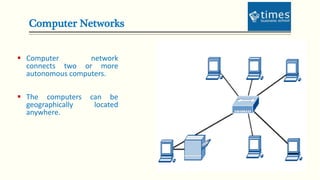
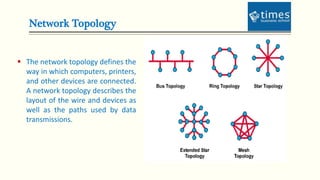
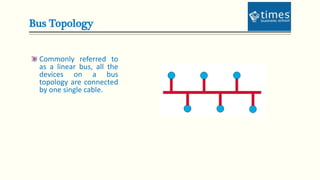
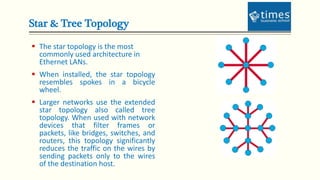
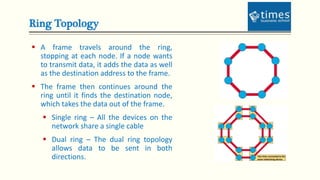
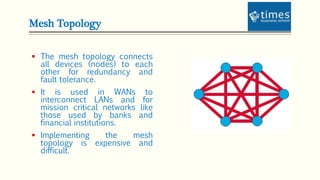
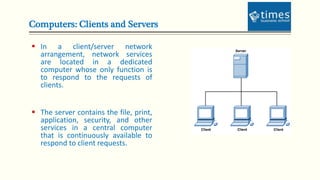
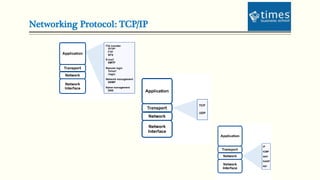
This document provides an introduction to computer networks. It defines different types of networks including LAN, MAN, and WAN. It describes how networks allow for resource and information sharing and communication capabilities. The document outlines different network topologies such as bus, star, ring, mesh and explains the components that make up a network including physical media, connecting devices, computers, networking software and applications. It provides details on clients, servers and the TCP/IP networking protocol. The document is presented by Dr. Pravin Madalia Parmar and provides a comprehensive overview of computer networks.