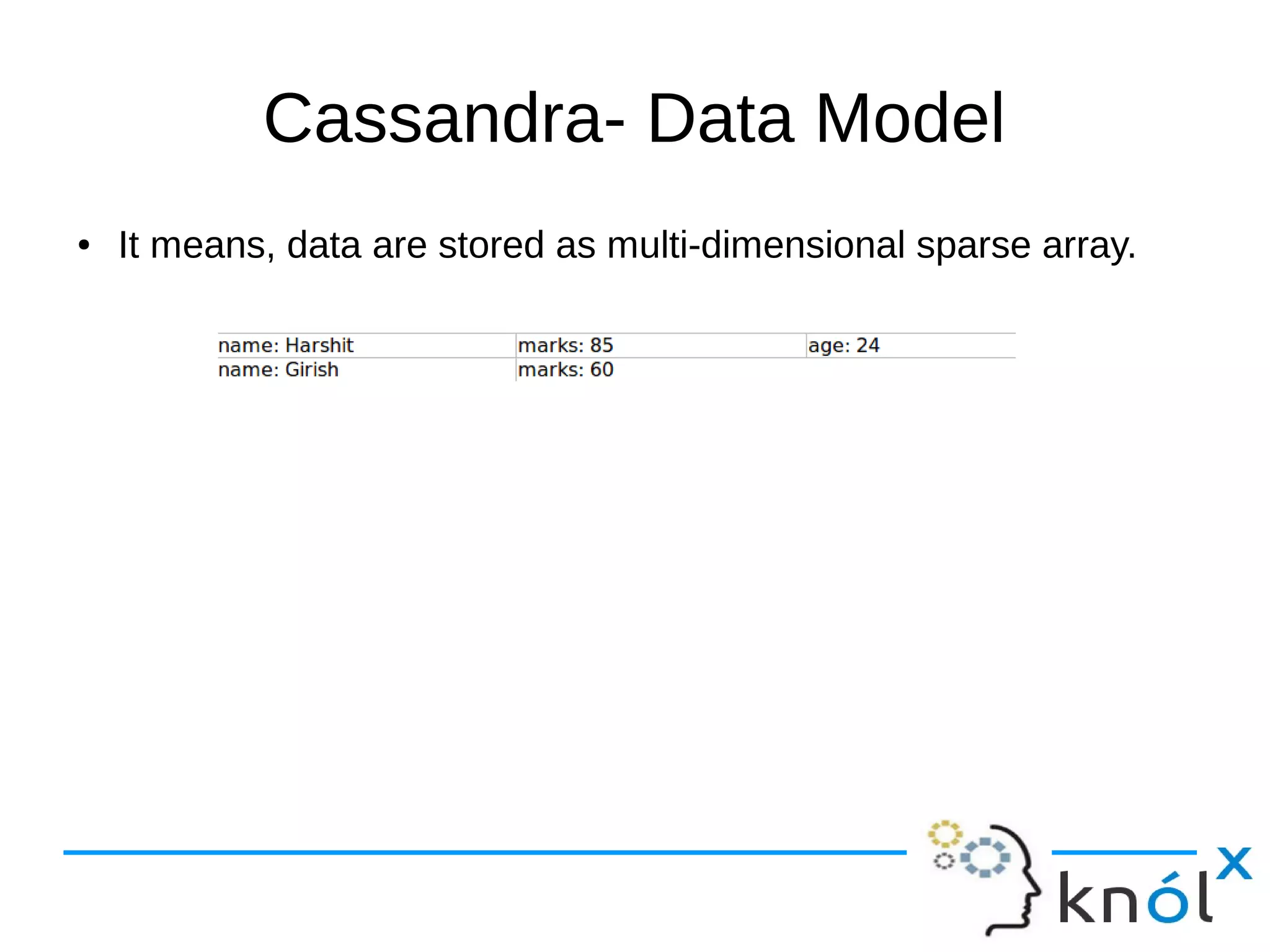
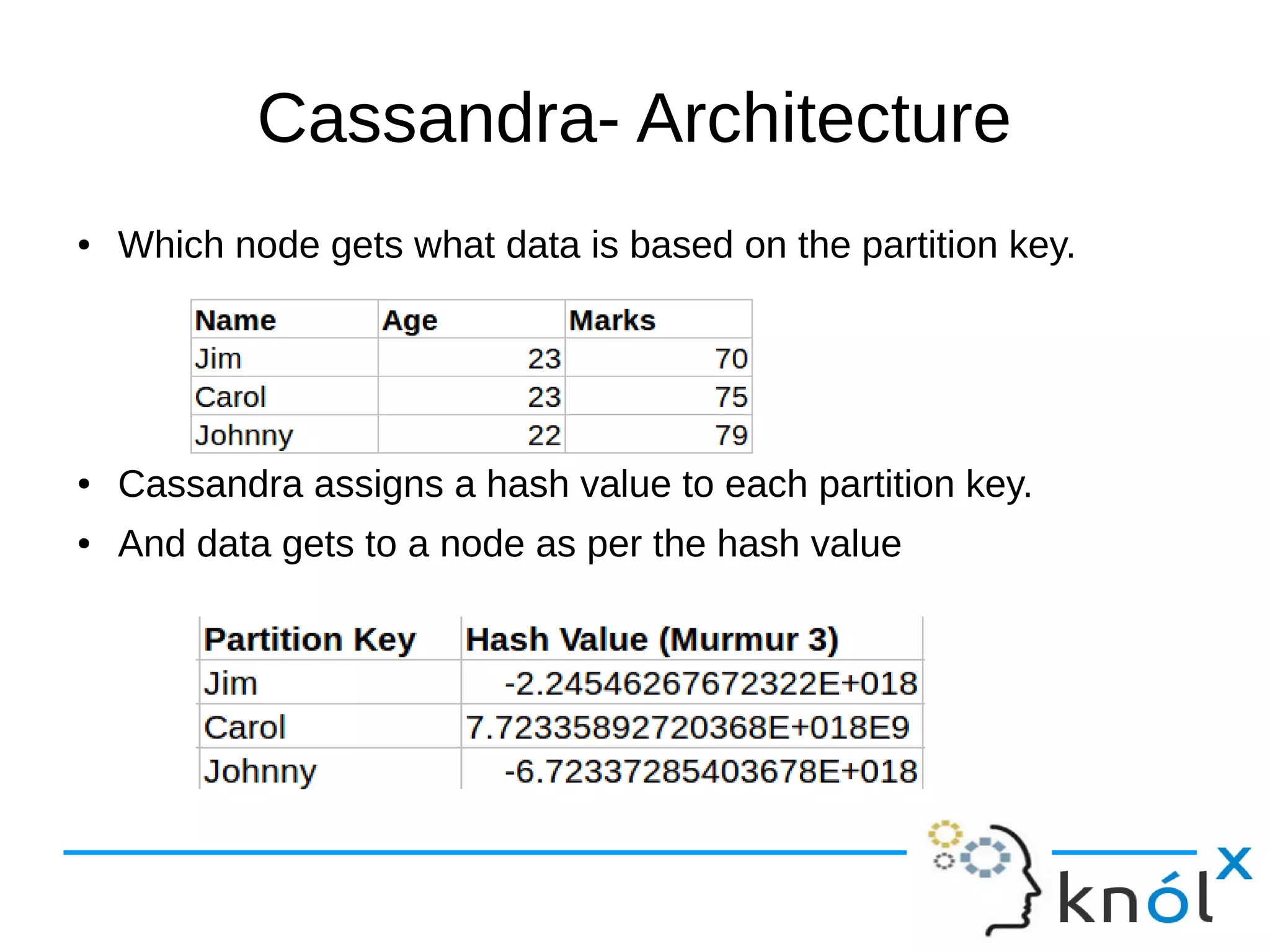
