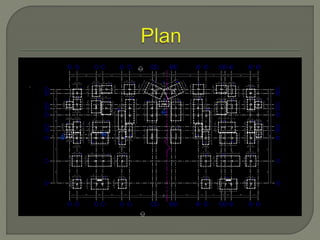
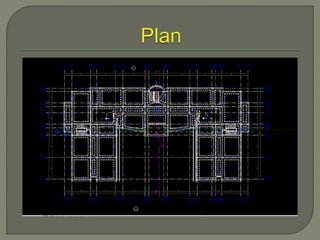
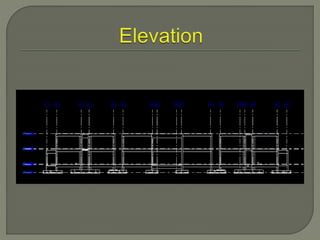
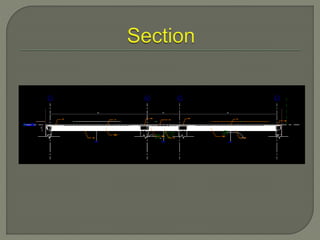
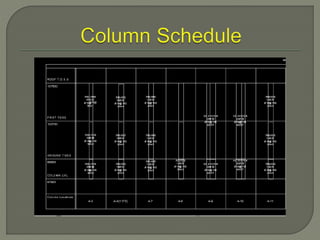
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a design methodology that uses coordinated, high-quality information stored in a single building model to enable design and construction teams to consistently and reliably manage project information across the entire scope. BIM supports large team workflows to improve project understanding and enable more predictable outcomes through increased coordination, accuracy, and earlier informed decisions. Software like Revit Structure uses intelligent, parametric objects and elements with associated information stored in a single model to automatically coordinate changes across any views of the model.