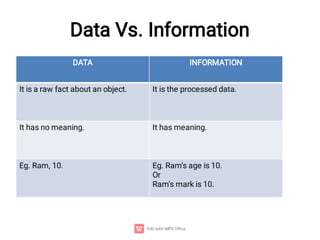
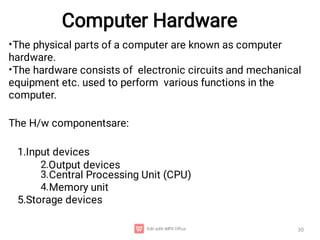
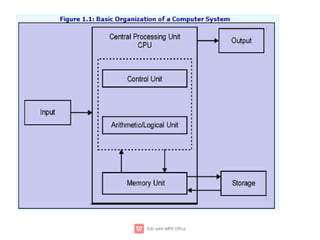
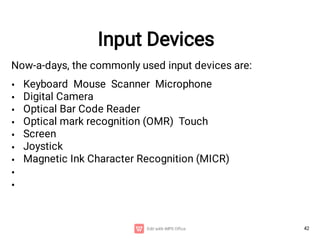
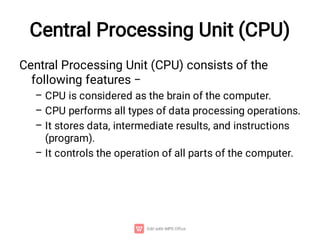
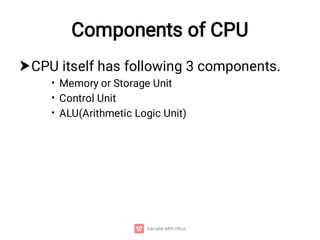
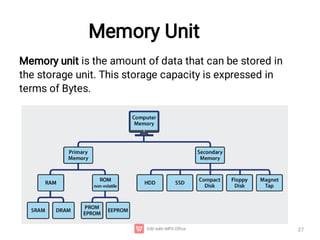
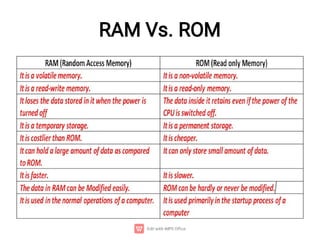
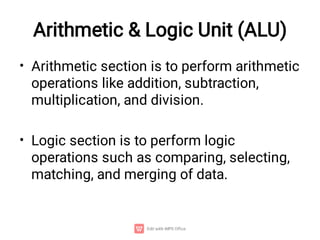
The document provides an introduction to computers, detailing their basic operations such as input, processing, output, and storage, along with the difference between data and information. It outlines the evolution of computer generations from the first generation using vacuum tubes to the current focus on artificial intelligence and ultra-large scale integration circuits. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of computers, various applications, and a classification of computer hardware and software components.