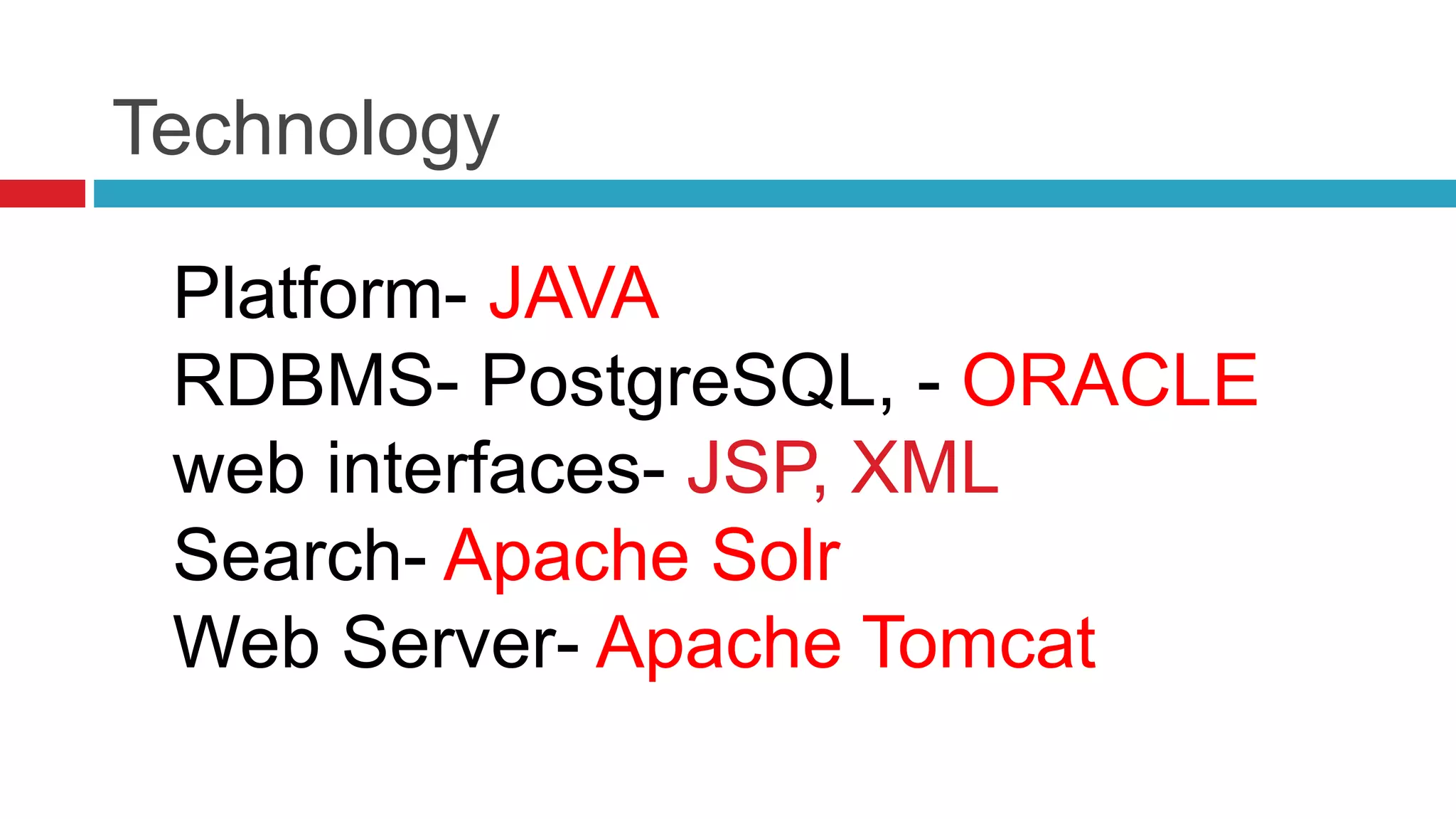
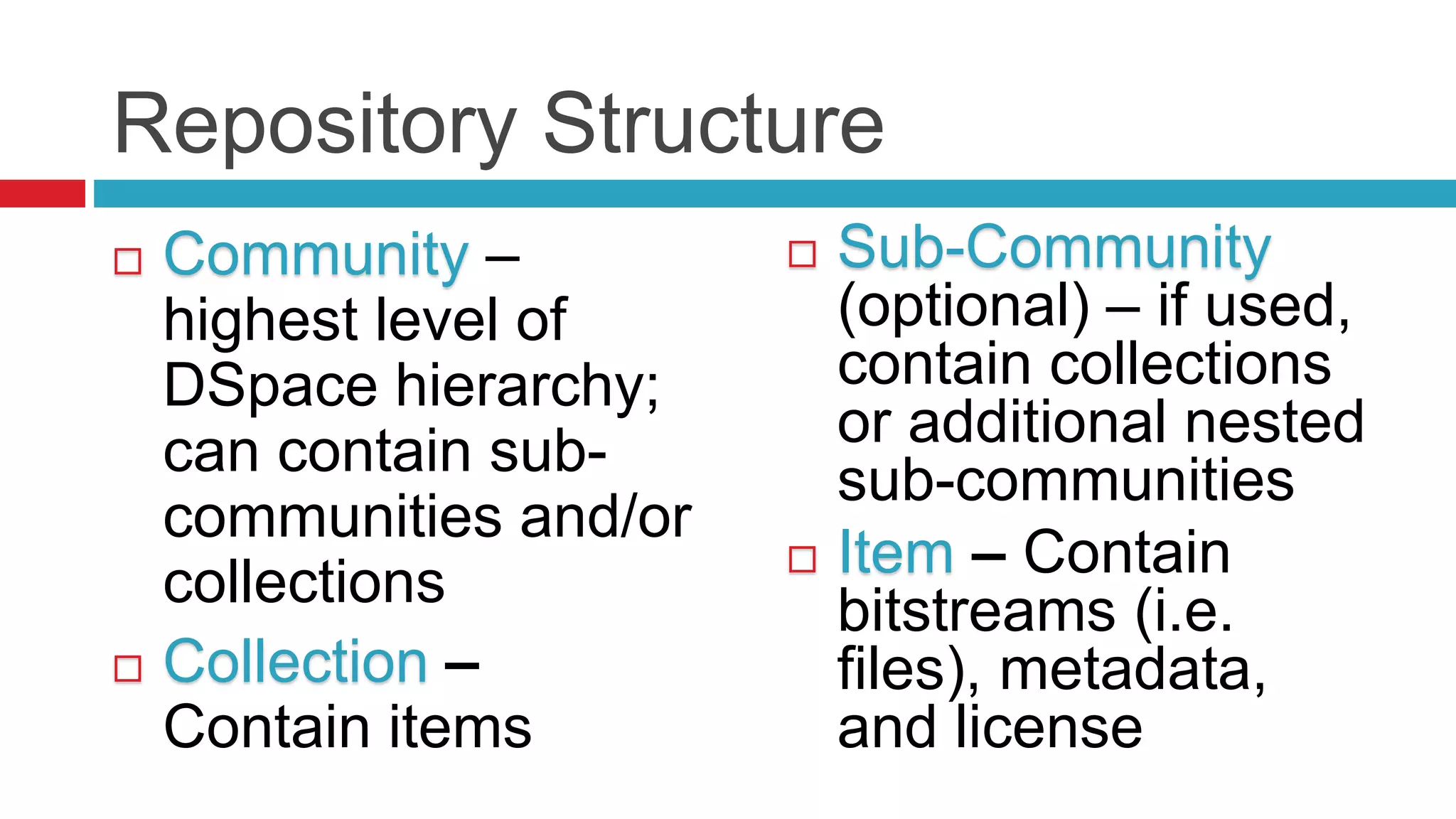
