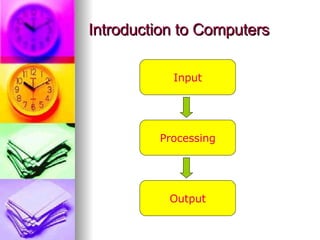
The document provides an introduction to different types of computers. It defines computers as devices that can accept input, process it, and provide output. Computers are categorized as analog, digital, or hybrid. Digital computers can further be classified as super computers, mainframe computers, mini computers, or micro computers. Micro computers include desktop computers, laptop computers, and palmtop computers. Hybrid computers demonstrate qualities of both analog and digital computers.