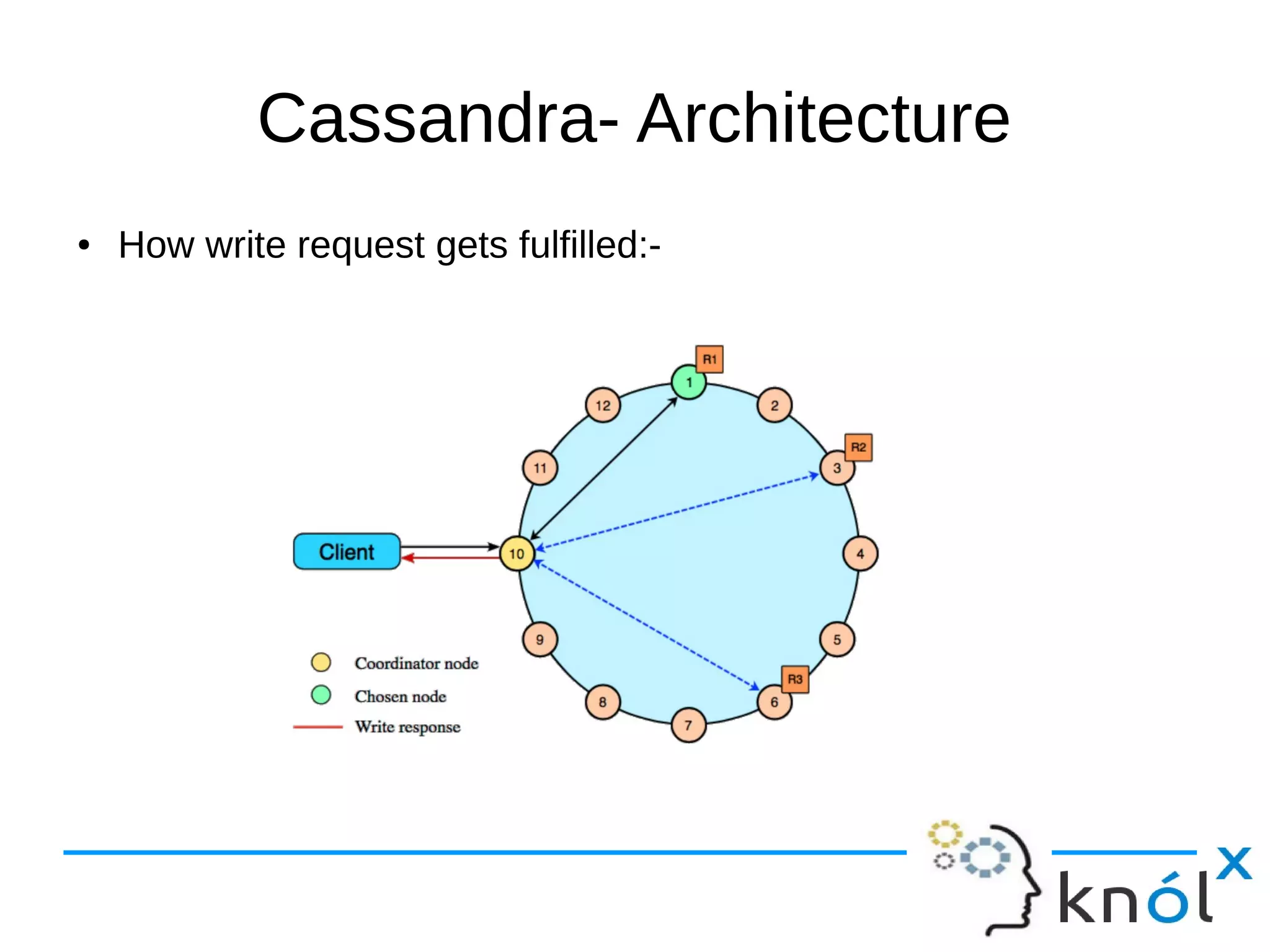
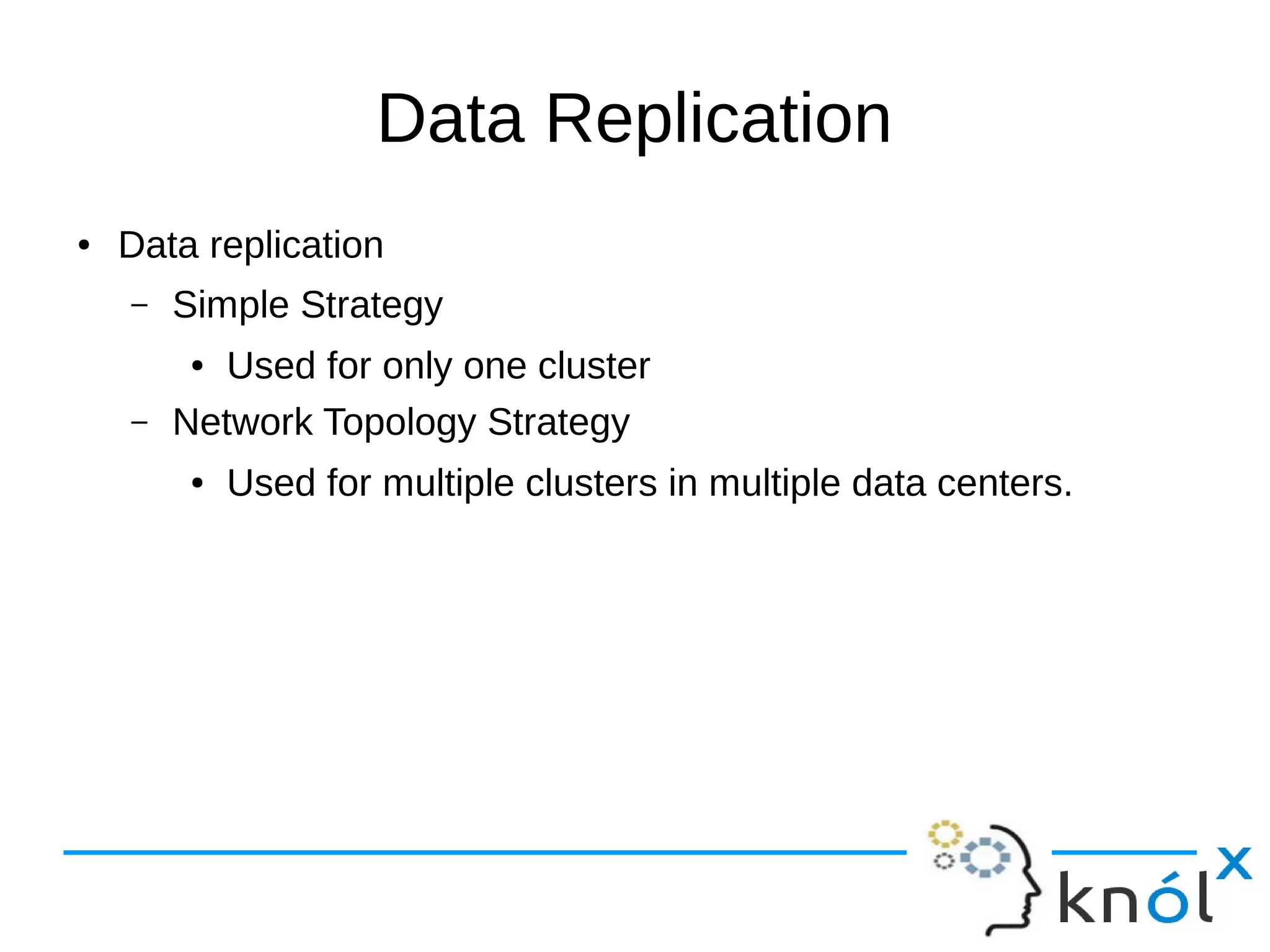
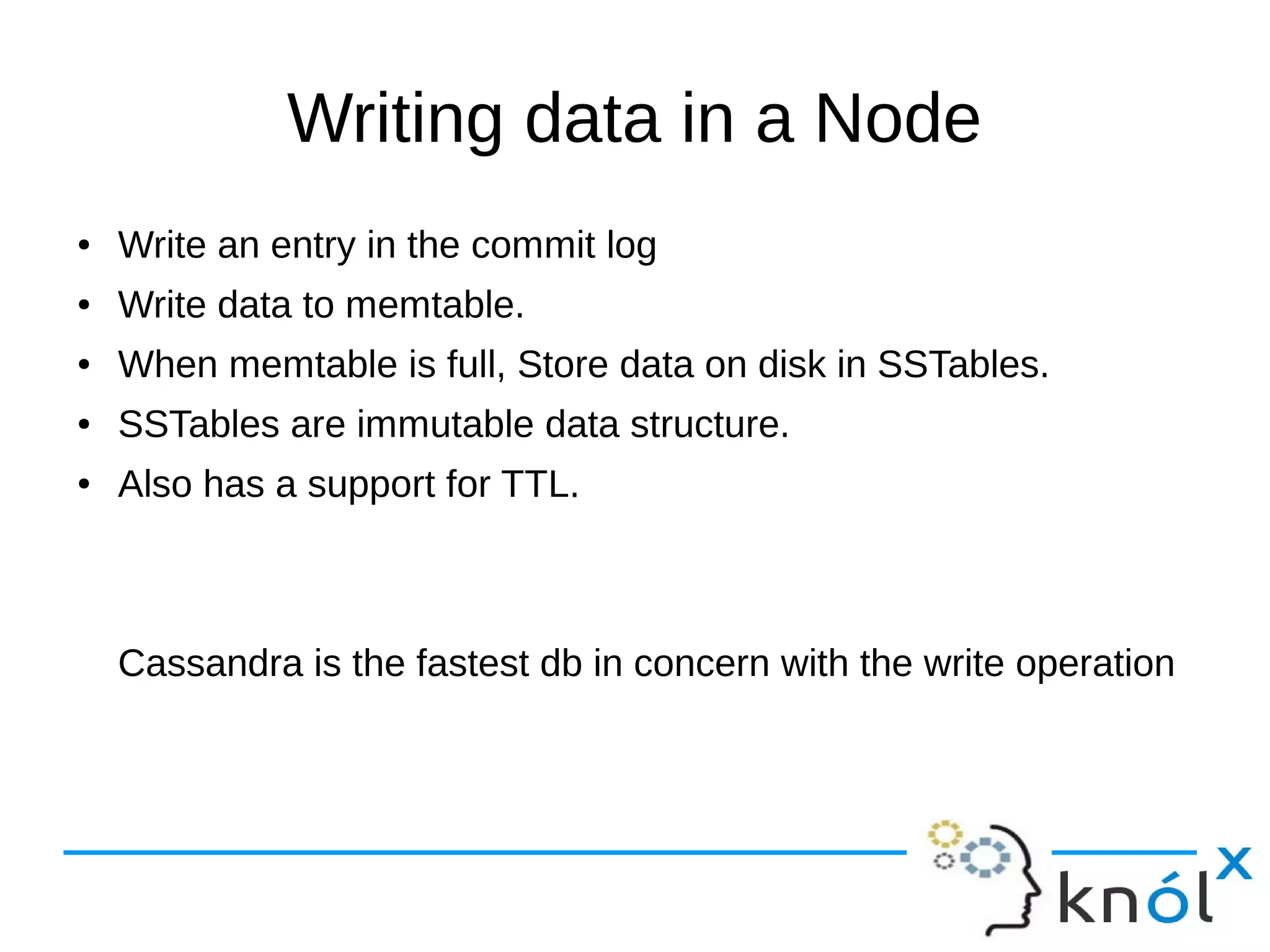
