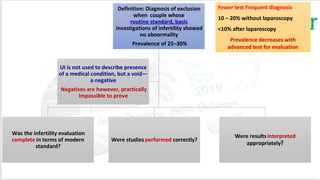
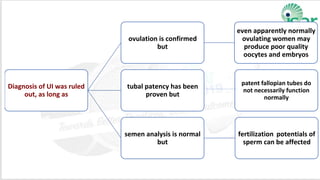
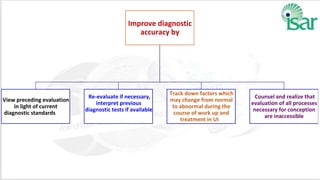
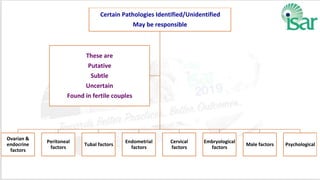
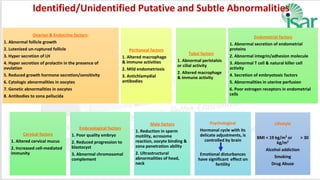
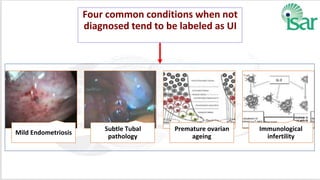
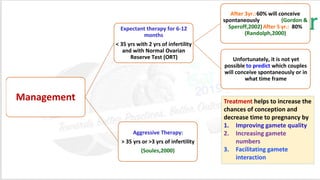
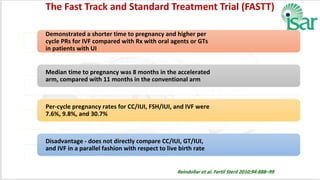
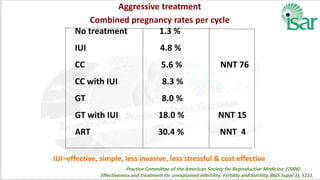
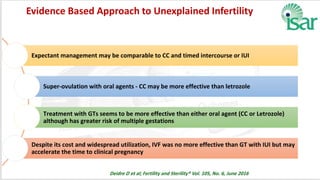
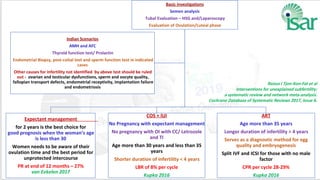
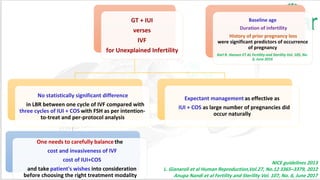
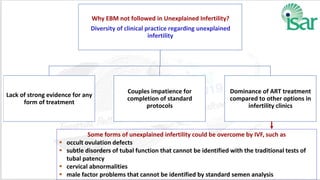
Unexplained infertility accounts for 10-20% of infertility cases. While basic tests like semen analysis, HSG, and ovulation documentation are recommended, more advanced tests like laparoscopy can provide diagnoses in some cases. Treatment options aim to improve gamete quality, increase gamete numbers, and facilitate interaction. Studies have found IVF to be more effective than IUI for unexplained infertility, resulting in higher pregnancy rates and fewer total treatment cycles. Some forms of unexplained infertility may be due to subtle, unidentified issues that IVF is better able to overcome compared to less invasive treatments.