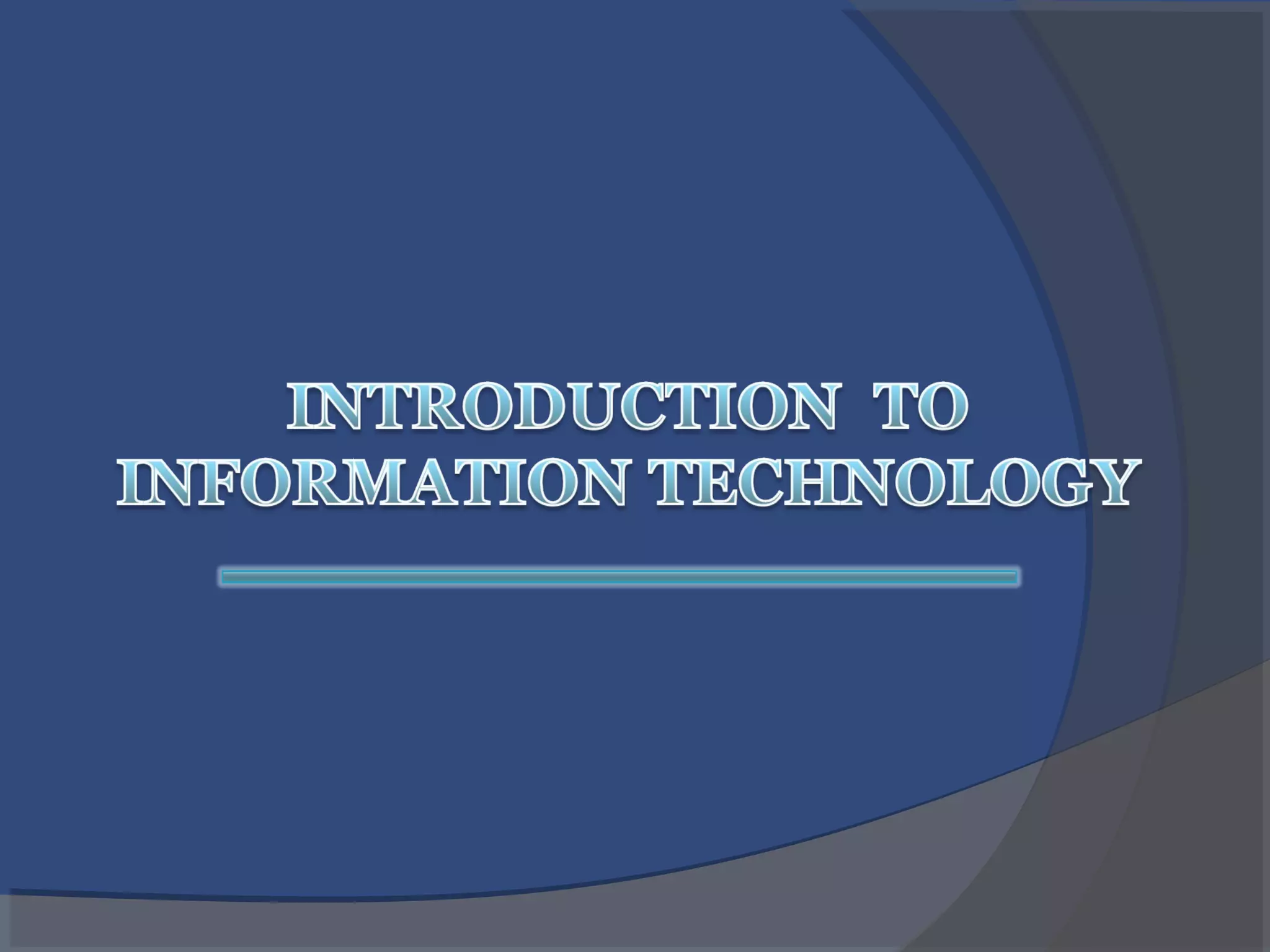
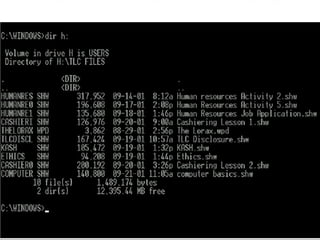
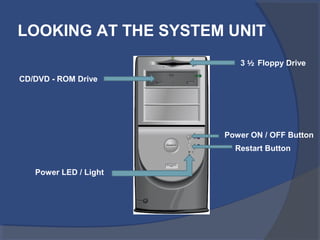
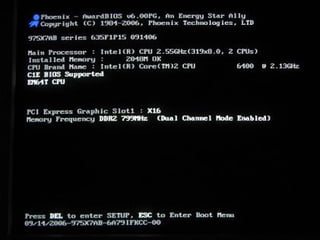
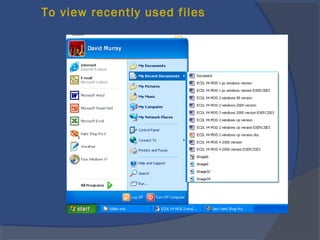
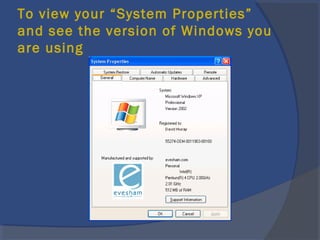
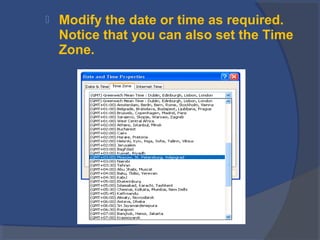
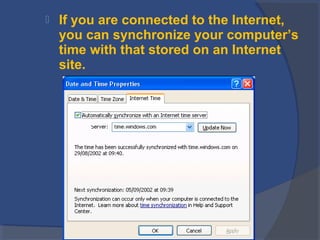
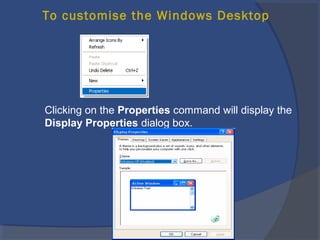
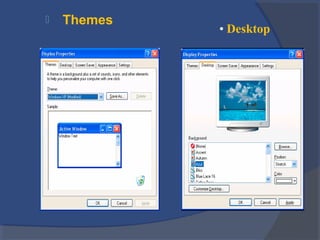
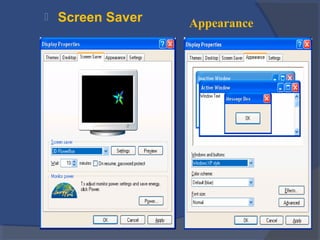
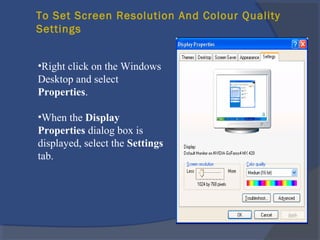
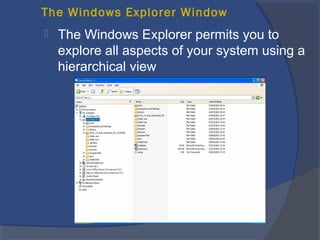
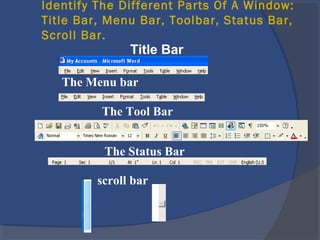
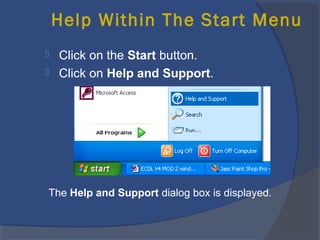
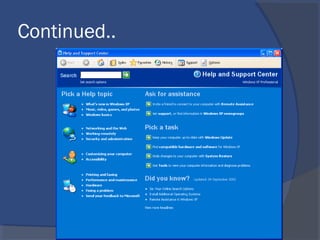
The document provides an overview of basic computer concepts, including definitions of a computer, types of computers like mainframes and personal computers, hardware components like the CPU and memory, software categories like operating systems and applications, and basic Windows functions. It describes what a computer is, the main parts that make up a computer system, common computer terminology, and introduces the Windows operating system.