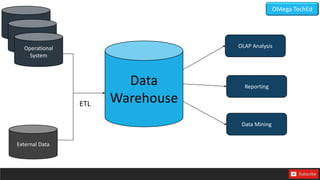
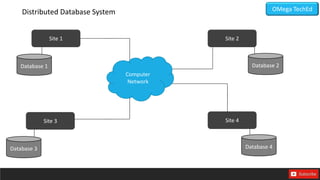
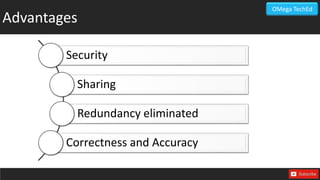
This document discusses databases and their types. It defines data as raw facts without meaning, and information as processed data. A database is described as a collection of organized data that can be easily accessed and managed. The main types of databases discussed are operational databases for day-to-day operations, data warehouses for historical reports, external databases containing internet data, analytical databases for summarized insights, distributed databases across networked sites, end-user databases created locally, and cloud databases relying on remote technology. Advantages of databases include security, data sharing, redundancy elimination, and ensuring correctness and accuracy.