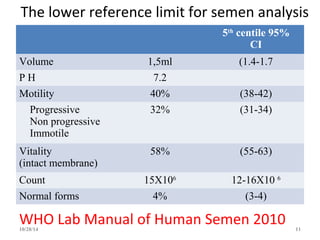
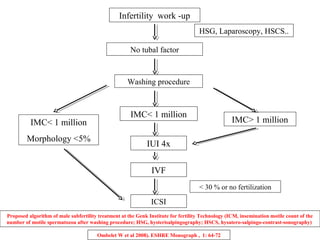
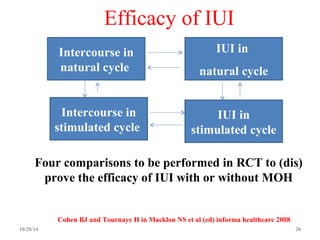
The document details intrauterine insemination (IUI) as a less invasive fertility treatment option, highlighting its advantages and indications for use. It discusses semen preparation techniques, timing for IUI, and factors influencing success rates, including male subfertility and female age. The effectiveness of IUI compared to other fertility treatments is examined, along with associated risks and complications.