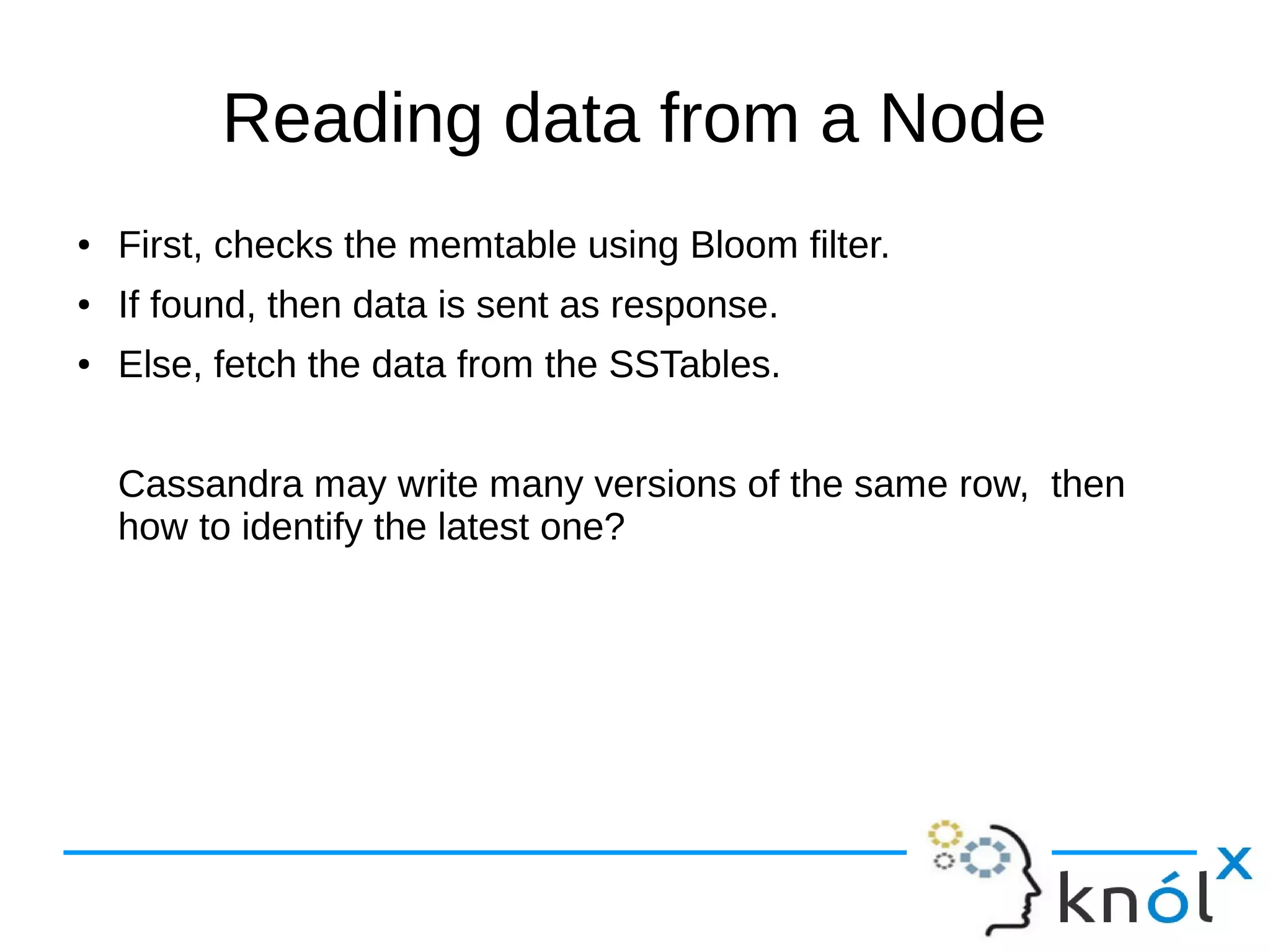
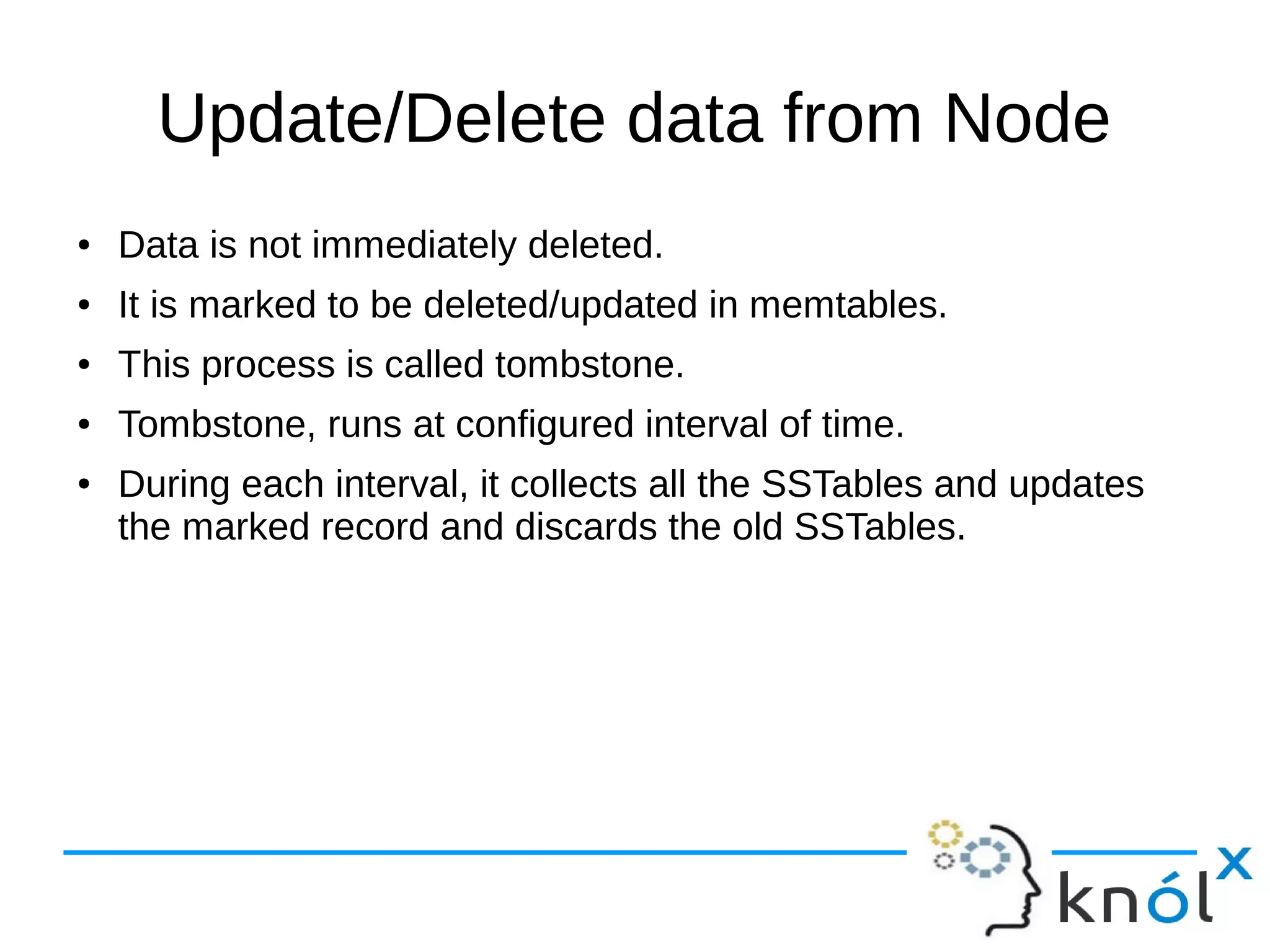