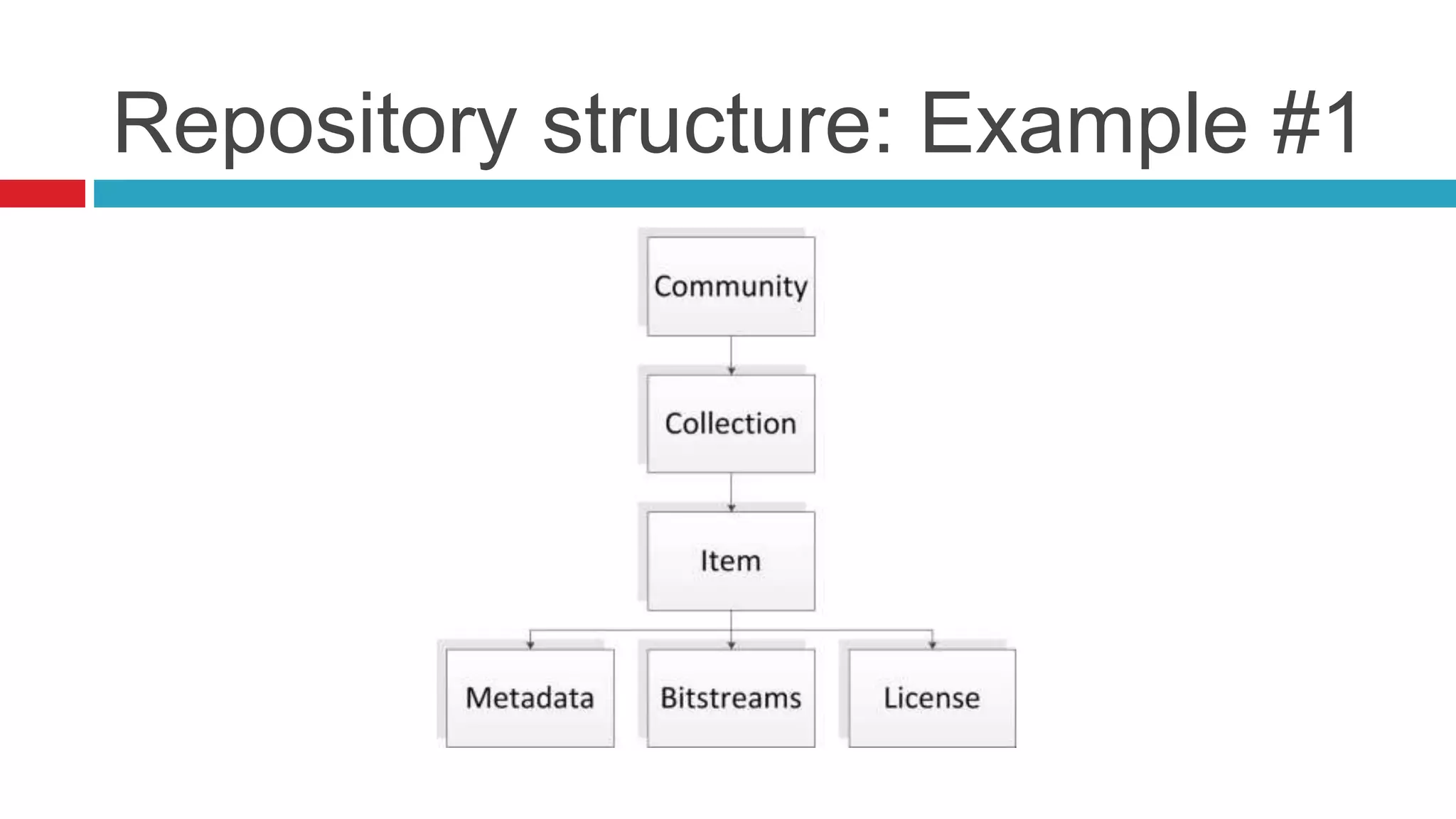
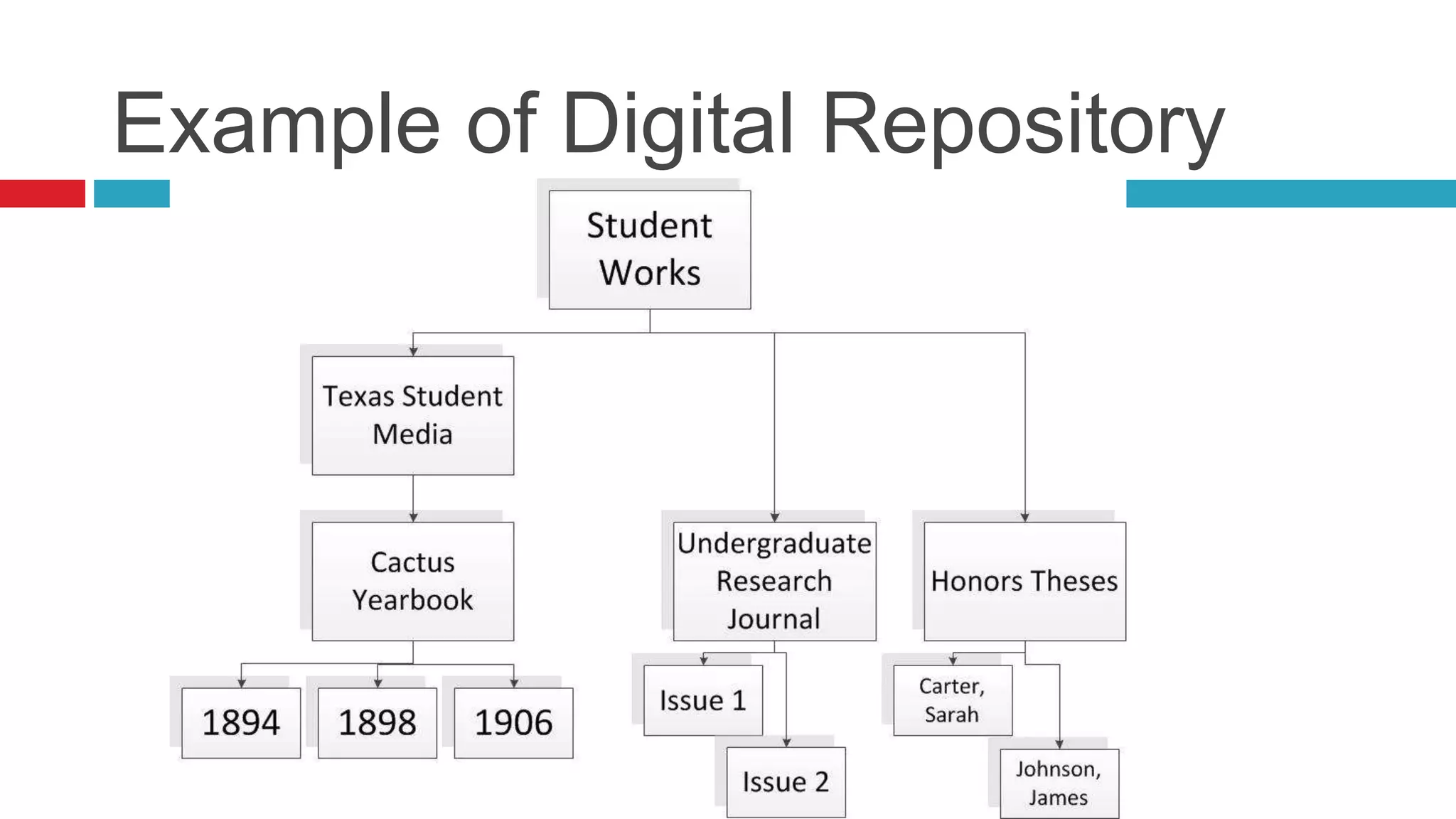
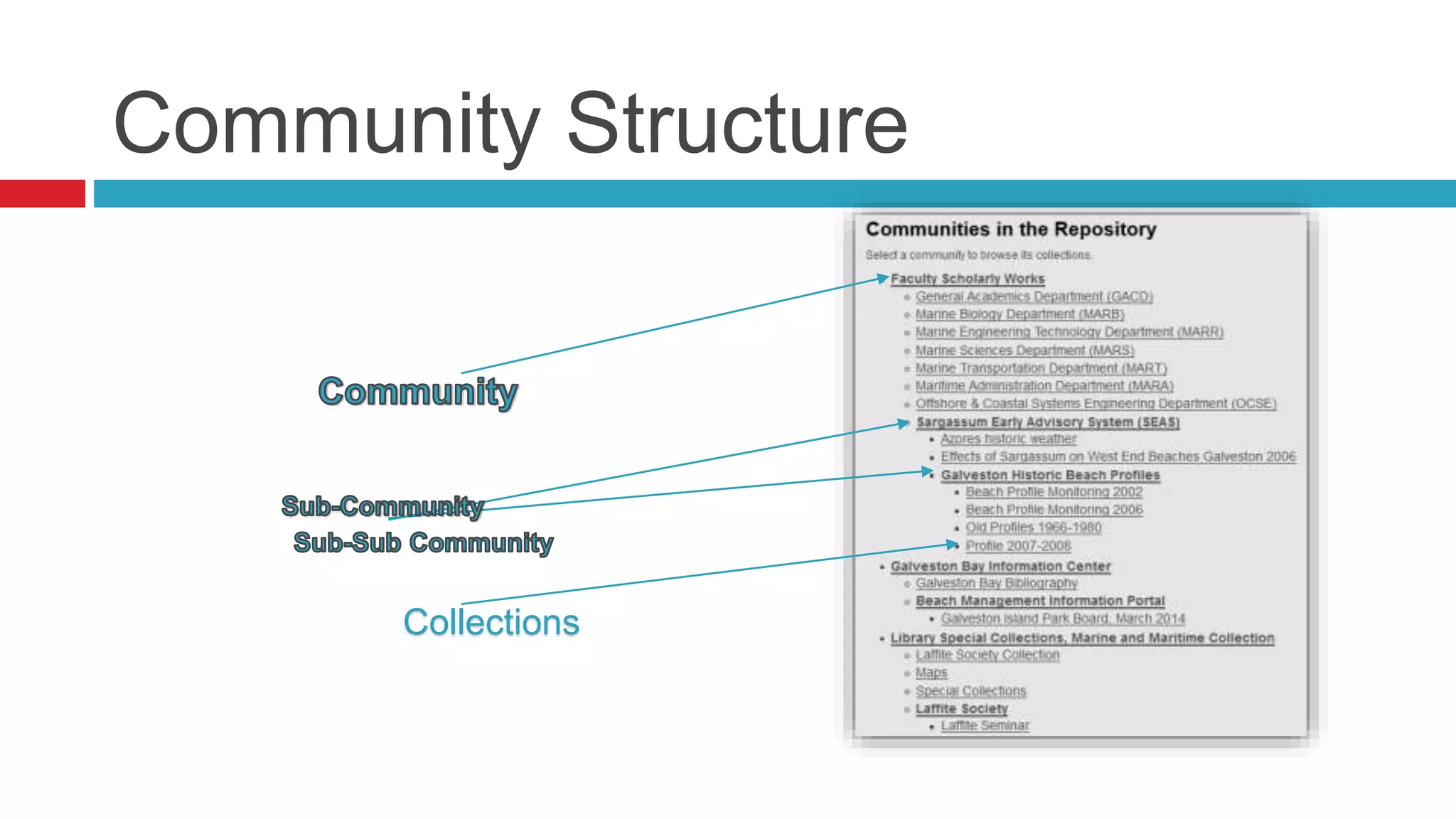
