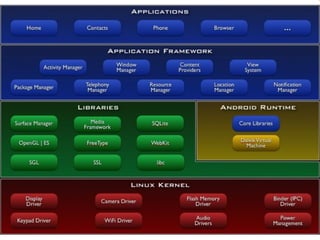
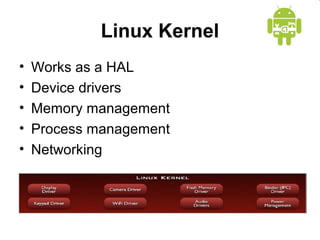
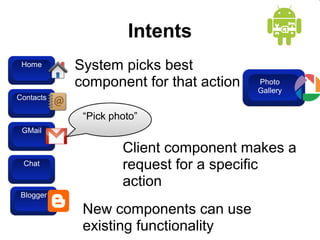
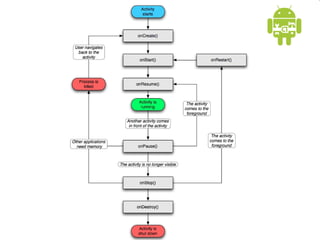
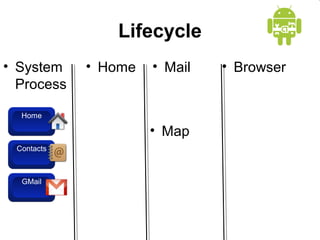
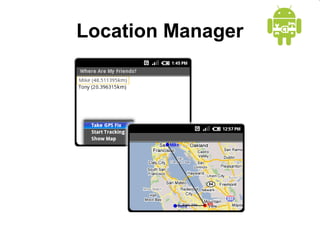
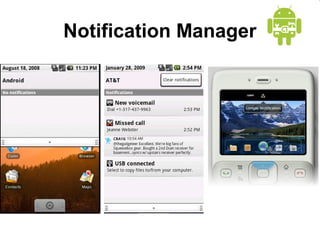
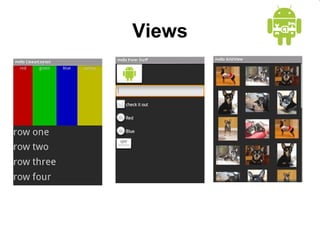
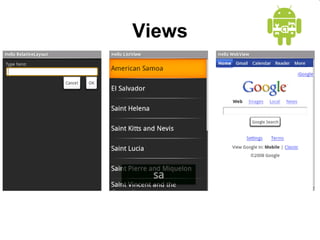
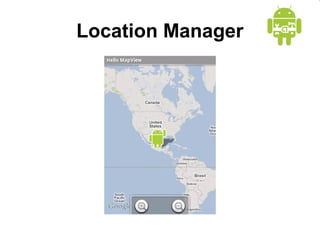
This document provides an overview of Android application development. It introduces the Android platform architecture which is based on the Linux kernel and includes libraries, a Java-compatible runtime, and an application framework. It describes the application building blocks of activities, intent receivers, services, and content providers. It also outlines the development tools used, including Eclipse and the emulator, and covers concepts like intents, notifications, and the application lifecycle. The objectives are to learn mobile application development on Android, understand the platform architecture and building blocks, and use the appropriate tools.