1) Search engine optimization (SEO) involves using techniques like optimizing HTML code, copywriting, site navigation, and link building to improve a website's rankings in search engines.
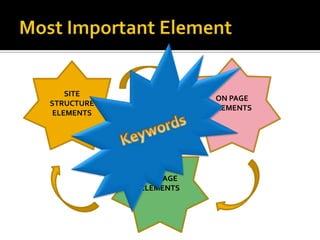
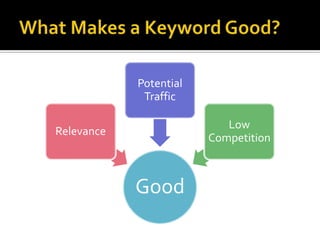
2) Keywords are extremely important for SEO - the best keywords accurately describe page content and what searchers would use to find the page.
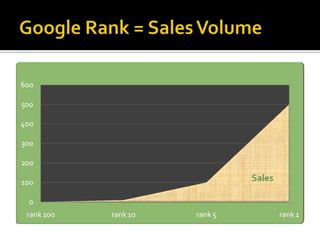
3) Proper keyword research and implementation, including using keywords in titles, headings, URLs, and on-page content, can help rank higher in search engines and drive more traffic.