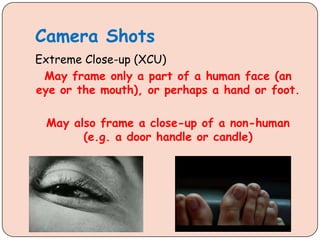
This document provides instructions for a student presentation on camerawork techniques. Students are asked to analyze the first minute of a film, identify 6 examples of shots or camera movements, and explain why they are effective for developing characters or engaging the audience. The document then defines various camera shots including close-up, medium shot, wide shot, and point-of-view shot. It also defines camera movements like pan, canted angle, high angle, and low angle shots. Sample filming scenarios are provided as examples to analyze.