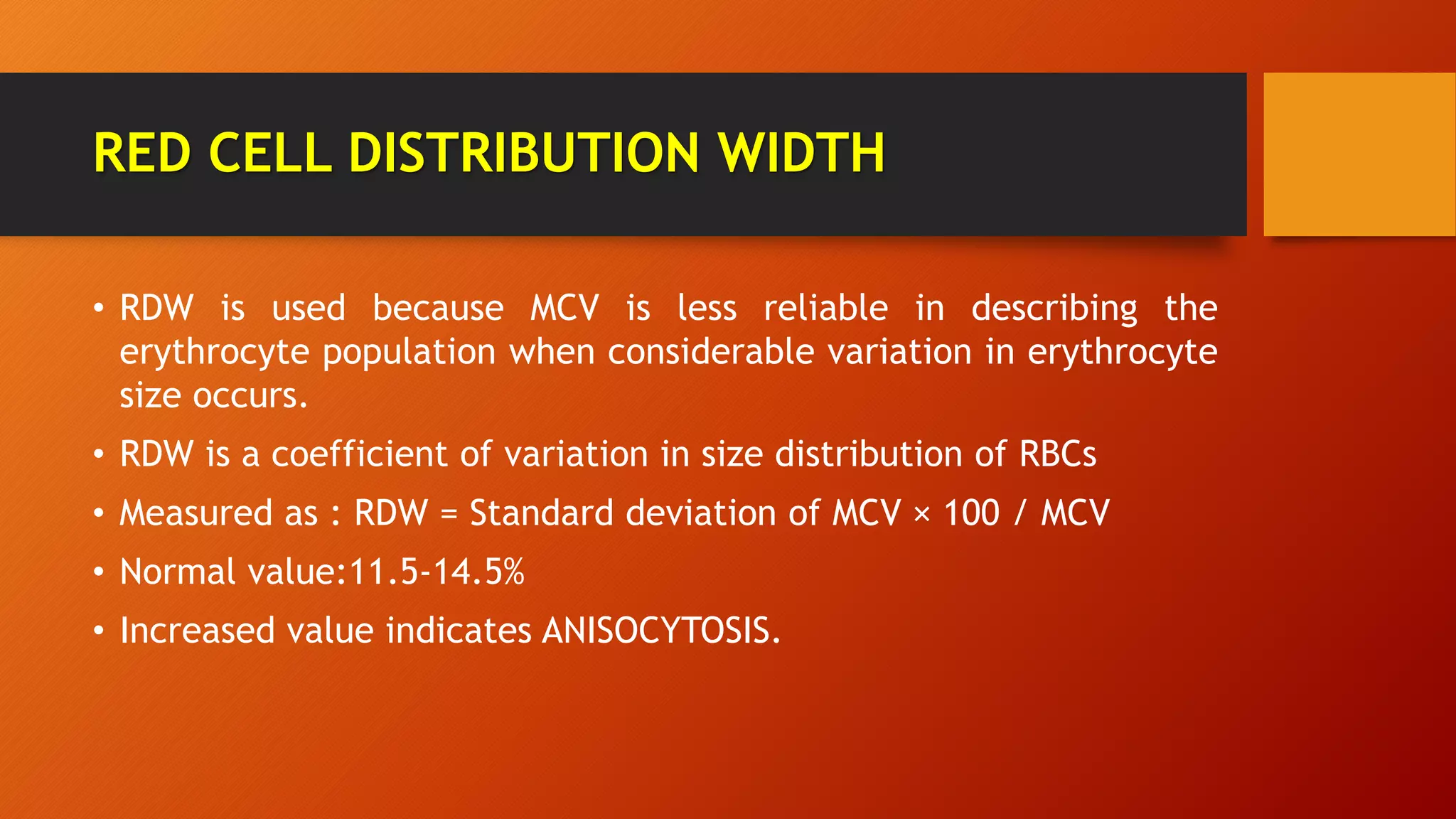
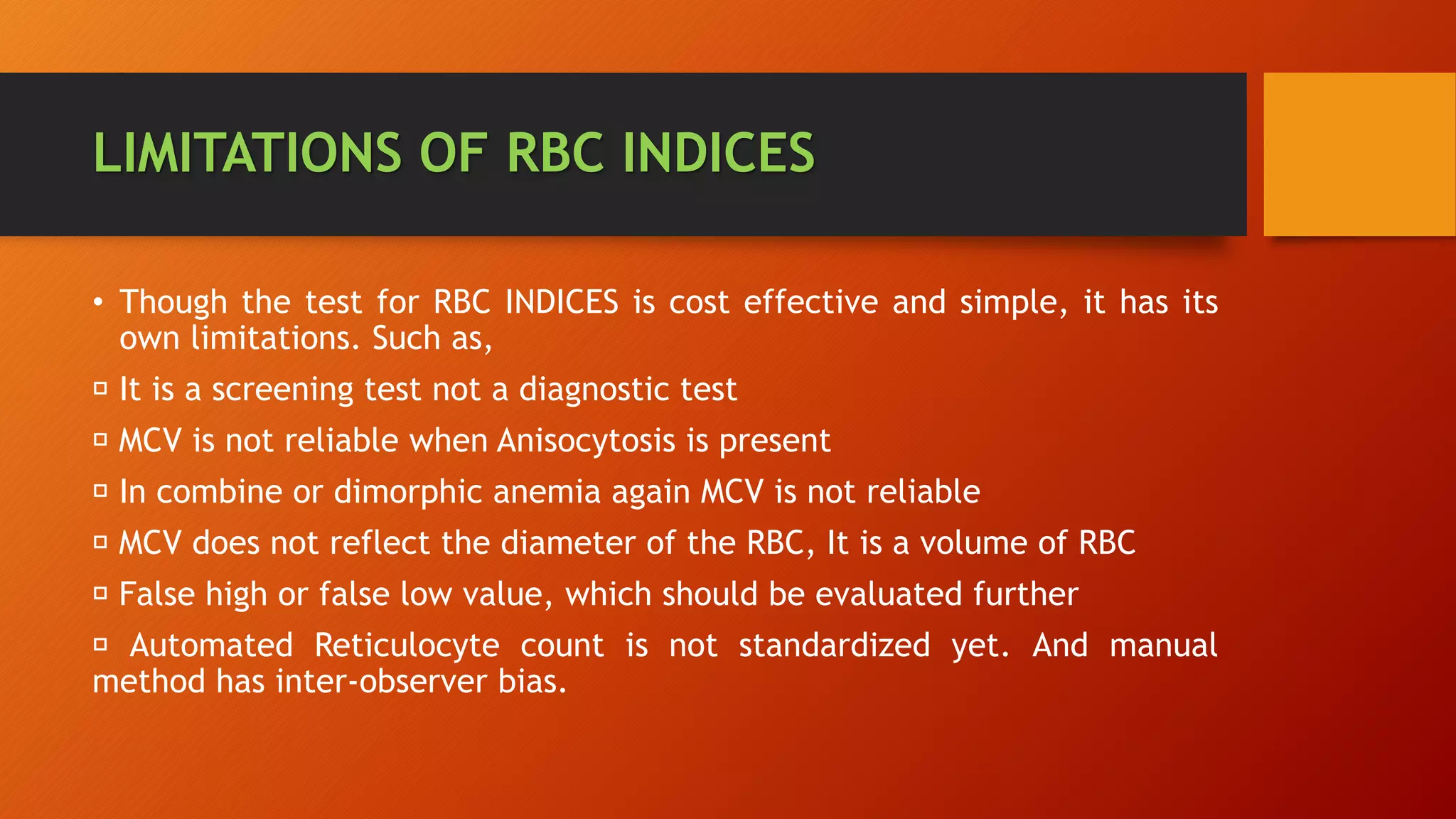
Red blood cell indices like mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) provide information about the size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells to help diagnose types of anemia. The red cell distribution width (RDW) indicates variation in cell size. Together with red blood cell count and hematocrit, the indices help classify anemias as microcytic, normocytic, or macrocytic. Reticulocyte count reflects bone marrow activity and response to iron therapy. While useful, red blood cell indices have limitations as screening tests and can be affected by technical issues.