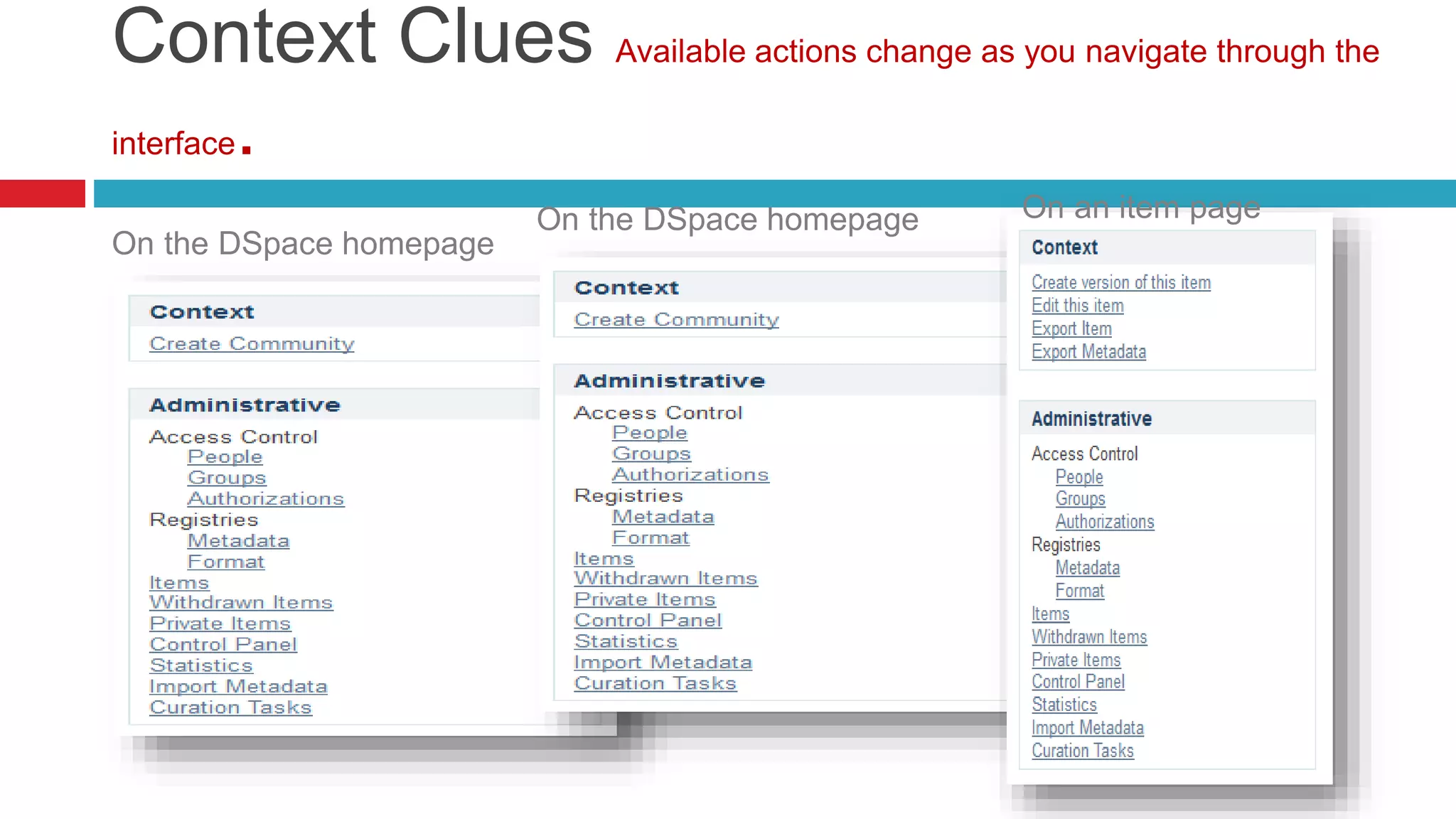
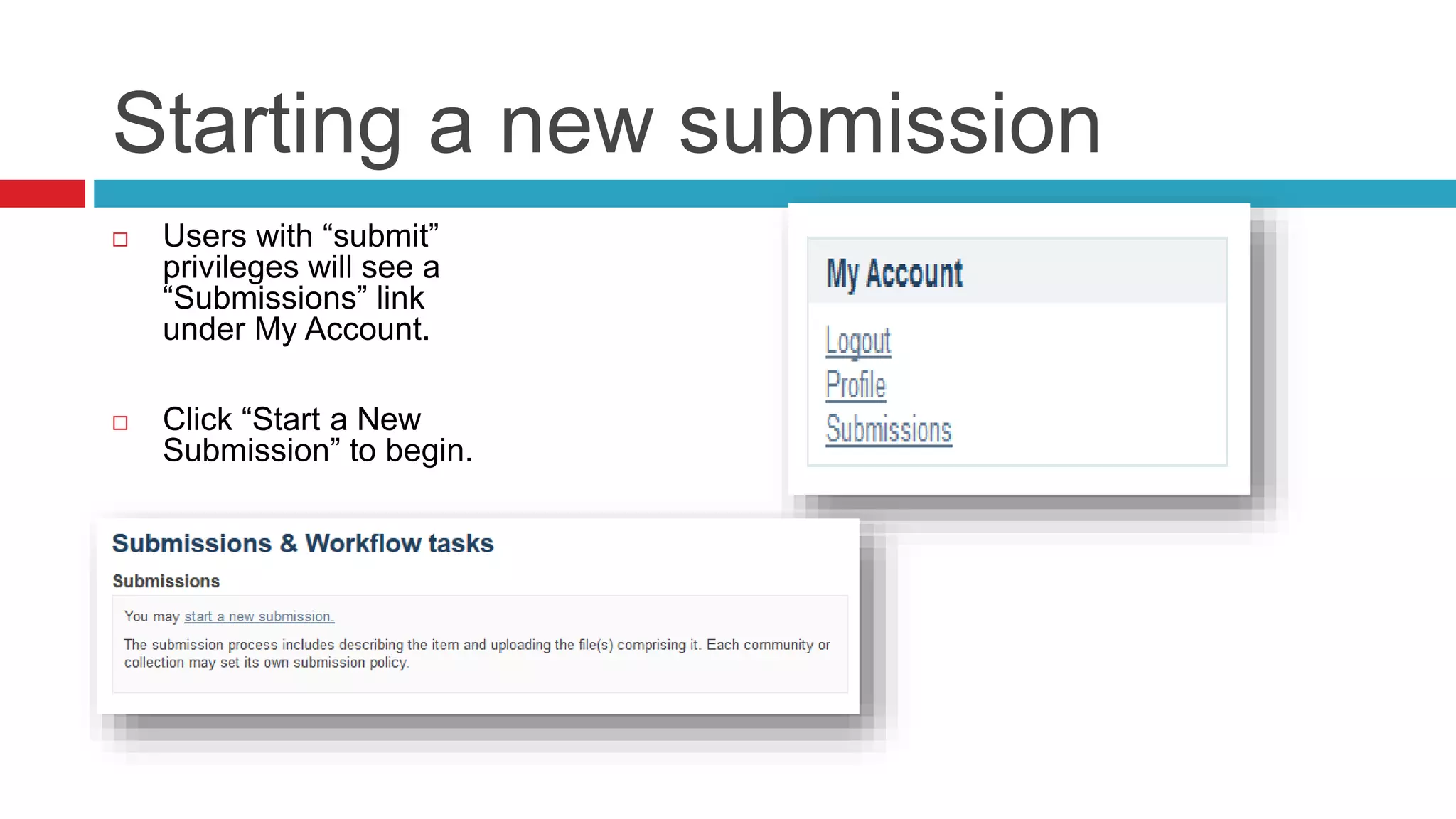
