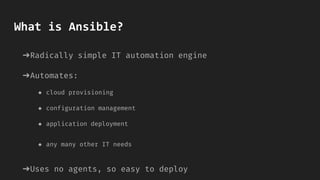
- Ansible is an automation tool that allows users to automate tasks like configuration management, application deployment, and other IT needs across multiple servers.
- It uses SSH to connect to remote servers and run commands without requiring any agents to be installed on the servers. Users only need to install Ansible on one central system.
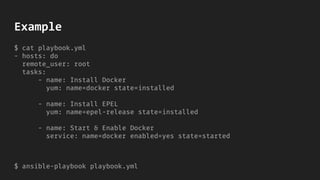
- Ansible uses simple YAML files called playbooks to define configurations and orchestrate deployments across servers. Playbooks allow rolling updates, delegating tasks, and interacting with other systems.