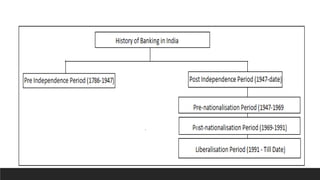
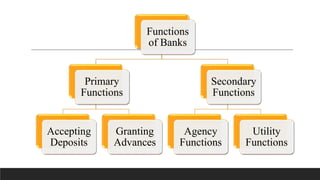
The document summarizes key concepts related to banking in India. It discusses the three phases of development of the Indian banking sector: the early phase from 1770-1969, the nationalization phase from 1969-1991, and the liberalization phase from 1991 onward. It also defines banking and the basic roles of banks. The primary functions of banks include accepting deposits and granting advances. Deposit accounts discussed include savings deposits, fixed deposits, current deposits, and recurring deposits. The document provides an overview of the historical development and functioning of the banking sector in India.