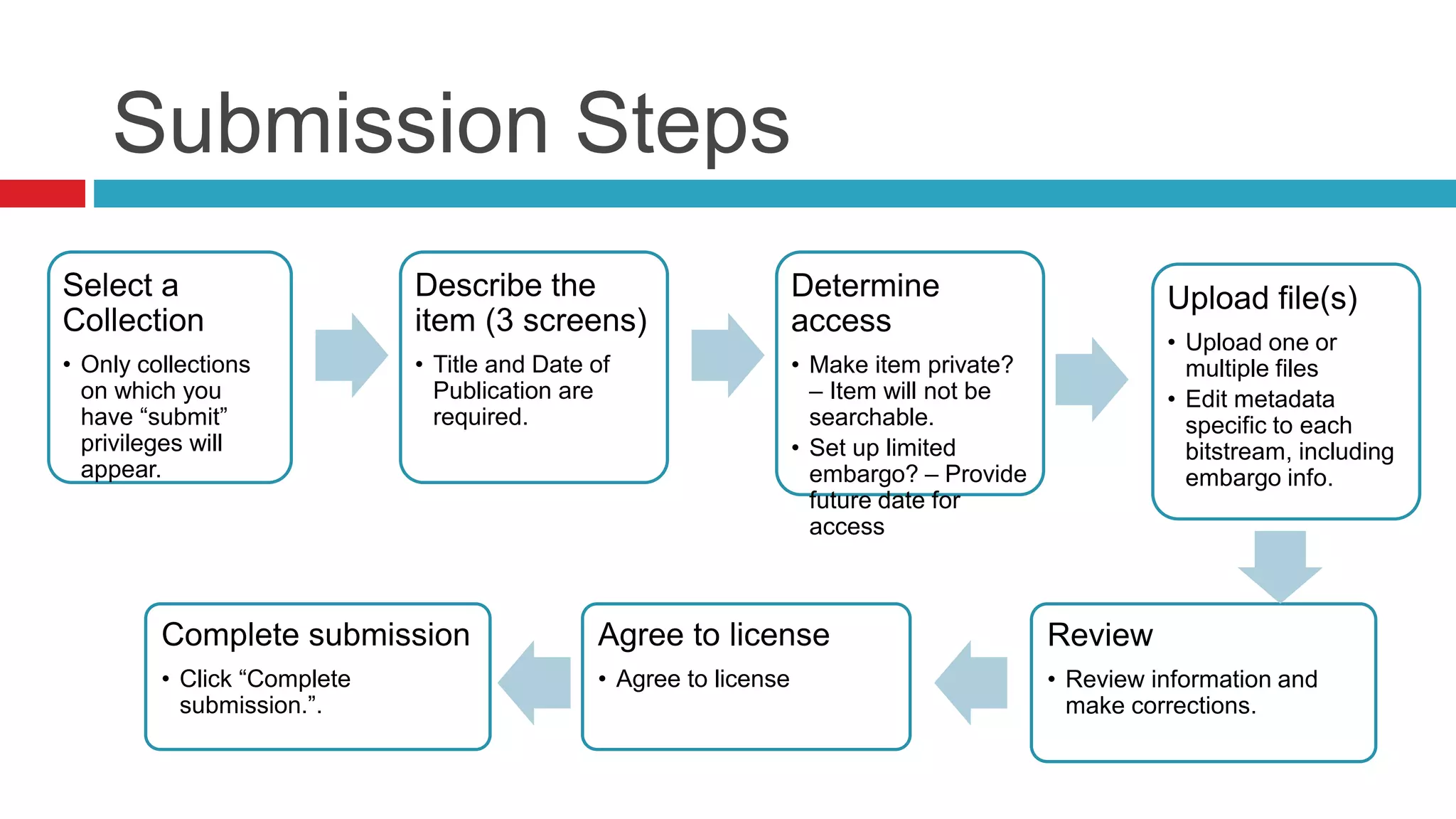
DSpace is an open source digital repository software package typically used to create open access repositories for scholarly content. It can store any digital media type and is optimized for text-based files. DSpace uses a Java platform with a PostgreSQL or Oracle database and has features like full-text search, persistent identifiers, and the ability to handle any file type. The community development model is open source under a BSD license.