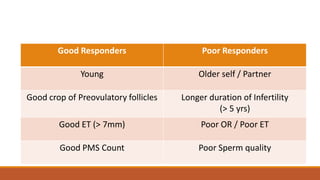
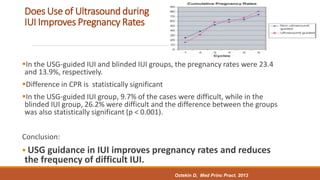
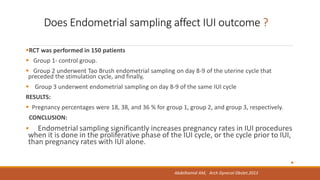
Dr. Laxmi Shrikhande is a renowned fertility specialist in India. She has received many prestigious awards and has held numerous leadership positions in national OB/GYN societies. She has extensive experience conducting research and publishing papers in national and international journals. She is highly skilled in IUI and optimizing outcomes through proper patient selection, semen preparation techniques, ovulation timing, and insemination procedures.