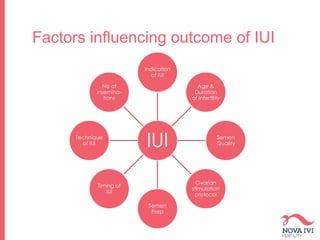
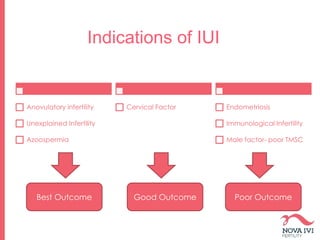
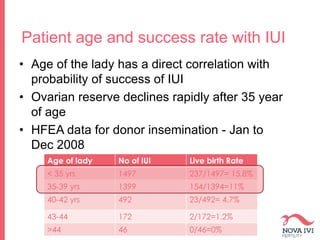
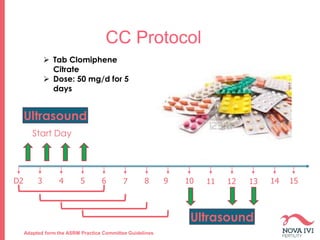
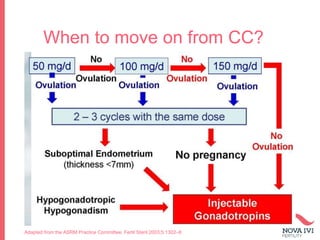
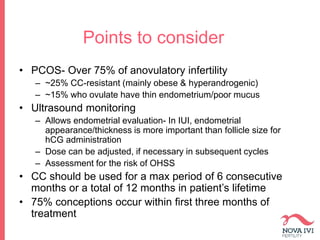
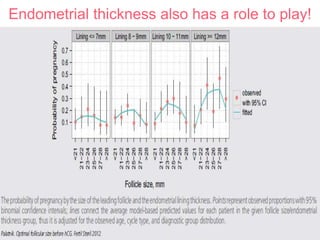
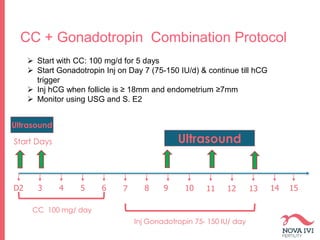
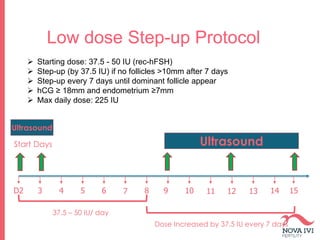
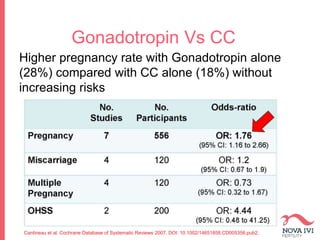
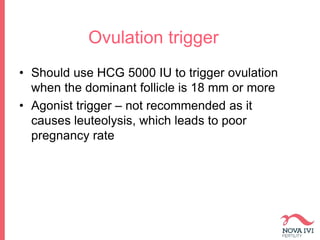
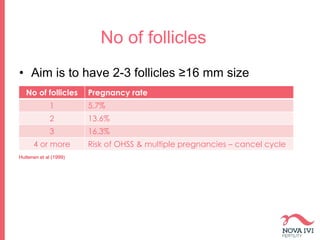
The document discusses Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), outlining its definition, procedures, and factors affecting its success rates. It presents statistics on delivery rates and emphasizes the importance of age, semen quality, and ovarian stimulation protocols in determining outcomes. Additionally, it provides recommendations on the number of IUI cycles, patient education, and the handling of different infertility factors.