This document provides an overview of intrauterine insemination (IUI). Some key points include:
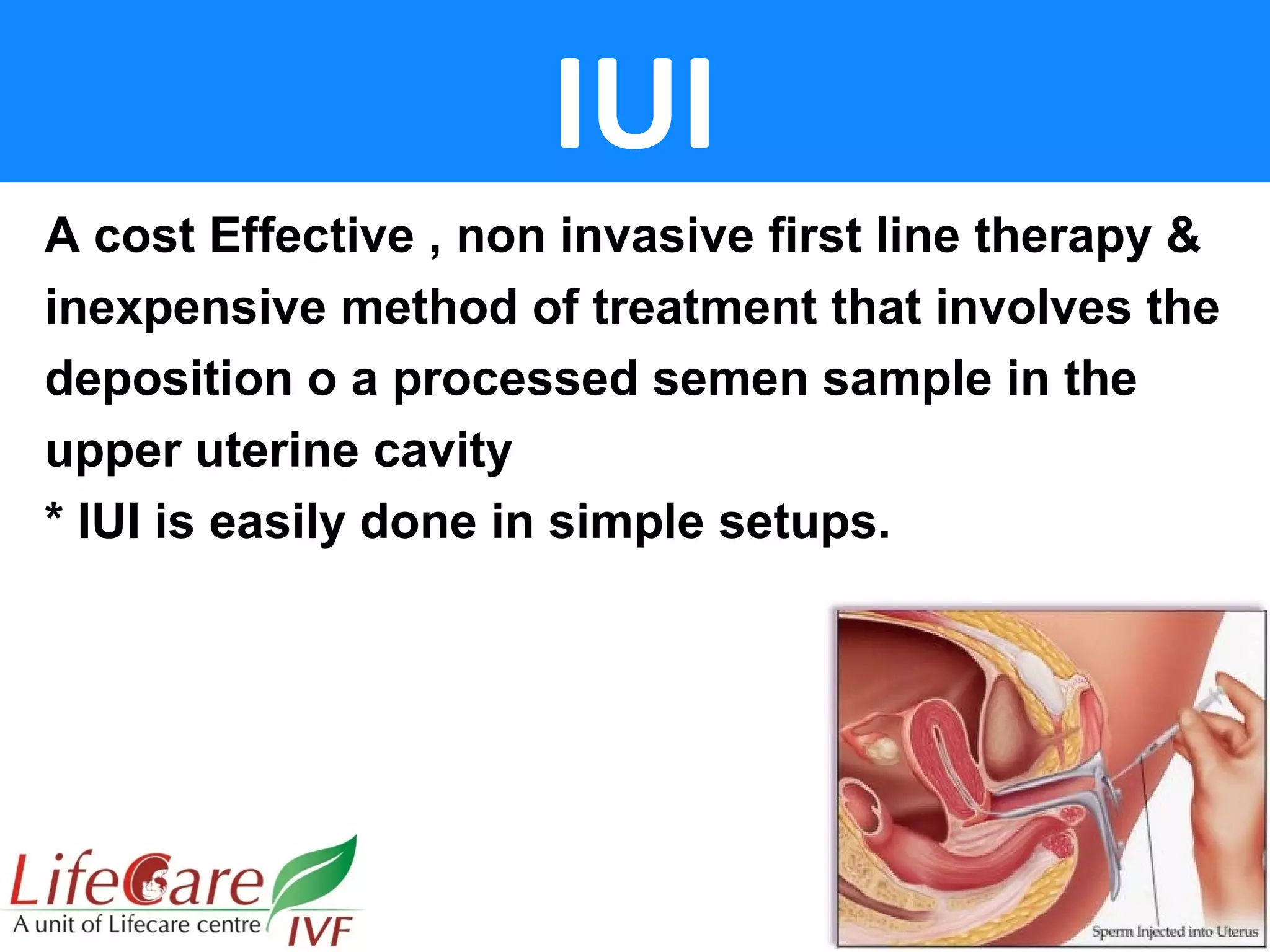
IUI is a first-line, non-invasive fertility treatment that involves placing processed sperm directly into the uterus. Success rates range from 6-20% depending on the stimulation protocol used. Factors like age, infertility duration and etiology, and semen quality impact success rates. Strict monitoring is important to minimize risks of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome while maximizing pregnancy chances. Proper sperm processing techniques and timing of insemination relative to ovulation are also important considerations for IUI.







![PREGNANCY RATE IN A.R.T.
million dollar information
Method Pregnancy Rate (%)
Intercourse (Timed) 4
IUI 6
CC 6
CC+IUI 8
FSH / HMG 7.7
CC / FSH /IUI 9-12
FSH/ HMG/IUI 17 – 20 %
In vitro fertilization 20 to maximum 40% [self cycle]
50 to 60 % donor cycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iuiupdate2018-180125102902/75/Intrauterine-Insemination-UPDATE-2018-9-2048.jpg)

![IMPOTANT PROGNOSTIC
INDICATORS OF SUCCESS with I.U.I.
• >35 YRS of AGE OF FEMALE PATIENT
• DURATION OF INFERTILITY
• STIMULATION PROTOCOL[review in slideshare.net 2017]
• INFERTILITY ETIOLOGY
• NUMBER OF IUI CYCLES
• TIMING OF INSMINATION
• TECHNIQUE OF IUI
• NUMBER OF PREOVULATORY FOLLICLES ON THE DAY OF
HCG
• SEMEN QUALITY & FEW OBSERVATION ON MALE FACTOR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iuiupdate2018-180125102902/75/Intrauterine-Insemination-UPDATE-2018-11-2048.jpg)







![CPR in IUI—8 to 20 %
depending upon indication & Protocols
• Anovulatory infertility
• Cervical infertility
• Azoospermia [AID]
• unexplained infertility
• Immunological abnormalities
• Mild degrees of male factor infertility
• Non-consummation of marriage due to –
ED/vaginismus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iuiupdate2018-180125102902/75/Intrauterine-Insemination-UPDATE-2018-19-2048.jpg)







![Male Factor & SEMEN PARAMETERS –
which impact IUI Outcome
• Oligospermia [ 10 million ]
• SEMEN PROCESSING TIME
• Pre wash TOTAL MOTILE SPERM COUNT
• Post Wash Sperm MOTILITY AFTER PROCESSING.
• SPERM MORFOLOGY
• Critical IUI INSEMINATION TIME [from sample production to
INSEMINATION
• 24-H SPERM SURVIVAL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iuiupdate2018-180125102902/75/Intrauterine-Insemination-UPDATE-2018-27-2048.jpg)






















![SINGLE v/s DOUBLE IUI
Single IUI IS GOOD Enough - if there is No Male
Factor
Double IUI recommended in Male factor
1st
18- 24 hrs
2nd
36 – 40 hrs [post-ovul]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iuiupdate2018-180125102902/75/Intrauterine-Insemination-UPDATE-2018-51-2048.jpg)



