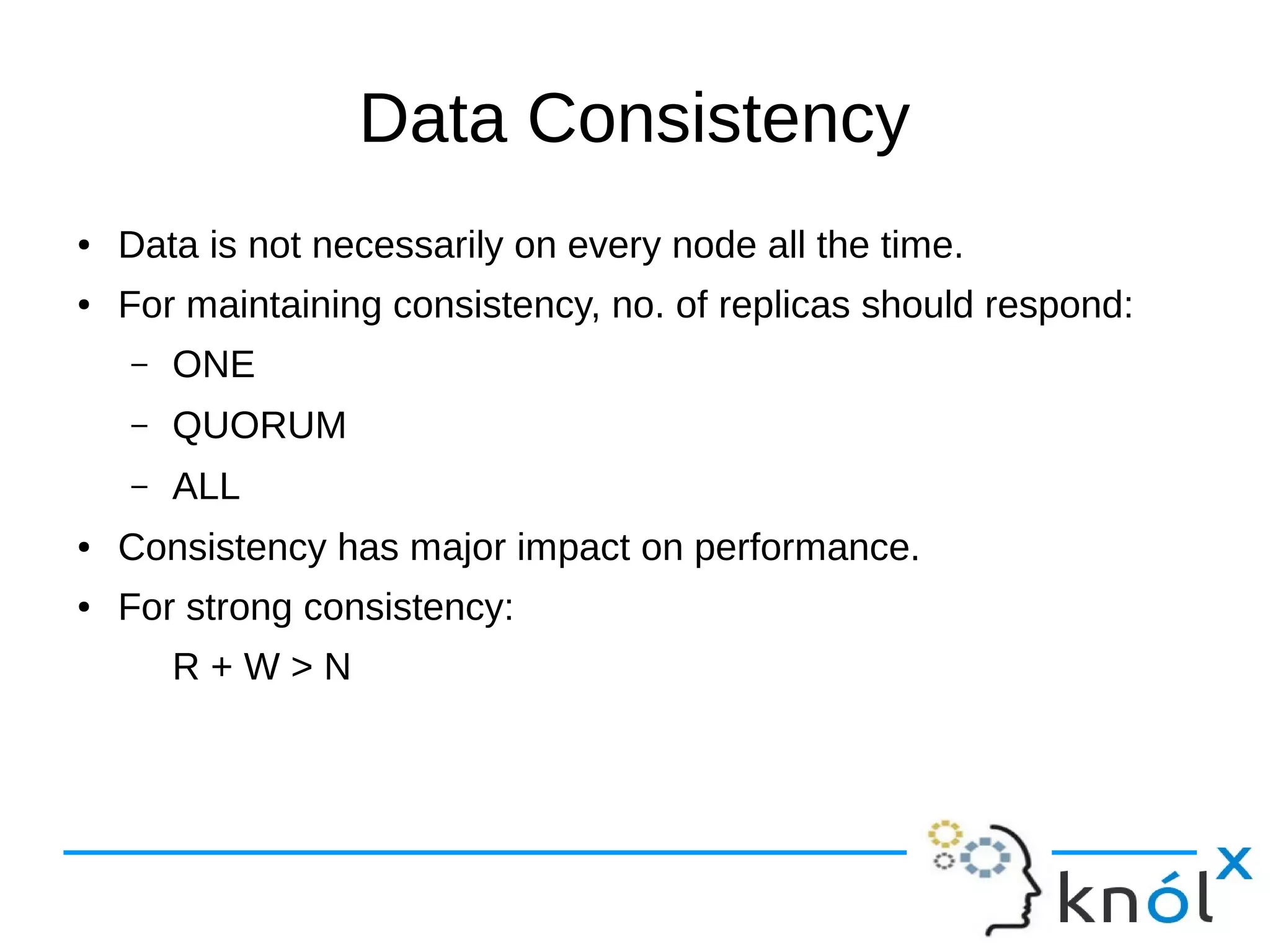
The document provides an overview of Apache Cassandra, highlighting its key features such as its schema-less, scalable architecture and the gossip communication protocol used for peer-to-peer node communication. It explains the data model structured as key/value pairs and details the write and read operations, including data replication strategies. Additionally, it covers aspects of data consistency and the management of records through tombstones.